Biology_Alevel_Ocr
-
4-1-communicable-diseases-disease-prevention-and-the-immune-system16 主题
-
4-1-1-common-pathogens-and-communicable-diseases
-
4-1-2-transmission-of-communicable-pathogens
-
4-1-3-plant-defences-against-pathogens
-
4-1-4-non-specific-immune-responses
-
4-1-5-phagocytes
-
4-1-6-blood-cells
-
4-1-7-the-t-lymphocyte-response
-
4-1-8-the-b-lymphocyte-response
-
4-1-9-primary-and-secondary-immune-responses
-
4-1-10-antibodies
-
4-1-11-opsonins-agglutinins-and-anti-toxins
-
4-1-12-types-of-immunity
-
4-1-13-autoimmune-diseases
-
4-1-14-principles-of-vaccination
-
4-1-15-sources-of-medicine
-
4-1-16-antibiotics
-
4-1-1-common-pathogens-and-communicable-diseases
-
4-2-biodiversity10 主题
-
4-2-1-biodiversity
-
4-2-2-sampling-to-determine-biodiversity
-
4-2-3-practical-investigating-biodiversity-using-sampling
-
4-2-4-measuring-species-richness-and-species-evenness
-
4-2-5-simpsons-index
-
4-2-6-genetic-diversity
-
4-2-7-factors-affecting-biodiversity
-
4-2-8-reasons-for-maintaining-biodiversity
-
4-2-9-methods-of-maintaining-biodiversity
-
4-2-10-conservation-agreements
-
4-2-1-biodiversity
-
4-3-classification-and-evolution15 主题
-
4-3-1-classification-of-species
-
4-3-2-binomial-system
-
4-3-3-classification-of-the-three-domains
-
4-3-4-classification-of-the-five-kingdoms
-
4-3-5-classification-and-phylogeny
-
4-3-6-evidence-of-evolution
-
4-3-7-types-of-variation
-
4-3-8-standard-deviation
-
4-3-9-variation-t-test-method
-
4-3-10-variation-t-test-worked-example
-
4-3-11-spearmans-rank-correlation
-
4-3-12-adaptation
-
4-3-13-natural-selection
-
4-3-14-evolution-of-resistance
-
4-3-15-consequences-of-resistance
-
4-3-1-classification-of-species
-
5-1-communication-and-homeostasis4 主题
-
5-2-excretion10 主题
-
5-2-1-the-importance-of-excretion
-
5-2-2-the-mammalian-liver-structure
-
5-2-3-the-mammalian-liver-function
-
5-2-4-the-liver-under-the-microscope
-
5-2-5-the-mammalian-kidney-structure
-
5-2-6-the-mammalian-kidney-function
-
5-2-7-the-kidney-under-the-microscope
-
5-2-8-osmoregulation
-
5-2-9-kidney-failure
-
5-2-10-excretory-products-and-medical-diagnosis
-
5-2-1-the-importance-of-excretion
-
5-3-neuronal-communication9 主题
-
5-4-hormonal-communication4 主题
-
5-5-plant-and-animal-responses16 主题
-
5-5-1-plant-responses
-
5-5-2-investigating-phototropism-and-geotropism
-
5-5-3-plant-hormones
-
5-5-4-auxins-and-apical-dominance
-
5-5-5-gibberellin
-
5-5-6-practical-effect-of-plant-hormones-on-growth
-
5-5-7-commercial-use-of-plant-hormones
-
5-5-8-mammalian-nervous-system
-
5-5-9-the-human-brain
-
5-5-10-reflex-actions
-
5-5-11-coordination-of-responses
-
5-5-12-factors-affecting-heart-rate
-
5-5-13-investigating-factors-affecting-heart-rate
-
5-5-14-mammalian-muscle-structure
-
5-5-15-transmission-across-a-neuromuscular-junction
-
5-5-16-the-sliding-filament-model
-
5-5-1-plant-responses
-
5-6-photosynthesis10 主题
-
5-6-1-photosynthesis-and-respiration
-
5-6-2-chloroplast-structure-and-function
-
5-6-3-photosynthetic-pigments
-
5-6-4-practical-investigating-photosynthetic-pigments-with-chromatography
-
5-6-5-the-light-dependent-stage
-
5-6-6-using-the-products-of-the-light-dependent-reaction
-
5-6-7-the-light-independent-stage
-
5-6-8-uses-of-triose-phosphate
-
5-6-9-factors-affecting-the-rate-of-photosynthesis
-
