Exam code:9609
Goods and services
-
Goods are physical, tangible items that can be touched, stored and owned
-
They are usually produced, then sold, and can be taken home or delivered
-
Examples include a loaf of bread, a car or a pair of shoes
-
-
-
Services are non-physical, intangible activities provided by people or businesses
-
They are usually performed at the time of purchase, and cannot be touched or stored
-
Examples include a haircut, a taxi ride or legal advice
-
-
-
In many situations, when a customer buys a product, they are also receiving a service as part of the overall experience
-
This is because businesses want to provide value beyond the physical item and improve customer satisfaction and loyalty
-
Case Study
Buying a new car – product and services combined
Priya and Henry decide to buy a brand-new electric car from a local dealership
The car itself is a tangible product, as it is a physical item they can see, test and drive away
However, their purchase also includes several services provided by the dealer to enhance their experience
-
Test drive and personalised advice
-
A salesperson offers Priya and Henry a free test drive and gives them advice on which model suits their needs based on their lifestyle and budget.
-
-
Finance and insurance assistance
-
The dealership helps them set up a car loan and offers optional car insurance plans
-
-
Free servicing for 12 months
-
As part of the deal, Priya and Henry receive a 12-month free servicing package, including checks and minor repairs
-
-
Home Delivery
-
Once the paperwork is complete, the car is delivered directly to their home
-
-
Customer support and warranty
-
They receive a 5-year warranty and access to customer support in case they need help with features or maintenance
-
Tangible and intangible product attributes
-
When a customer buys a product, they are influenced by both tangible and intangible attributes
-
These are the features that affect how the product looks, feels, performs or is experienced
-
Tangible and intangible attributes of a pair of trainers
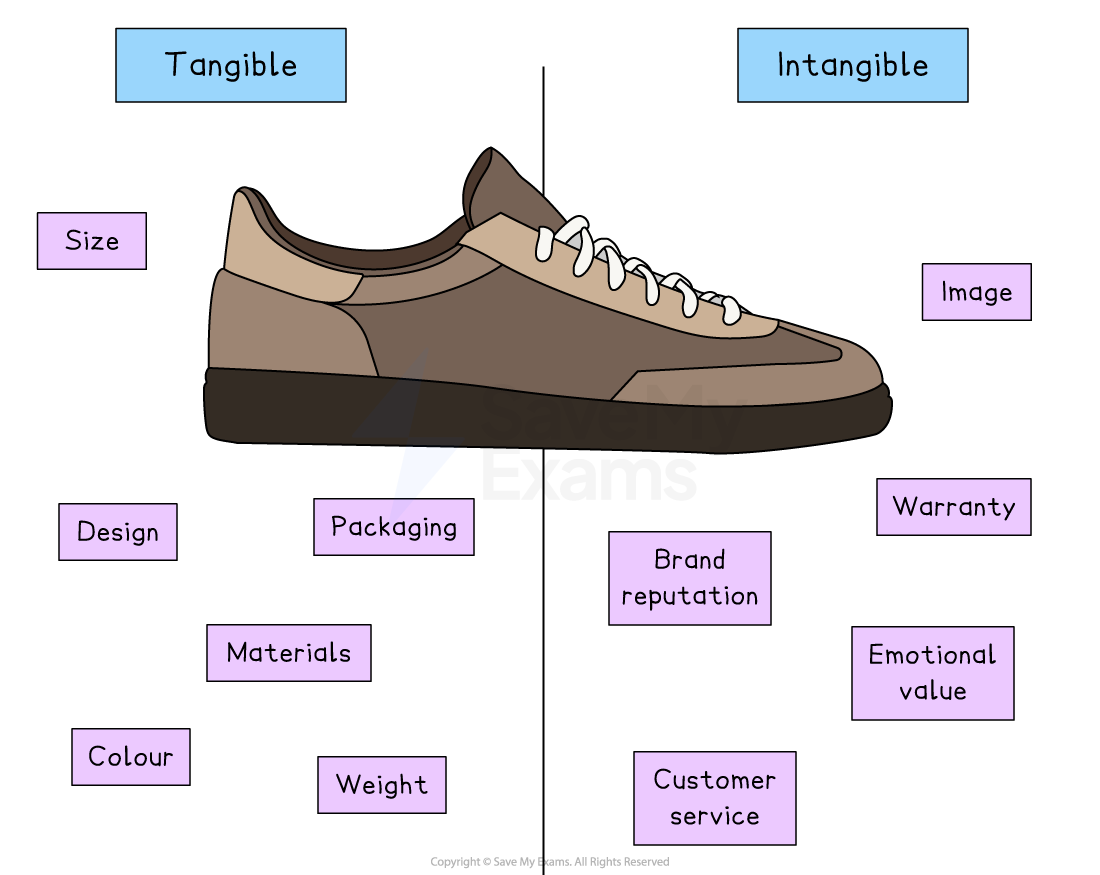
Tangible attributes
-
These are the physical features of a product that can be touched, seen, or measured
-
They include things like size, colour, design, packaging, materials, and weight
-
Customers can compare tangible features before buying
-
E.g. When buying a pair of running shoes, the tangible attributes include the shape, colour, sole type, weight and material used
-
The customer can try them on and feel the comfort and fit
-
Intangible attributes
-
These are non-physical features that relate to the experience or perception of the product
-
They include things like brand reputation, warranty, customer service, image and emotional value
-
These features are often the reason a customer chooses one brand over another, even if the tangible features are similar
-
E.g. The same running shoes may come with a trusted brand name, a 12-month warranty, and a ‘satisfaction guarantee’
-
The buyer may also feel a sense of pride or motivation wearing a well-known performance brand
-
The importance of product development
-
Product development is the process of creating and launching new goods or services
-
It can help a business grow, stay competitive and meet changing customer needs
-
Without developing new products, a business risks becoming outdated or losing its market share
-
Why product development is important
-
Responding to changing customer needs
-
Customers’ tastes, preferences, and lifestyles change over time
-
Developing new products helps businesses stay relevant and meet these new demands
-
-
Staying ahead of competitors
-
By launching innovative or improved products, businesses can attract new customers and keep existing ones from switching to rivals
-
E.g. A tech company that releases a new smartphone with unique features may gain an advantage over competitors
-
-
-
Increasing sales and market share
-
New products can generate excitement, attract more attention, and increase overall sales
-
They may also open up opportunities to reach new market segments
-
-
Extending the product life cycle
-
As older products reach the end of their life cycle, new products can replace them and keep the brand fresh and active in the market
-
-
Taking advantage of new technology
-
Businesses can use advances in technology to improve performance, design, or sustainability, which can make their products more attractive
-
E.g. A home appliance company might develop smart, energy-efficient models to appeal to eco-conscious consumers
-
-
Costs of new product development
|
Cost |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Market research collection and analysis can be time-consuming and expensive |
|
|
Investment in research, development, and design is often very costly |
|
|
The cost of producing trial products can be significant |
|
|
There may be low sales if the product does not meet market expectations |
|
|
A failed product can damage the brand and other products in the range |
|
Product differentiation
-
Differentiation is where a business distinguishes its products from those of competitors
-
This involves creating functions or features of the product (or firm) which help it to stand out from its competitors
-
Strong product differentiation helps the firm to develop its competitive advantage
-
Methods of differentiation
-
Successful business or product differentiation helps the business to increase demand for its products, increase brand loyalty, and allow the business to charge higher prices

Differentiation methods
|
Method |
Explanation |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Marketing and branding |
|
|
|
Packaging |
|
|
|
Functions and features |
|
|

Responses