Exam code:9609
An introduction to management styles
-
Management styles are different approaches to leading and managing a team or business
-
An effective manager will be able to use a variety of styles depending on the situation to achieve the best results for the business
Common management styles
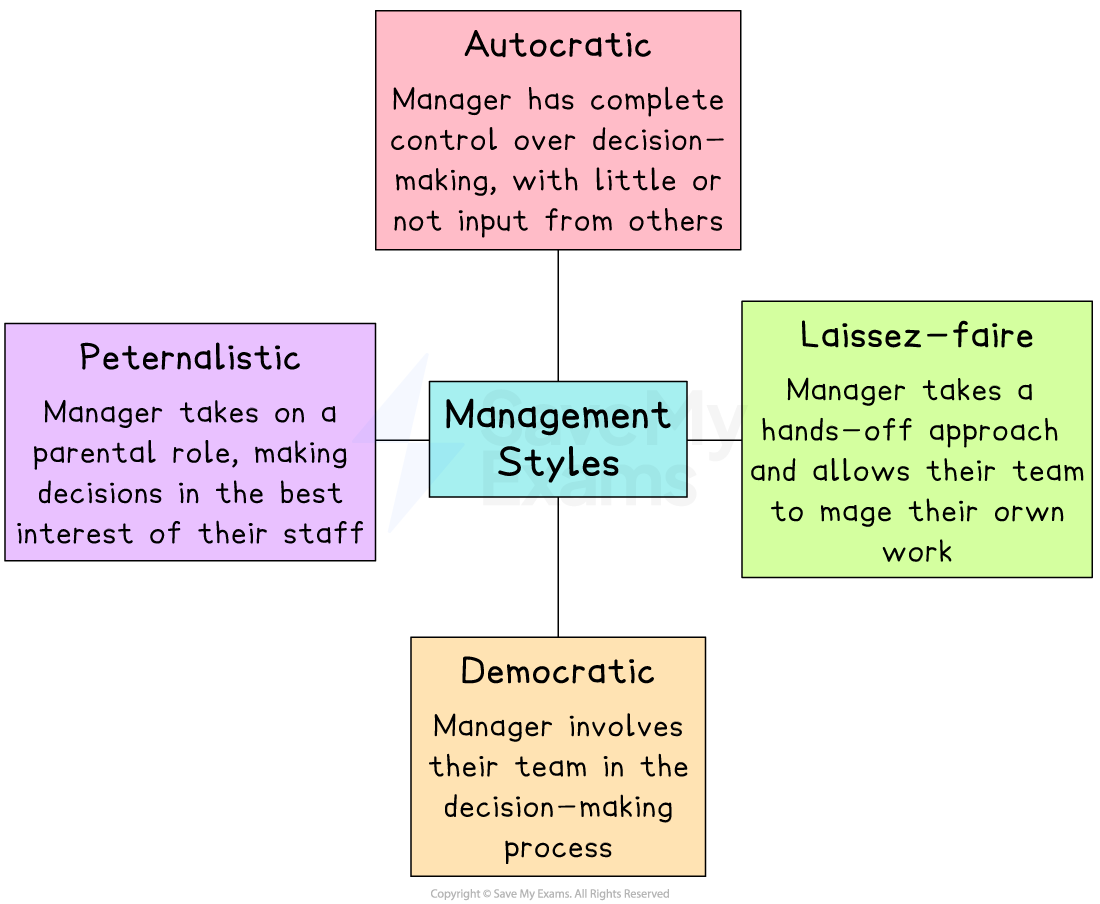
-
The choice of management style can be influenced by business circumstances, as well as its nature and size
Autocratic management
-
An autocratic manager holds absolute power and authority over a business
-
The manager makes decisions without seeking input or agreement from others
-
They typically expect strict obedience and compliance from their subordinates
-
-
Autocratic managers often have complete control over the decision-making process
-
They set the direction and goals of the business
-
They do not usually consider the opinions, ideas, or expertise of their team members
-
Their decisions are generally not open to discussion or debate
-
Situations where autocratic management is effective
|
Situation |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Crisis situations |
|
|
Hierarchical organisations |
|
|
Time-sensitive projects |
|
|
Inexperienced or unmotivated teams |
|
|
Maintaining order and discipline |
|
-
Autocratic management has drawbacks, including
-
Reduced employee morale as workers have no input into decision-making
-
Limited creativity, as employees are required to follow strict instructions and are closely monitored
-
Lack of input from team members restricts an important source of problem-solving ideas and innovation
-
Paternalistic management
-
Paternalistic managers assume a ‘fatherly’ role towards their subordinates, acting in a protective and authoritarian manner
-
The manager makes decisions for employees while also showing concern for the well-being and development of subordinates
-
The manager takes on responsibility for the welfare of their employees
-
They may provide guidance, support, and resources to ensure the success of their employees
-
Huawei’s Ren Zhengfei is viewed as a paternalist who has shaped the businesses culture with well-defined goals, employee devotion and absolute obedience in return for highly competitive pay and opportunities for staff to buy shares in the company
-
-
-
Paternalistic management can create a sense of security and support among employees, increasing their loyalty and reducing staff turnover
-
It can also be perceived as controlling and limits creativity and innovation within a business
-
It may create a dependency on managers, which restricts personal growth and professional development among employees
