Biology_Edexcel_A-snab_Alevel
-
the-circulatory-system8 主题
-
diet-and-health11 主题
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport8 主题
-
nucleic-acids3 主题
-
proteins10 主题
-
inheritance7 主题
-
cell-structure-and-organisation7 主题
-
cell-division3 主题
-
reproduction-and-inheritance4 主题
-
differentiation-and-variation5 主题
-
biodiversity9 主题
-
resources-from-plants10 主题
-
plant-cell-structure
-
plant-stems
-
importance-of-water-and-inorganic-ions-to-plants
-
starch-and-cellulose-structure-and-function
-
plant-fibres
-
practical-identifying-tissue-types-within-stems
-
tensile-strength-plant-fibres
-
development-of-drug-testing
-
antimicrobial-properties-of-plants
-
sustainability-and-plant-materials
-
plant-cell-structure
-
ecosystems-and-energy-transfer7 主题
-
photosynthesis7 主题
-
climate-change10 主题
-
the-effects-of-climate-change
-
temperature-and-enzyme-activity
-
practical-temperature-and-development-of-organisms
-
climate-change-and-the-scientific-community
-
carbon-cycle-and-reduction-of-atmospheric-carbon-dioxide
-
reducing-climate-change
-
introduction-to-climate-change
-
evidence-for-the-causes-of-climate-change
-
the-greenhouse-effect
-
models-of-future-climate-change
-
the-effects-of-climate-change
-
evolution3 主题
-
forensics3 主题
-
microorganisms-and-immunity11 主题
-
muscles-and-movement3 主题
-
respiration7 主题
-
homeostasis4 主题
-
exercise4 主题
-
response-to-the-environment8 主题
-
the-brain-behaviour-and-disease10 主题
neurones-structure-and-function
Neurones: Structure & Function
-
Neurones are specialised cells of the nervous system which carry electrical impulses around the body
-
A bundle of neurones is known as a nerve
-
There are different types of neurones, but the following features are found in all types
-
A long fibre known as an axon
-
A cell body that contains the nucleus and other cellular structures
-
The end of the axon, known as the axon terminal, has many nerve endings
-
The nerve endings at the axon terminals allow neurones to connect to and receive impulses from other neurones, forming a network for easy communication
-
-
-
Some neurones are myelinated, meaning that their axon is insulated by a fatty layer known as the myelin sheath
-
The myelin sheath is made up of specialised cells known as Schwann cells which wrap themselves around the axon
-
There are uninsulated gaps between the Schwann cells known as the nodes of Ranvier
-
Electrical impulses in myelinated cells do not travel down the whole axon, but jump from one node to the next, speeding up impulse transmission
-
-
In non-myelinated neurones the axon is not insulated by Schwann cells
-
The impulse travels more slowly as it moves through the entire length of the axon
-
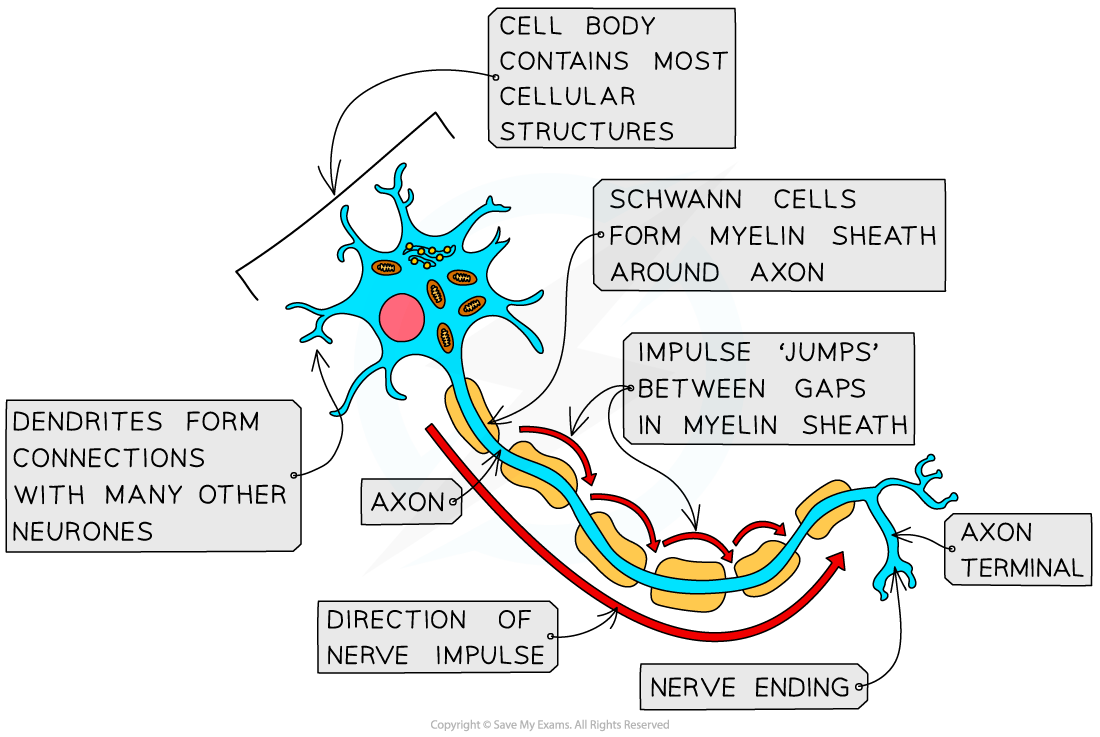
Neurones have a long axon, a cell body, and an axon terminal, and some neurones are myelinated
-
There are three main types of neurones
-
Sensory neurones carry impulses from receptors to the brain and spinal cord in the CNS
-
Relay neurones are found entirely within the CNS and connect sensory and motor neurones
-
Motor neurones carry impulses from the CNS to effector muscles or glands
-
-
Each type of neurone has a slightly different structure
-
Motor neurones
-
A large cell body at one end that lies within the spinal cord or brain
-
Many highly-branched dendrites extending from the cell body, providing many connections with the axon terminals of other neurones
-
-
Relay neurones
-
Short neurones with axons and highly branched dendrites
-
-
Sensory neurones
-
A cell body that branches off in the middle of the axon
-
The dendrites are attached to a receptor cell
-
The section of neurone that links the axon terminal (at the receptors) with the cell body is known as a dendron; it delivers the electrical impulse to the cell body
-
The section of neurone that connects the cell body with the CNS is the axon
-
-

Different types of neurone differ in both structure and function