5-6-10-practical-investigating-factors-affecting-the-rate-of-photosynthesis
-
5-6-1-photosynthesis-and-respiration
-
5-7-respiration14 主题
-
5-7-14-practical-respirometer
-
5-7-1-the-need-for-cellular-respiration
-
5-7-2-structure-of-the-mitochondrion
-
5-7-3-the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
5-7-4-glycolysis
-
5-7-5-the-link-reaction
-
5-7-6-the-krebs-cycle
-
5-7-7-the-role-of-coenzymes
-
5-7-8-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
5-7-9-anaerobic-respiration
-
5-7-10-energy-yield-of-aerobic-vs-anaerobic-respiration
-
5-7-11-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-respiration
-
5-7-12-respiratory-substrates
-
5-7-13-respiratory-quotient-rq
-
5-7-14-practical-respirometer
-
6-1-cellular-control7 主题
-
6-2-patterns-of-inheritance13 主题
-
6-2-1-key-terms-in-genetics
-
6-2-2-variation-phenotype
-
6-2-3-variation-sexual-reproduction
-
6-2-4-predicting-inheritance-monohybrid-crosses
-
6-2-5-predicting-inheritance-dihybrid-crosses
-
6-2-6-predicting-inheritance-identifying-linkage
-
6-2-7-predicting-inheritance-identifying-epistasis
-
6-2-8-predicting-inheritance-chi-squared-test
-
6-2-9-continuous-and-discontinuous-variation
-
6-2-10-factors-affecting-evolution
-
6-2-11-the-hardy-weinberg-principle
-
6-2-12-isolation-and-speciation
-
6-2-13-artificial-selection
-
6-2-1-key-terms-in-genetics
-
6-3-manipulating-genomes11 主题
-
6-3-1-dna-sequencing
-
6-3-2-comparing-genomes
-
6-3-3-non-coding-dna-and-regulatory-genes
-
6-3-4-synthetic-biology
-
6-3-5-polymerase-chain-reaction
-
6-3-6-electrophoresis
-
6-3-7-dna-profiling
-
6-3-8-genetic-engineering
-
6-3-9-genetic-engineering-techniques
-
6-3-10-uses-of-genetic-engineering
-
6-3-11-gene-therapy
-
6-3-1-dna-sequencing
-
6-4-cloning-and-biotechnology14 主题
-
6-4-1-natural-clones-in-plants
-
6-4-2-producing-cuttings
-
6-4-3-production-of-artificial-clones-in-plants
-
6-4-4-uses-of-plant-cloning
-
6-4-5-natural-clones-in-animals
-
6-4-6-production-of-artificial-clones-in-animals
-
6-4-7-uses-of-animal-cloning
-
6-4-8-microorganisms-and-biotechnology
-
6-4-9-microorganisms-and-food-production
-
6-4-10-culturing-microorganisms
-
6-4-11-batch-and-continuous-fermentation
-
6-4-12-standard-growth-curve-of-microorganisms
-
6-4-13-factors-affecting-the-growth-of-microorganisms
-
6-4-14-immobilised-enzymes-in-biotechnology
-
6-4-1-natural-clones-in-plants
-
6-5-ecosystems7 主题
-
6-6-populations-and-sustainability6 主题
-
1-1-practical-skills-written-assessment7 主题
-
1-2-practical-skills-endorsement-assessment16 主题
-
1-2-1-practical-ethical-use-of-organisms
-
1-2-2-practical-aseptic-techniques
-
1-2-3-practical-dissection-of-gas-exchange-surfaces-in-fish-and-insects
-
1-2-4-drawing-cells-from-blood-smears
-
1-2-5-practical-investigating-biodiversity-using-sampling
-
1-2-6-practical-data-loggers-and-computer-modelling
-
1-2-7-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-diffusion
-
1-2-8-practical-investigating-water-potential
-
1-2-9-practical-factors-affecting-membrane-structure-and-permeability
-
1-2-10-biochemical-tests-reducing-sugars-and-starch
-
1-2-11-biochemical-tests-lipids
-
1-2-12-biochemical-tests-proteins
-
1-2-13-chromatography
-
1-2-14-serial-dilutions
-
1-2-15-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-transpiration
-
1-2-16-practical-using-a-light-microscope
-