Democratic management
-
Democratic managers actively involve employees in the decision-making process and encourage discussion, though they have the final say
-
Consultation, collaboration, delegation and teamwork are common features of democratic management
-
-
This management style is most effective in organisations with skilled, experienced and creative employees
Evaluation of democratic management
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Laissez-faire management
-
Laissez-faire managers play a minimal role in directing their business team
-
They allow subordinates significant autonomy and freedom in making decisions and completing tasks
-
-
Laissez-faire management is most appropriate where workers are highly skilled and self-motivated and require minimal supervision
Evaluation of laissez-faire management
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y managers
-
Douglas McGregor developed two contrasting theories that explained how managers’ assumptions about what motivates workers affects the style of management they adopt
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
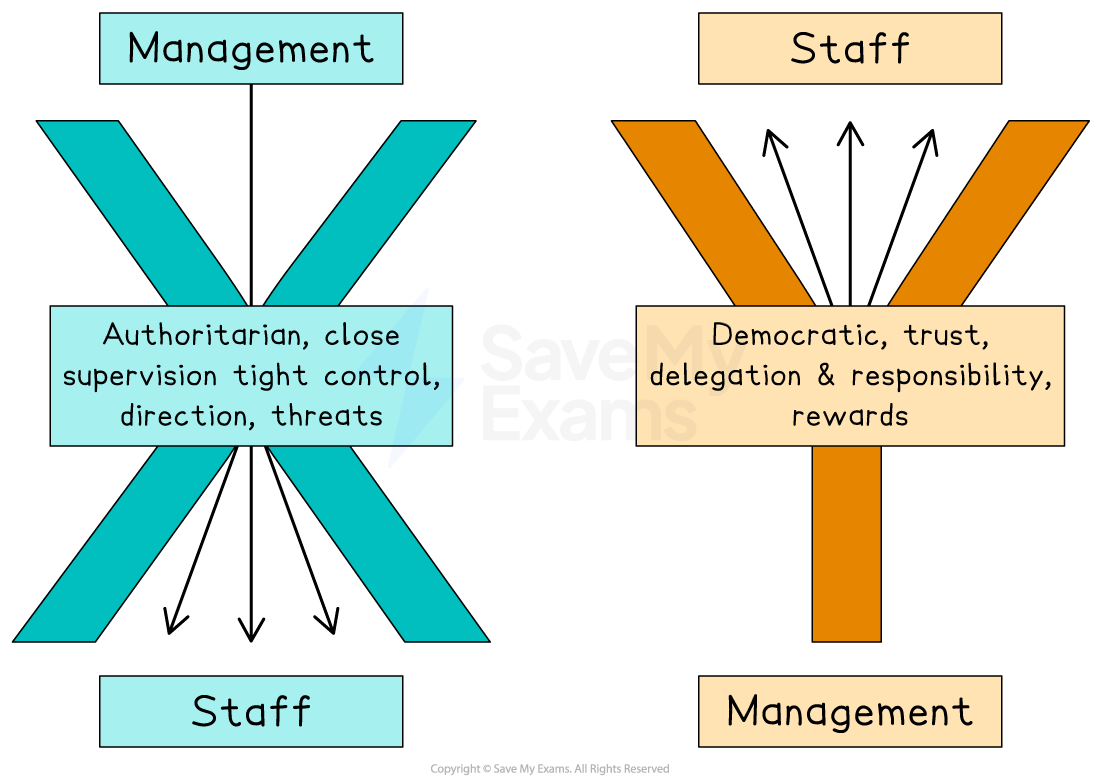
Assumptions of Theory X and Theory Y managers
|
Theory X |
Theory Y |
|---|---|
|
|
-
Holding these assumptions about their workers means that managers are likely to adopt different approaches with their employees
Theory X and Theory Y approaches to management
-
Theory X managers closely supervise employees
-
They provide clearly defined tasks and the promise of higher pay or the threat of punishment as means of motivation
-
They may use autocratic measures, which can result in mistrust and resentment among employees
-
McGregor recognised that this approach can be appropriate, especially where workers lack experience or maturity
-
-
Theory Y managers establish a positive working environment
-
The organisation’s objectives match employees’ personal objectives
-
They develop a cooperative relationship with employees and allow them freedom to make and contribute to decisions
-
McGregor acknowledged that this theory isn’t appropriate in every situation
-
It is an alternative to persuade managers to adopt a positive mindset when managing subordinates
-
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Your exam case study is likely to provide some hints about the management style adopted within a business. You may find that a manager adopts elements of different styles and should be able to explain why this may be. You may consider the business context, business objectives, the type of workers, timescales, and the level of risk in your explanation.

Responses