Exam code:9609
An introduction to sources of finance
-
Businesses have different sources of finance available to them
-
When the finance comes from inside the business, it is called an internal source of finance
-
When the finance comes from outside the business, it is called an external source of finance
-
Internal and external sources of finance
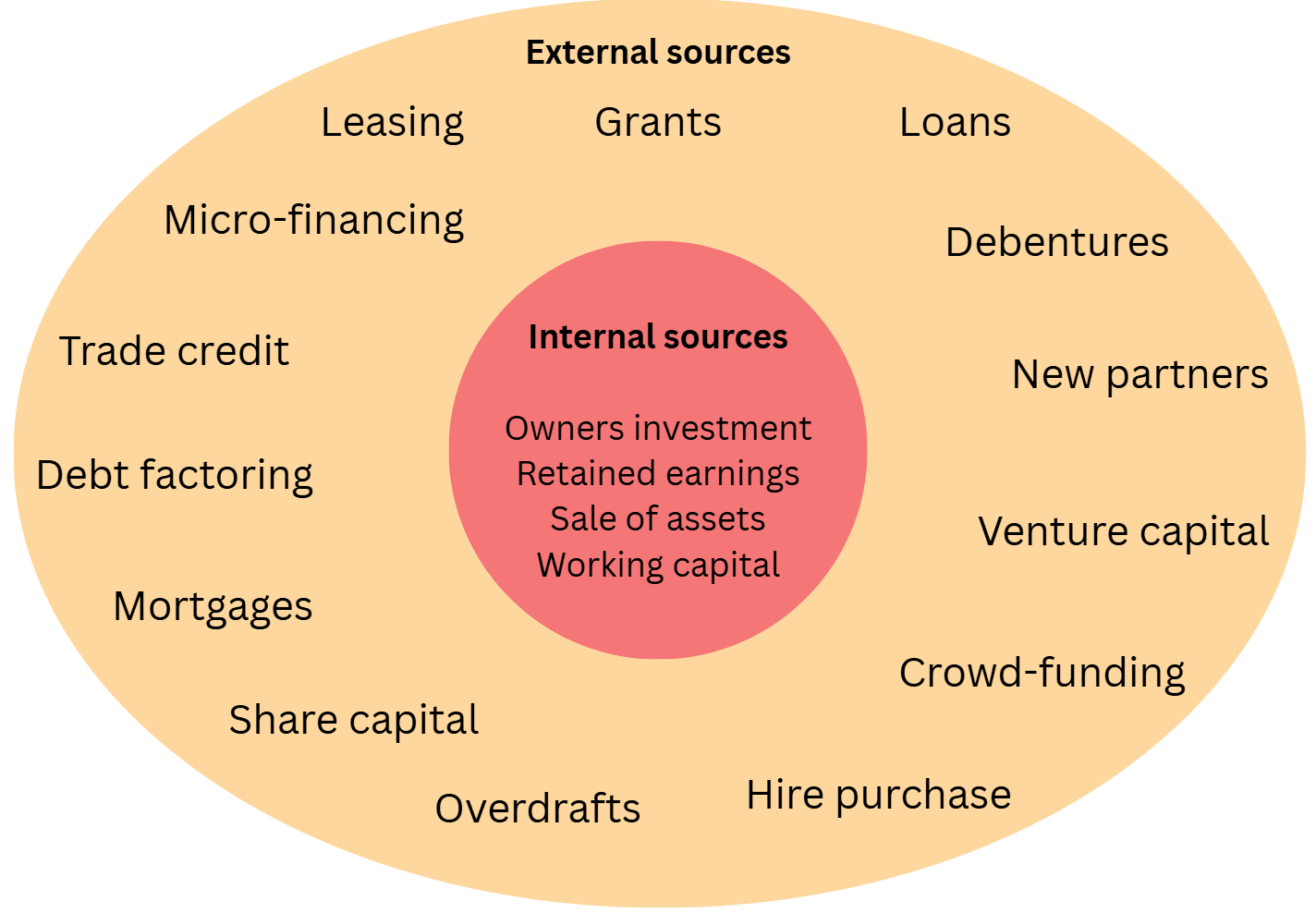
Owner’s investment
-
Owners’ investment is a key source of funds when a business starts up
-
Owners may introduce their savings or another lump sum, e.g. money received following a redundancy
-
-
Owners may invest more as the business grows or if there is a specific need, e.g. a short-term cash-flow problem
Evaluating owner’s investment
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Retained earnings
-
This is profit generated in previous years and not distributed to owners that is reinvested in the business
-
This is a cheap source of finance, as it does not involve borrowing and associated interest and arrangement fees
-
The opportunity cost of investing the money back into the business is that shareholders do not receive extra profit for their investments
Evaluating the use of retained earnings
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Sale of unwanted assets
-
Selling fixed assets that are no longer required, such as machinery, land or buildings, generates finance
-
Businesses use this method for a range of reasons
-
To raise cash quickly without taking on debt
-
To free up capital tied up in unused or outdated assets
-
To support short-term cash flow needs or fund new investment
-
Evaluating raising finance by selling unwanted assets
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Sale and leaseback of non-current assets
-
A non-current asset is an interchangeable term with fixed asset
-
A sale and leaseback arrangement may be made if a business wants to continue to use an asset but needs cash
-
The business sells an asset, such as a building, for which it receives cash
-
The business then rents the asset from the new owners or a specialist leasing company
-
E.g. in early 2023, Sainsbury’s announced that it was in talks to sell some of its prime retail property for £500m, which it would then lease back from the new owners, LXi Reit
-
-
Evaluating sale and leaseback of non-current assets
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Working capital
-
Working capital is the money a business has available for day-to-day operations, such as paying wages, suppliers, and utility bills
-
A business can adjust the way it manages working capital to free up cash and improve its short-term financial position without needing to borrow money
-
Delaying payment to suppliers gives the business more time to hold onto cash
-
Reducing stock levels means less money is tied up in unsold goods
-
Speeding up payments from customers brings in cash more quickly
-
Using existing cash reserves to cover expenses
-
Evaluating working capital as a source of finance
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
-
Further notes on managing working capital can be reviewed here
Internal sources of finance and business ownership
-
The type of business ownership, such as a sole trader, partnership, or limited company, can influence which internal sources of finance are available and suitable
-
Sole traders and partnerships tend to rely more on owner’s investment and working capital because they often have limited retained profit and fewer fixed assets to sell
-
Case Study
Ali’s Mobile Repairs

-
Ali’s Mobile Repairs is a small sole trader business based in Nairobi
-
Ali needs money to buy new tools but doesn’t want to take out a loan
-
As a sole trader, he decides to use his own savings (owners’ investment) and delays a stock order by a week to free up some working capital
-
Companies are more likely to use retained profit, sale of fixed assets, or sale and leaseback, as they operate on a larger scale and have more internal resources
Case Study
Ecosap Ltd

Responses