Exam code:7131
Managing the supply chain effectively
-
The supply chain is the network of organisations, people, activities and resources that move a product from its basic raw material right through to the final customer
-
It includes the following:
-
Stock control: planning, implementing and monitoring the movement of raw materials, components, work-in-progress and finished goods
-
Quality control: ensuring output meets standards so that the end product is safe and meets customer expectations
-
Transport networks: ensuring efficient deliveries of goods to customers, taking account of speed, reliability and costs
-
Supplier networks: developing strong relationships with suppliers willing to work collaboratively to improve quality
-
-
Global supply chains require these activities to be coordinated across international borders
-
Some stages can be completed at lower cost in certain countries
-
E.g. China has a reputation for producing high quality, low-cost electronics components
-
-
Labour-intensive processing, such as clothes manufacturing, is outsourced to countries with low labour costs, such as Vietnam
-
Scarce raw materials may only be available in certain countries/regions
-
Building an effective supply chain
|
Decision area |
What it involves |
|---|---|
|
Make or buy (produce in-house or outsource) |
|
|
Choosing suppliers |
|
|
Purchasing approach |
|
|
Information sharing and use of technology |
|
|
Logistics structure |
|
Why an effective supply chain matters
-
Faster delivery to customers
-
When every link is well-coordinated, products move quickly from factory to shelf, beating slower rivals
-
-
Lower operating costs
-
Just-in-time (JIT) deliveries and bulk purchasing agreements reduce storage, handling and material expenses
-
E.g. Aldi negotiates long-term contracts with a small group of trusted suppliers, helping it minimise warehouse inventory and keep prices low
-
-
Consistent quality
-
Close, long-term relationships with suppliers make it easier to enforce standards and fix problems early
-
-
Greater resilience to shocks
-
A well-planned supply chain includes backup suppliers and effective data sharing so the business can adapt when something goes wrong
-
Modern supply chains
-
Modern supply chains stretch across the world, rely on real-time data and face tough questions about ethics and sustainability
-
Businesses now use digital tools, closer partnerships and greener standards to keep those long chains working smoothly
Ways to manage more complex supply chains
|
Way |
Explanation |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Use live data to trace every item |
|
|
|
Predict problems with artificial intelligence (AI) |
|
|
|
Increase transparency for consumers and investors |
|
|
|
Share IT platforms and paperwork digitally |
|
|
|
Monitor operations with connected sensors |
|
|
Influences on the choice of suppliers
-
Businesses often go to great lengths to find suitable suppliers of raw materials and components
-
Factors including the price, quality and reliability of supplies determine whether a business can efficiently produce high-quality products at a reasonable cost
-
-
There are several factors that can influence the supplier chosen by a business
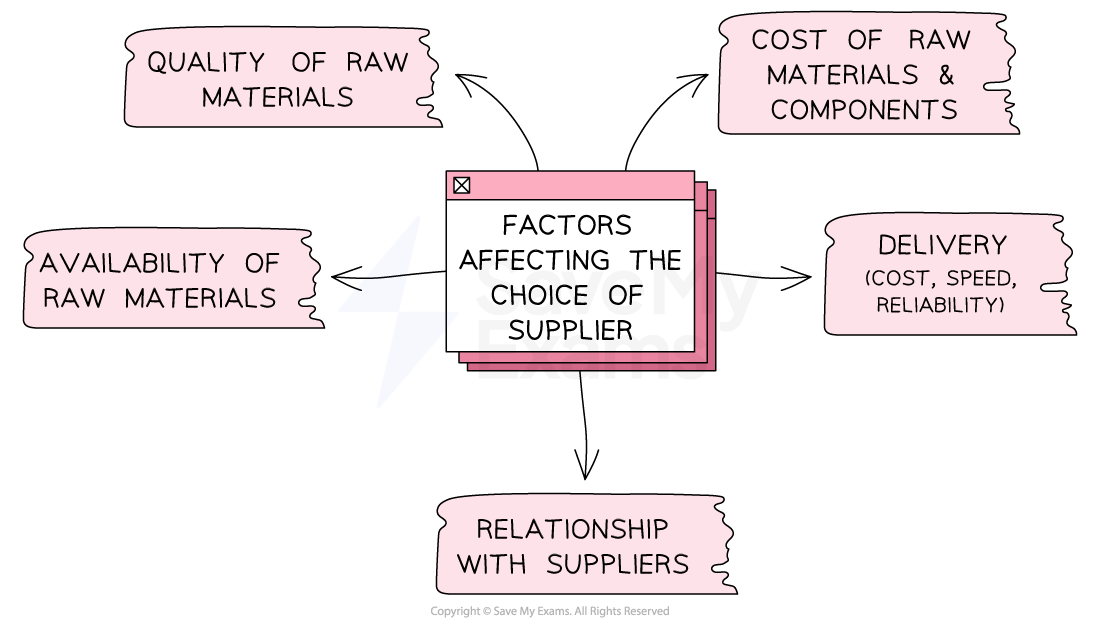
Factors that guide the choice of supplier
|
Factor |
Why it matters |
|---|---|
|
Quality |
|
|
Delivery reliability |
|
|
Availability and supply security |
|
|
Price and payment terms |
|
|
Ethical and sustainability standards |
|
|
Relationship and trust |
|
|
Flexibility and responsiveness |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Explain why reliability might outrank price for JIT firms, but price could still dominate for cost‑leaders
Weigh at least two factors before choosing a supplier to reach evaluation marks
The value of outsourcing
-
Outsourcing is the process through which a business delegates specific business activities (IT, customer support, HR, etc.) to external service providers
-
Businesses choose to outsource these functions to reduce costs, access specialised expertise or focus on core competencies
-
Advantages of outsourcing
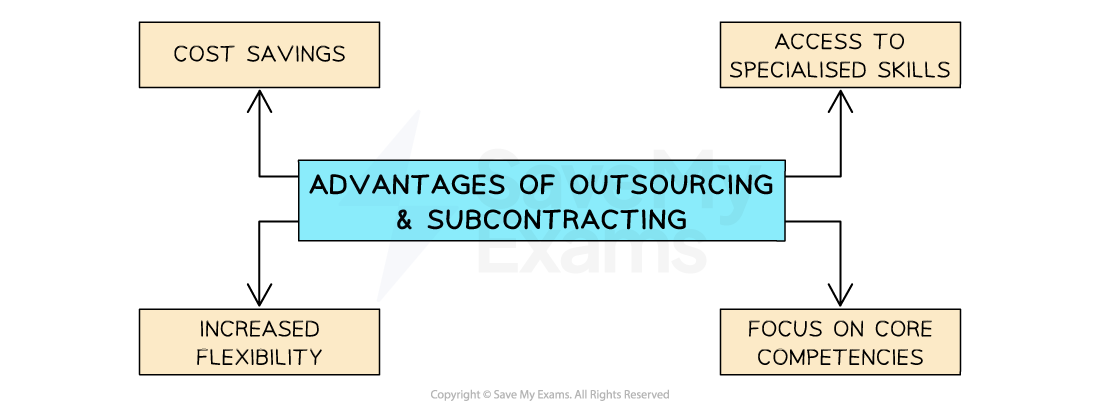
-
Cost savings
-
Businesses can often reduce expenses associated with operations such as hiring and training employees, maintaining infrastructure and managing IT systems
-
-
Access to specialised skills
-
External specialists have resources that the business lacks internally, whic
-

Responses