1-2-1-practical-ethical-use-of-organisms
-
2-1-cell-structure9 主题
-
2-2-biological-molecules17 主题
-
2-2-1-properties-of-water
-
2-2-2-monomers-and-polymers
-
2-2-3-monosaccharides
-
2-2-4-the-glycosidic-bond
-
2-2-5-polysaccharides
-
2-2-6-biochemical-tests-reducing-sugars-and-starch
-
2-2-7-lipids-and-ester-bonds
-
2-2-8-lipids-structure-and-function
-
2-2-9-biochemical-tests-lipids
-
2-2-10-amino-acids-and-peptide-bonds
-
2-2-11-protein-structure
-
2-2-12-globular-proteins
-
2-2-13-fibrous-proteins
-
2-2-14-inorganic-ions
-
2-2-15-biochemical-tests-proteins
-
2-2-16-finding-the-concentration-of-a-substance
-
2-2-17-chromatography
-
2-2-1-properties-of-water
-
2-3-nucleotides-and-nucleic-acids8 主题
-
2-4-enzymes9 主题
-
2-4-1-the-role-of-enzymes
-
2-4-2-enzyme-action
-
2-4-3-enzyme-activity-ph
-
2-4-4-enzyme-activity-temperature
-
2-4-5-enzyme-activity-enzyme-concentration
-
2-4-6-enzyme-activity-substrate-concentration
-
2-4-7-enzyme-activity-enzyme-inhibitors
-
2-4-8-coenzymes-cofactors-and-prosthetic-groups
-
2-4-9-practical-measuring-enzyme-activity
-
2-4-1-the-role-of-enzymes
-
2-5-biological-membranes9 主题
-
2-5-1-the-cell-surface-membrane
-
2-5-2-membrane-structure-and-permeability
-
2-5-3-diffusion-and-facilitated-diffusion
-
2-5-4-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-diffusion
-
2-5-5-active-transport
-
2-5-6-endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
2-5-7-osmosis
-
2-5-8-osmosis-in-animal-and-plant-cells
-
2-5-9-practical-investigating-water-potential
-
2-5-1-the-cell-surface-membrane
-
2-6-cell-division-cell-diversity-and-cellular-organisation11 主题
-
2-6-1-the-cell-cycle
-
2-6-2-the-stages-of-mitosis
-
2-6-3-identifying-mitosis-in-plant-cells
-
2-6-4-the-significance-of-mitosis
-
2-6-5-the-stages-of-meiosis
-
2-6-6-the-significance-of-meiosis
-
2-6-7-specialised-cells
-
2-6-8-the-organisation-of-cells
-
2-6-9-stem-cells
-
2-6-10-stem-cells-in-animals-and-plants
-
2-6-11-the-use-of-stem-cells
-
2-6-1-the-cell-cycle
-
3-1-exchange-surfaces7 主题
-
3-2-transport-in-animals12 主题
-
3-2-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-animals
-
3-2-2-circulatory-systems
-
3-2-3-blood-vessels
-
3-2-4-tissue-fluid
-
3-2-5-the-mammalian-heart
-
3-2-6-practical-mammalian-heart-dissection
-
3-2-7-the-cardiac-cycle
-
3-2-8-cardiac-output
-
3-2-9-heart-action-initiation-and-control
-
3-2-10-electrocardiograms-ecgs
-
3-2-11-the-role-of-haemoglobin
-
3-2-12-adult-and-fetal-haemoglobin
-
3-2-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-animals
-
3-3-transport-in-plants11 主题
-
3-3-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-plants
-
3-3-2-the-xylem-and-phloem
-
3-3-3-the-xylem
-
3-3-4-the-phloem
-
3-3-5-transverse-sections-stems-roots-and-leaves
-
3-3-6-the-process-of-transpiration
-
3-3-7-transpiration-in-plants
-
3-3-8-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-transpiration
-
3-3-9-translocation
-
3-3-10-the-mass-flow-hypothesis
-
3-3-11-the-adaptations-of-xerophytic-and-hydrophytic-plants
-
3-3-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-plants
4-3-10-variation-t-test-worked-example
Variation: t-test worked example
-
The t test method can be used to determine whether the means of two data sets are significantly different
Worked Example
The ear lengths of two populations of rabbits were measured.
