Biology_Edexcel_A-snab_Alevel
-
the-circulatory-system8 主题
-
diet-and-health11 主题
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport8 主题
-
nucleic-acids3 主题
-
proteins10 主题
-
inheritance7 主题
-
cell-structure-and-organisation7 主题
-
cell-division3 主题
-
reproduction-and-inheritance4 主题
-
differentiation-and-variation5 主题
-
biodiversity9 主题
-
resources-from-plants10 主题
-
plant-cell-structure
-
plant-stems
-
importance-of-water-and-inorganic-ions-to-plants
-
starch-and-cellulose-structure-and-function
-
plant-fibres
-
practical-identifying-tissue-types-within-stems
-
tensile-strength-plant-fibres
-
development-of-drug-testing
-
antimicrobial-properties-of-plants
-
sustainability-and-plant-materials
-
plant-cell-structure
-
ecosystems-and-energy-transfer7 主题
-
photosynthesis7 主题
-
climate-change10 主题
-
the-effects-of-climate-change
-
temperature-and-enzyme-activity
-
practical-temperature-and-development-of-organisms
-
climate-change-and-the-scientific-community
-
carbon-cycle-and-reduction-of-atmospheric-carbon-dioxide
-
reducing-climate-change
-
introduction-to-climate-change
-
evidence-for-the-causes-of-climate-change
-
the-greenhouse-effect
-
models-of-future-climate-change
-
the-effects-of-climate-change
-
evolution3 主题
-
forensics3 主题
-
microorganisms-and-immunity11 主题
-
muscles-and-movement3 主题
-
respiration7 主题
-
homeostasis4 主题
-
exercise4 主题
-
response-to-the-environment8 主题
-
the-brain-behaviour-and-disease10 主题
plant-stems
Plant Stems
Xylem vessels
-
The functions of xylem tissue in a plant are:
-
Vascular tissue that transports dissolved minerals and water around the plant
-
Structural support
-
-
Their cell walls contain lignin, which enables the vessels to withstand the pressure created by the moving column of water
-
Xylem vessels form long, hollow straw-like structures that are formed by dead cells (due to lignification of cell walls)
-
This means that they do not contain any cytoplasm or organelles that could slow down the flow of water
-
There are small regions in the walls that are not lignified, known as pits, which allows for lateral movement of water and minerals between xylem vessels

Images of xylem vessel elements: A = photomicrograph (drawing) in longitudinal section (lignin is stained red), B = scanning electron micrograph (drawing) in transverse section, C = microscope image (drawing) in transverse section (lignin is stained purple)
Structure and Function of Xylem Vessels Table

Sclerenchyma fibres
-
Sclerenchyma fibres are not involved in transport of substances, they provide support
-
Similar to xylem, they consist of bundles of dead cells
-
They form long, hollow tubes, but they do have end walls present
-
Lignification of cell walls occur, but they do not have pits like xylem vessels
-
They have more cellulose in their walls compared to other plant cells
Phloem tissue
-
The functions of phloem tissue in a plant are:
-
Transport organic compounds (assimilates), particularly sucrose, from sources (e.g. leaves) to sinks (e.g. roots). The transport of these compounds can occur up and down the plant
-
This is known as translocation
-
Phloem has no support function in a plant
-
-
The organic compounds are dissolved in water to form sap
-
Phloem is a complex tissue made up of various cell types; its bulk is made up of sieve tube elements which are the main conducting cells and companion cells
-
Other cell types of phloem tissue also include parenchyma for storage and strengthening fibres
-
Mature phloem tissue contains living cells, unlike xylem tissue

Structure of phloem tissue: A = microscope slide image (and below drawing) of a sieve tube element and companion cell in transverse section, B = photomicrograph image (and below drawing) of a sieve tube element and companion cell in longitudinal section

Structure of phloem tissue: C = transmission electron micrograph image (and drawing) of a sieve tube element and companion cell in transverse section
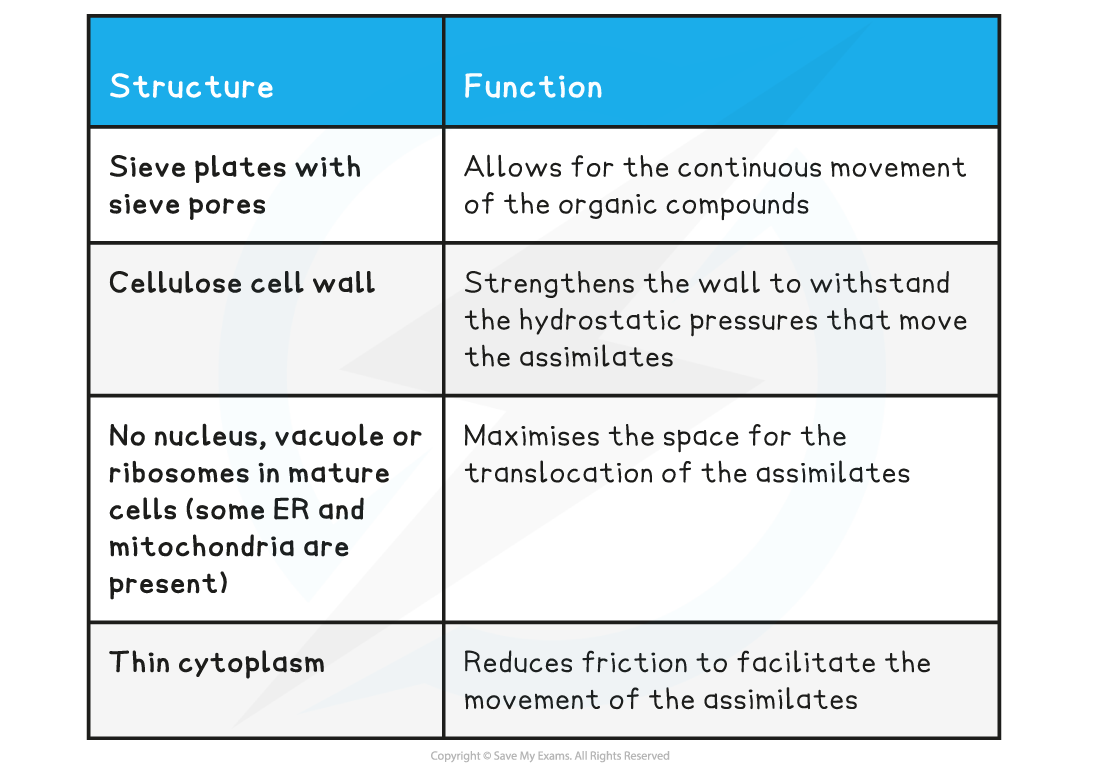
Sieve tube elements
-
Sieve tube elements line up end to end to form a continuous tube
Phloem Sieve Tube Elements Structure & Function Table
Companion cells
-
Each sieve tube element has a companion cell associated with it as companion cells control the metabolism of their associated sieve tube member
-
They also play a role in loading and unloading of sugars into the phloem sieve tube elements
Phloem Companion Cells Structure & Function Table

Vascular bundles in a stem
-
Vascular bundles consist of xylem vessels which are group together with phloem tissue
-
In a stem, the xylem vessels are always located towards the middle of the stem, while the phloem is located closer towards the outside of the stem
-
Sclerenchyma fibres are associated with the vascular bundles and provide additional support to the stem

Transverse section through a stem, showing the positions o
