Business_A-level_Aqa
-
1-1-the-nature-and-purpose-of-business3 主题
-
1-2-forms-of-business5 主题
-
1-3-the-external-environment5 主题
-
2-1-management-and-leadership3 主题
-
2-2-management-decision-making4 主题
-
2-3-the-role-and-importance-of-stakeholders3 主题
-
3-1-marketing-objectives1 主题
-
3-2-understanding-markets-and-customers5 主题
-
3-3-making-marketing-decisions2 主题
-
3-4-the-marketing-mix7 主题
-
4-1-operational-objectives2 主题
-
4-2-operational-performance1 主题
-
4-3-efficiency-and-productivity3 主题
-
4-4-quality1 主题
-
4-5-inventory-and-supply-chain-management3 主题
-
5-1-financial-objectives2 主题
-
5-2-financial-performance6 主题
-
5-3-sources-of-finance3 主题
-
5-4-cash-flow-and-profit1 主题
-
6-1-human-resource-objectives1 主题
-
6-2-human-resource-performance1 主题
-
6-3-organisational-design3 主题
-
6-4-human-resource-planning4 主题
-
6-5-motivation4 主题
-
6-6-improving-employer-employee-relations2 主题
-
7-1-mission-objectives-and-strategy4 主题
-
7-2-assessing-the-internal-position-of-a-business10 主题
-
7-3-changes-in-the-external-environment7 主题
-
7-4-the-competitive-environment1 主题
-
7-5-investment-appraisal2 主题
-
8-1-strategic-direction1 主题
-
8-2-strategic-positioning2 主题
-
9-1-changes-in-scale4 主题
-
9-2-innovation2 主题
-
9-3-globalisation-and-internationalisation4 主题
-
9-4-digital-technology1 主题
-
10-1-managing-change3 主题
-
10-2-organisational-culture2 主题
-
10-3-implementing-strategy2 主题
-
10-4-strategic-failure2 主题
setting-operational-objectives
An introduction to operational objectives
-
Operational objectives are short-term goals set by the operations function to help the business run more efficiently and meet its overall aims
-
They focus on how products are made or services are delivered and typically include:
-
costs — keeping production or service delivery as efficient and cost-effective as possible
-
quality — ensuring products or services meet customer expectations
-
speed of response — how quickly the business can meet customer demand
-
flexibility — the ability to adapt to changes in demand or customise products
-
environmental objectives — minimising the business’s impact on the environment
-
added value — increasing the value of a product or service through design, quality or customer service
-
-
Each of these areas helps the business improve its competitiveness and customer satisfaction
-
More detail on each objective is below
-
Costs and quality
-
Operations objectives often focus on reducing costs or improving quality
-
Spending less to make each product leaves a firm with more gross profit or allows it to lower its prices to beat rivals
-
Products that work well every time keep customers happy and loyal, protecting a brand’s good name
-
Objectives to reduce costs and improve quality
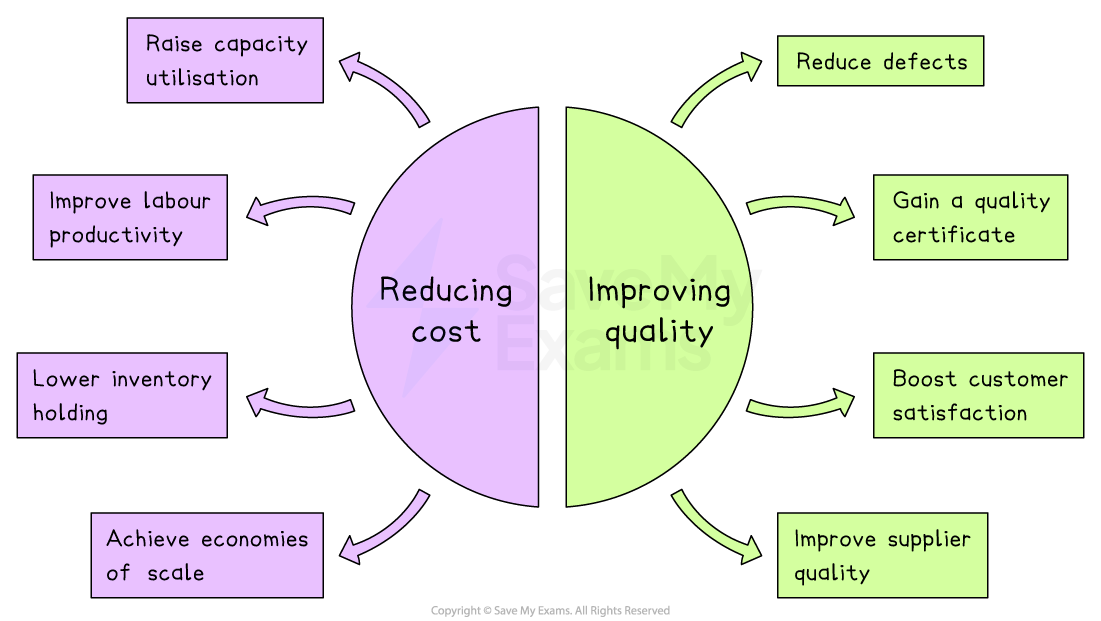
Reducing costs
-
Common objectives a business may set to reduce costs include:
-
raising capacity utilisation
-
This spreads fixed costs over more output, lowering the unit cost
-
E.g. run the factory at 90% of available hours rather than 70%.