Ear lengths of population A (mm):
62, 60, 59, 61, 60, 58, 59, 60, 57, 56, 59, 58, 60, 59, 57
Ear lengths of population B (mm):
58, 59, 57, 59, 59, 57, 55, 60, 57, 58, 59, 58, 57, 58, 59
Use the t-test to determine whether there is a significant difference in ear length between the two populations.
-
Null hypothesis: There is no significant difference between the ear lengths of the rabbits in populations A and B
-
Sample sizes:
-
Population A: n1 = 15
-
Population B: n2 = 15
-
Step 1: calculate the mean for each data set:
Mean for population A x̅1 = 885 ÷ 15 = 59 mm
Mean for population B x̅2 = 870 ÷ 15 = 58 mm
Step 2: calculate the standard deviation (s) for each data set
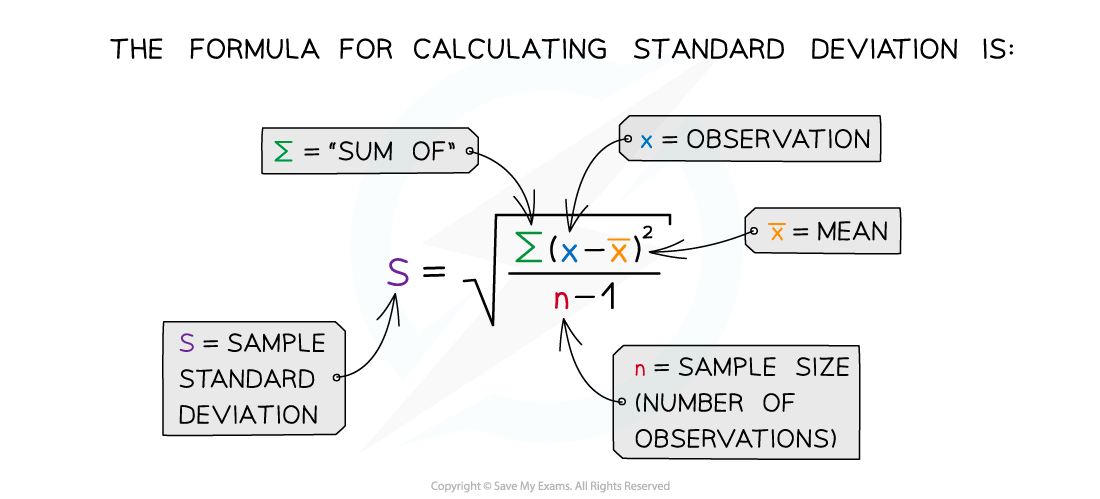
-
Calculate ∑(x – x̄)2
|
Population A |
Population B |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Difference between value and mean (x – x̄) |
Difference between value and mean squared (x – x̄)2 |
Difference between value and mean (x – x̄) |
Difference between value and mean squared (x – x̄)2 |
|
62 – 59 = 3 |
9 |
58 – 58 = 0 |
0 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
59 – 58 = 1 |
1 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
57 – 58 = -1 |
1 |
|
61 – 59 = 2 |
4 |
59 – 58 = 1 |
1 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
59 – 58 = 1 |
1 |
|
58 – 59 = -1 |
1 |
57 – 58 = -1 |
1 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
55 – 58 = -3 |
9 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
60 – 58 = 2 |
4 |
|
57 – 59 = -2 |
4 |
57 – 58 = -1 |
1 |
|
56 – 59 = -3 |
9 |
58 – 58 = 0 |
0 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
59 – 58 = 1 |
1 |
|
58 – 59 = -1 |
1 |
58 – 58 = 0 |
0 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
57 – 58 = -1 |
1 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
58 – 58 = 0 |
0 |
|
57 – 59 = -2 |
4 |
59 – 58 = 1 |
1 |
|
Total ∑(x – x̄)2 |
36 |
Total ∑(x – x̄)2 |
22 |
-
Calculate
|
Population A (n1 = 15) </ |
|---|
