Exam code:8132
An introduction to organisational structures
-
An organisational structure outlines the reporting relationships, roles, and responsibilities of employees
-
Businesses need to choose a suitable structure to enable them to effectively implement ideas and achieve their objectives
-
They should consider how the structure may affect the management and effectiveness of operations and communication
-
A well-designed organisational structure helps to provide clarity, efficiency and accountability
-
It can be visually represented using an organisation chart
-
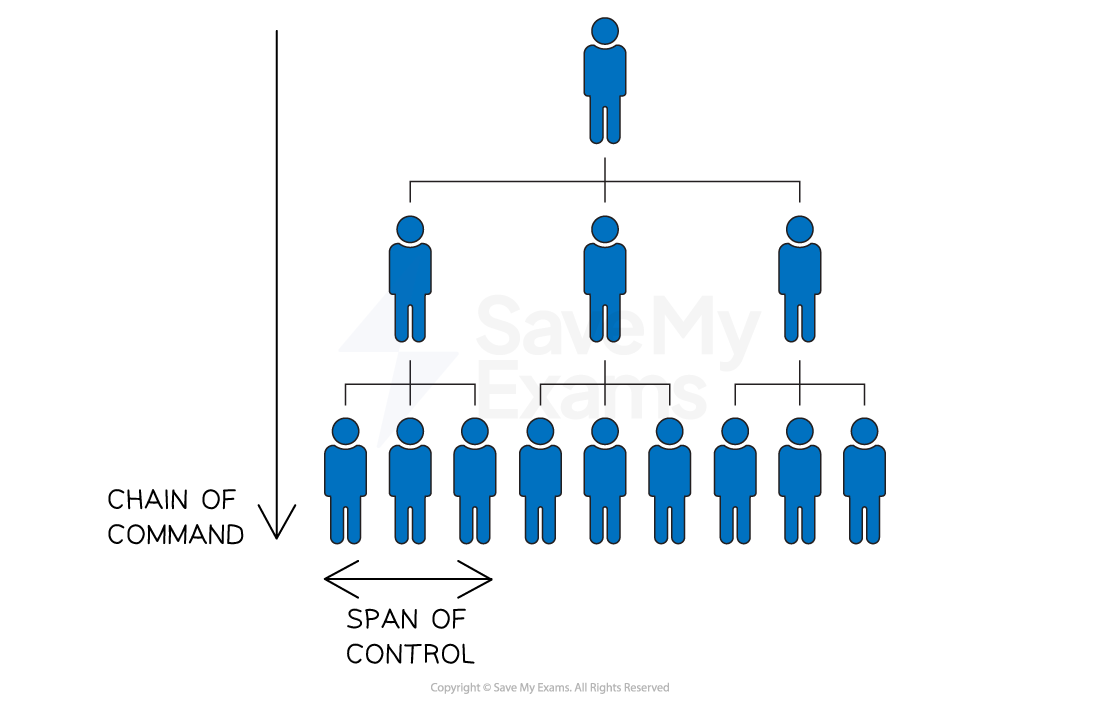
Organisational chart example
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, you may be asked to explain a reason for having an internal organisational structure. Explain questions, worth two marks, require you to make a correct point and develop it.
An example answer might look like this:
An internal structure allows a business to organise its workers [1] so that they know their roles in relation to others in the organisation [1].