-
-
improving labour productivity
-
This means fewer labour hours are needed for the same output, lowering wage costs
-
E.g. increase units produced per employee by 10% through better training
-
-
lowering inventory holding
-
This frees cash tied up in materials and cuts storage, insurance and spoilage costs
-
E.g. switch from holding 30 days’ stock to 10 days’ stock through just‑in‑time deliveries
-
-
achieving purchasing economies of scale
-
Direct costs fall, lowering the overall unit cost
-
E.g. negotiate bulk contracts to lower raw material prices by 5%
-
-
Improving quality
-
Objectives focused on improving quality may include:
-
reducing defects
-
Fewer defects mean happier customers and fewer returns
-
E.g. lower the proportion of faulty units from 3% to 0.5% by adding extra final quality checks
-
-
gaining an industry quality certificate (e.g. ISO 9001)
-
Certification reassures buyers that the firm follows reliable standardised procedures
-
Pass the quality audit and earn the certification within 12 months
-
-
boosting customer satisfaction scores
-
Direct feedback confirms that customers value the level of quality of goods
-
E.g. increase satisfaction survey ratings from 82% to 90% by updating user instructions
-
-
improving supplier quality
-
Better inputs mean fewer problems during production
-
E.g. require key suppliers to hit 99% on‑time, defect‑free deliveries
-
-
Flexibility and speed of response
-
Flexibility matters because customer tastes and order sizes can change without warning
-
A flexible business can switch products or change the volume of output quickly, preventing lost sales or overstocking
-
-
Speed of response is vital because modern buyers expect rapid delivery
-
Cutting lead times keeps customers satisfied, earns repeat business and provides a competitive edge over slower rivals
-
-
Objectives to improve flexibility or reduce speed of response could include:
-
a multi‑skilled workforce
-
Staff can fill gaps or swap tasks quickly when demand changes
-
E.g. train every staff member to run at least two different machines
-
-
modular product design
-
New versions of products can be launched quickly without redesigning the whole item
-
E.g. introduce common parts that clip together in different ways in product manufacture
-
-
preventative maintenance
-
Keep production lines running and orders on schedule
-
E.g. introduce weekly machine checks to reduce unexpected breakdowns
-
-
Environmental objectives
-
Operations objectives with an environmental focus matter because a business now has to meet stricter environmental laws, rising energy costs and growing customer concern about sustainability
-
Setting objectives, such as cutting carbon emissions, reducing packaging waste or using renewable energy, helps a business adhere to the law, save money and gain environmentally conscious customers
Examples of environment‑focused operational objectives
|
Business |
Objective |
Tactics |
|---|---|---|
|
IKEA |
|
|
|
Unilever |
|
|
Added value
-
Adding value is the process of taking raw materials and using them in such a way that the end product created is worth more than the cost of the raw materials used to create it
-
The added value is the difference between the price that is charged to the customer and the cost of inputs required to create the product
-
E.g. customers are prepared to pay more for potatoes when they are packaged as oven chips than they would be willing to pay for a bag of whole potatoes
-
-
If value is not added to the materials and components that a business buys, fixed costs cannot be paid and no profit will be made
Examples of operational objectives focused on added value
|
Business |
Operations objective |
Added value |
|---|---|---|
|
Tesla |
|
|
|
Starbucks |
|
|
|
Nike |
|
|
