Exam code:7131
The importance of quality
-
Quality products are those whose characteristics and features satisfy the needs of customers
-
Customers may consider products or services to be of good quality if they:
-
look good and are sold by a reputable business or brand
-
are reliable and durable
-
are safe and fit for purpose
-
receive good customer service, including after-sales service
-
Factors that influence quality perception

-
Many businesses set quality targets to focus staff and resources on meeting customer expectations
-
Pizza chain Domino’s sets targets for home deliveries completed within 30 minutes of customers placing an order
-
Customers are fully refunded if their pizza arrives after this time
-
-
-
The quality of a business’s products can provide a competitive advantage
-
High levels of quality can be used in promotional activity and provide a unique selling point for businesses in competitive markets
-
Successfully developing a USP for quality can ease expansion into new markets as a result of the positive reputation it creates
-
Increased finance may be available to fund marketing activity to improve brand recognition and attract new customers
-
-
Quality is closely linked to price
-
High-quality products can usually command a high price
-
Lower-quality products may need to be sold at a discount to persuade customers to buy them
-
Methods of improving quality
Quality control
-
Quality control is a traditional method of checking quality at the end of the production process by using quality inspectors to find faults
-
It is not possible to achieve perfection in every production process
-
E.g. there will always be some variation in terms of materials used, production skills applied or reliability of the finished product
-
Benefits and drawbacks of quality control
|
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Quality assurance
-
Quality assurance involves inspecting the quality of production throughout the process
-
Workers check their own work and, sometimes, the work of others at various stages of production
-
-
Some business take a whole-business approach to quality assurance, with systems such as quality circles, benchmarking and total quality management (TQM)