Key terminology
Hierarchy
-
A hierarchy refers to the levels of authority within an organisation
-
It describes the ranking of positions from top to bottom
-
The higher the position in the hierarchy, the more authority and power it holds
-
The hierarchy usually includes top-level management, middle-level management, and lower-level employees
-
Chain of command
-
The chain of command is the formal line of authority that flows downward from top management to lower-level employees
-
It defines who reports to whom and who is responsible for making decisions
-
The chain of command helps to establish a clear communication channel and helps to maintain accountability within the organisation
-
Span of control
-
The span of control refers to the number of employees that a manager or supervisor directly manages
-
It is based on the principle that a manager can only effectively manage a limited number of employees
-
A narrower span of control means that there are more layers of management
-
A wider span of control means that there are fewer layers of management
-
Types of organisational structures
-
Organisational structures can be tall or flat
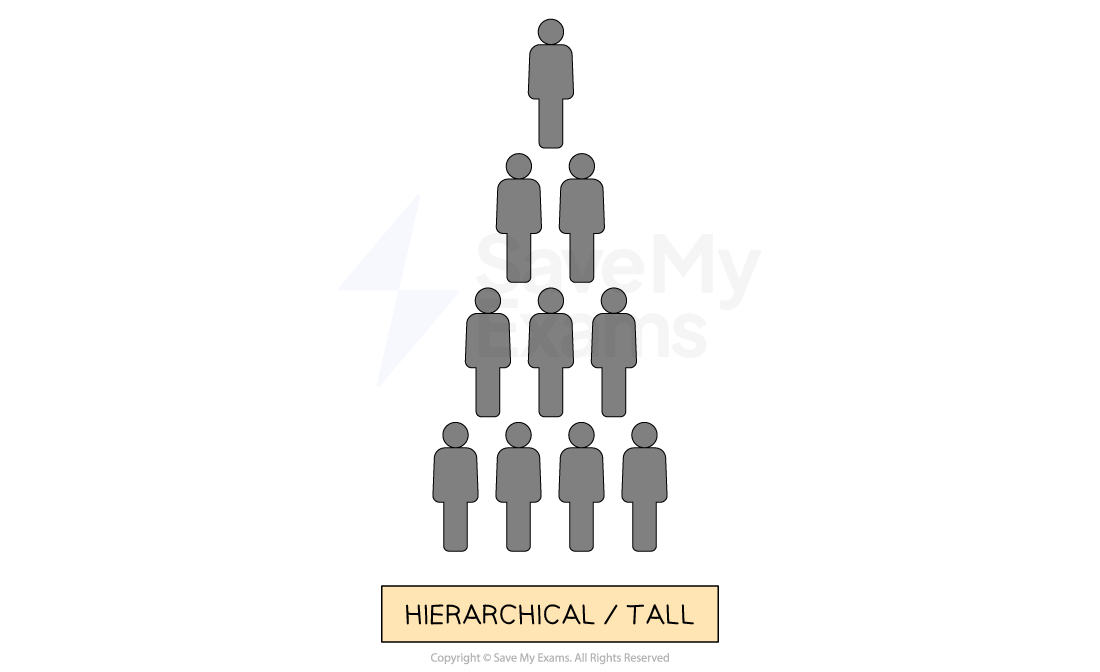
Tall organisational structure
-
A long chain of command usually results in a narrow span of control
-
Tall structures have multiple levels of management
-
Common in large organisations with complex operations
-
E.g. Government agencies and universities
-
-
Flat organisational structure
-
A short chain of command usually results in a wide span of control
-
Flat structures have few levels of management
-
Common in small organisations or start-ups
-
E.g. tech start-ups and small businesses
-
-

Evaluation of tall and flat structures
|
Structure |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Tall |
|
|
|
Flat |
|
|
Delayering
-
Delayering is the process of flattening tall organisational structures by removing one or more levels of hierarchy
-
It usually involves making middle management redundancies or choosing not to replace managers who leave
-
Benefits of delayering include:
-
Communication is likely to improve
-
Significant cost savings can be made as fewer management salaries need to be paid
-
-
However, some drawbacks include
-
Delayering can increase the workload of other employees
-
Remaining managers’ spans of control widen, affecting coordination
-
-
-
Centralisation and decentralisation
-
A centralised organisational structure is where authority for decision-making rests with senior management at the centre of a business
-
A decentralised structure is where authority for decision-making is delegated further down the hierarchy towards functional or middle managers
-
In reality, few businesses are wholly centralised or decentralised
-
In most businesses, strategic decisions are made by senior leaders, whilst operational decisions are delegated to functional areas and middle managers
-
Evaluation of centralised and decentralised organisational structures
|
Structure |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Centralised |
|
|
|
Decentralised |
|
|
The main job roles and responsibilities in business
-
The organisational structure of a business determines the roles, responsibilities and relationships between individuals in an organisation

Responses