Exam code:7131
Primary marketing research
-
Primary research is the process of gathering information directly from consumers in the target market using field research methods such as surveys and interviews
-
The acquired information is new and does not necessarily exist in any format
-
-
Businesses can choose from a range of primary marketing research methods and may combine a selection of methods to obtain comprehensive first-hand data

Surveys
-
The most widely used method for gathering primary research data is sampling through surveys
-
A series of questions are posed to a certain number of people (respondents)
-
The results from the “sample” are used to make inferences, which tare extrapolated to be true for the wider population
-
-
A wide range of respondents can be reached using online survey tools such as SurveyMonkey
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Observation
-
This involves hiring someone to stand in an appropriate location and study consumer behaviour in a store or perhaps judge the potential consumer traffic at a particular location
-
Researchers may observe the impact of packaging or the particular placement of a product in a store on consumer choice
-
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Interviews
-
The questions may be set up in a very similar way to a survey; however, an interviewer asks the questions
-
This method takes longer, but it does allow the interviewee to ask follow-up questions and gather information that might easily be missed when conducting surveys
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Test marketing
-
Free samples are provided to the target market for a limited period to gauge their response to the product
-
Adjustments to the product or other elements of the marketing mix can be made following feedback
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Focus groups
-
A marketing specialist leads free-form discussions to collect detailed feedback from the target market on all aspects of the marketing mix
-
Usually limited to a small group of 12–15 people
-
The group typically meets for 90 minutes to 3 hours
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
-
Businesses must choose a primary marketing research method that allows them to capture the correct form of data that can support decision-making
-
Each method has a range of advantages and disadvantages, which must be considered when making this choice
-
Evaluation of primary marketing research
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Technology and marketing research
-
Traditionally, primary research has been relatively difficult and expensive for businesses to gather
-
The rise of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and TikTok has changed this, providing businesses with incredible primary research opportunities
-
The speed of communication between businesses and customers can be almost instantaneous. E.g. by using online polls, thousands of responses can potentially be received in several hours
-
The cost of gathering this information can be very low. E.g. online polls take a few minutes to set up, and software automatically gathers and analyses the results
-
Social media helps businesses generate an interactive relationship with their customers, which helps to strengthen brand loyalty
-
Customers can also quickly provide feedback on products — or offer innovative ideas on how they want the products to be changed
-
This feedback may help the firm develop extension strategies within the product life cycle
-
Sampling
-
Sampling involves getting opinions from a selected group of people in order to find out about the market as a whole
-
It is expensive and time-consuming to collect data from all customers in a market
-
Marketing researchers use carefully designed sampling methods from which conclusions can be drawn about the market as a whole
-
In general, the larger the sample size, the more likely that results from marketing research activities will reflect the market as a whole
-
The main sampling methods
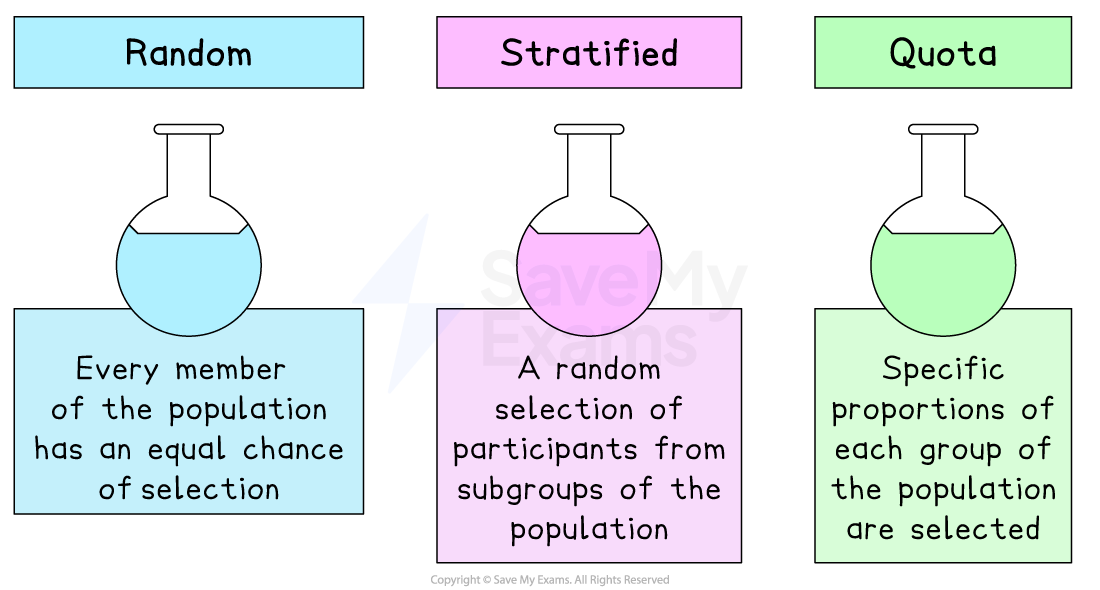
Random sampling
-
This method ensures that every member of the population has an equal chance of selection
-
E.g. a survey of gym members may be sent to a random selection of customers taken from the membership database
-
Advantages
-
Simple to design and interpret
-
As anyone in the population can be asked, bias should be avoided
Disadvantages
-
As anyone may be selected, the sample may not be representative of the market as a whole
-
Researchers need a complete and accurate population listing
Stratified sampling
-
This method involves the random selection of participants from subgroups of the population, such as age, gender, income level or education groups
-
E.g. a survey of school pupils may be carried out only on Year 10 girls
-
Advantages
-
Focuses on people from the key subgroup (for example, age or region), so the research results are likely to be highly relevant
Disadvantages
-
Setting up and running mini‑samples is likely to be more complex than organising one simple sample
Quota sampling
-
This method obtains a representative sample by determining specific proportions of each group of the population upon which to carry out research
-
E.g. a researcher conducting a survey for a family car manufacturer may seek to interview a sample comprising 25% of individuals aged 18–24, 50% aged 25–45 and 25% aged 46 and above
-
Advantages
-
Quick and easy way of obtaining a sample
-
It guarantees that hard‑to‑reach groups (such as older teens) appear in the right numbers in survey results
Disadvantages
-
Not random, so there is some risk of bias
-
Understanding the population is necessary in order to apply the results to the market as a whole
The choice of sampling method
-
The choice of sampling method will depend upon a wide range of factors
-
Time available
-
Where little time is available to carry out marketing research, a random sample may be most appropriate, as it is usually very quick and straightforward to organise
-
-
Knowledge of the target population
-
Where a business has good knowledge of the target population, a quota sample should provide a set of research data that lacks bias
-
-
Skills of researchers
-
Where researchers lack experience or expertise in marketing research, a focused stratified sample is likely to provide a useful set of data that can be easily interpreted
-
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A research population refers to the group of people in whom the business has an interest when conducting marketing research — a common mistake is to assume that research focuses on, say, the whole population of a country or region.

Responses