Benefits and drawbacks of quality assurance
|
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Benefits and difficulties of improving quality
-
The quality of a business’s products can provide a competitive advantage
-
Unit costs are likely to be low if a business effectively manages quality
-
Low costs may allow a business to reduce its selling price to better compete with or undercut its rivals
-
-
High levels of quality can be used in promotional activity and provide a unique selling point for businesses in competitive markets
-
Successfully developing a USP for quality can ease expansion into new markets as a result of the positive reputation it creates
-
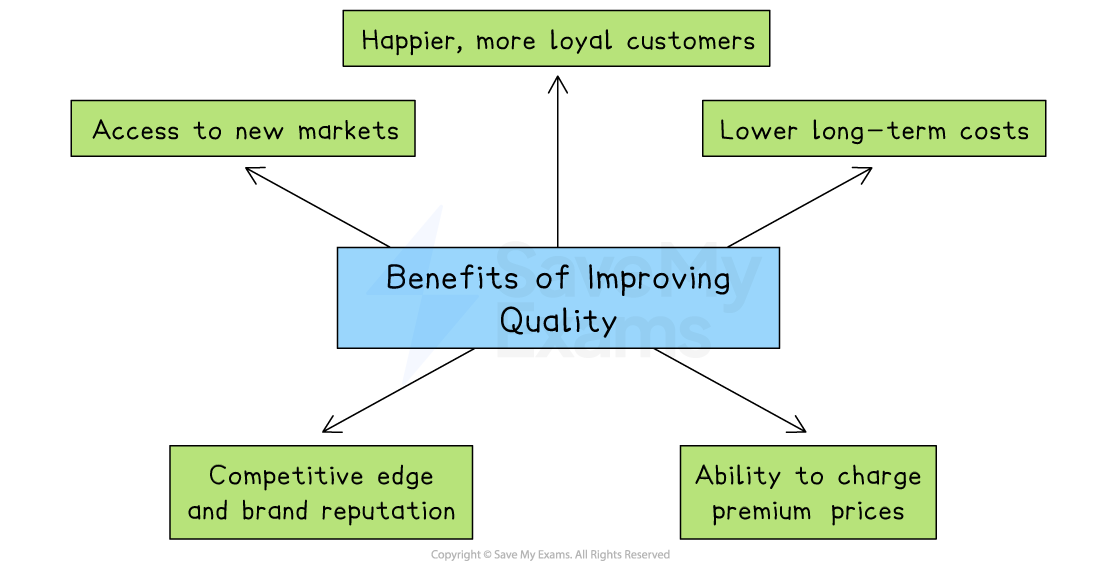
Benefits of improving quality
|
Benefit |
Explanation |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Happier, more loyal customers |
|
|
|
Ability to charge premium prices |
|
|
|
Lower long‑term costs |
|
|
|
Access to new markets |
|
|
|
Competitive edge and brand reputation |
|
|
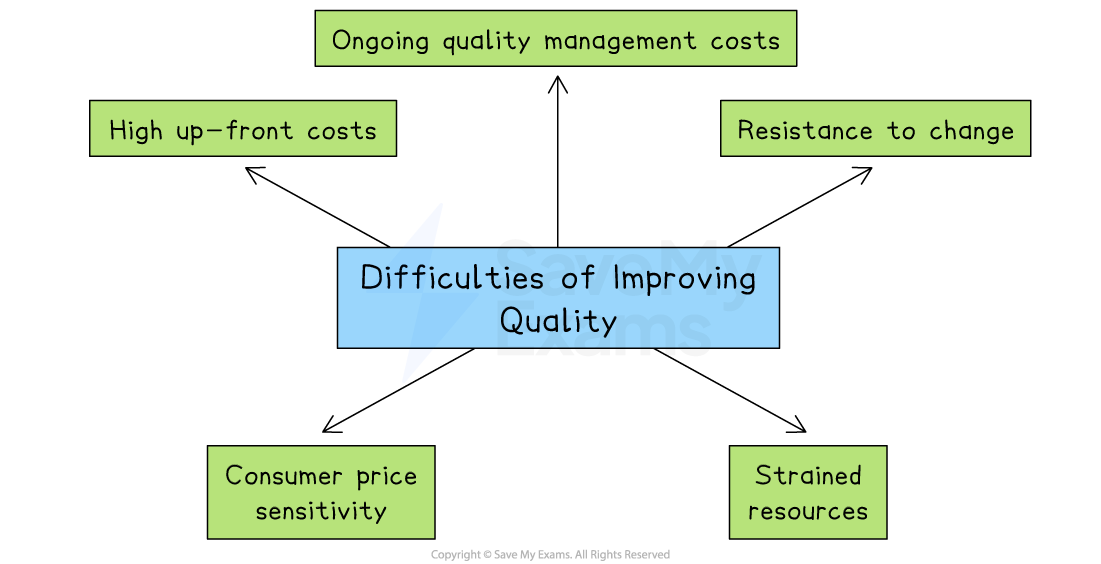
Difficulties of improving quality
-
High up‑front and ongoing quality management costs
-
Small firms often struggle to pay for staff training, better materials and certification fees
-
-
Staff or union resistance to new quality systems
-
Changing routines and adding checks can meet resistance from workers, slowing down their introduction
-
-
Customer price sensitivity
-
Better quality can push costs and, consequently, prices up
-
Price‑sensitive shoppers may switch brands
-
-
Strain on resources
-
If funds are scarce, pushing for higher quality can overstretch staff and cut service levels
-
Consequences of poor quality
-
Poor quality can cause a range of problems for a business
-
Costly recalls and repairs
-
Faulty goods must be taken back, fixed or refunded, which can have a significant impact on cash flow and profit
-
-
Heavy fines or legal payouts
-
Safety failures can end up in court, where fines, penalties and compensation bills are huge
-
-
Damaged brand reputation and lost customers
-
News of defects spreads quickly, making buyers switch to rivals they trust more
-
-
A sharp drop in sales and profits
-
Negative headlines can reduce sales and share price, and recovery can take years
-
-

Responses