Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
phloem-sieve-tube-elements
Phloem sieve tube elements & companion cells: structure & function
-
The function of phloem tissue in a plant is to:
-
Transport organic compounds (assimilates), particularly sucrose, from the source (e.g. leaf) to the sink (e.g. roots)
-
The transport of these compounds in phloem tissue can occur up and down the plant
-
-
-
The organic compounds are dissolved in water to form sap
-
Phloem is a complex tissue made up of various cell types
-
Its bulk is made up of sieve tube elements which are the main conducting cells and companion cells
-
Other cell types of phloem tissue also include parenchyma for storage and strengthening fibres
-
-
Mature phloem tissue contains living cells, unlike xylem tissue
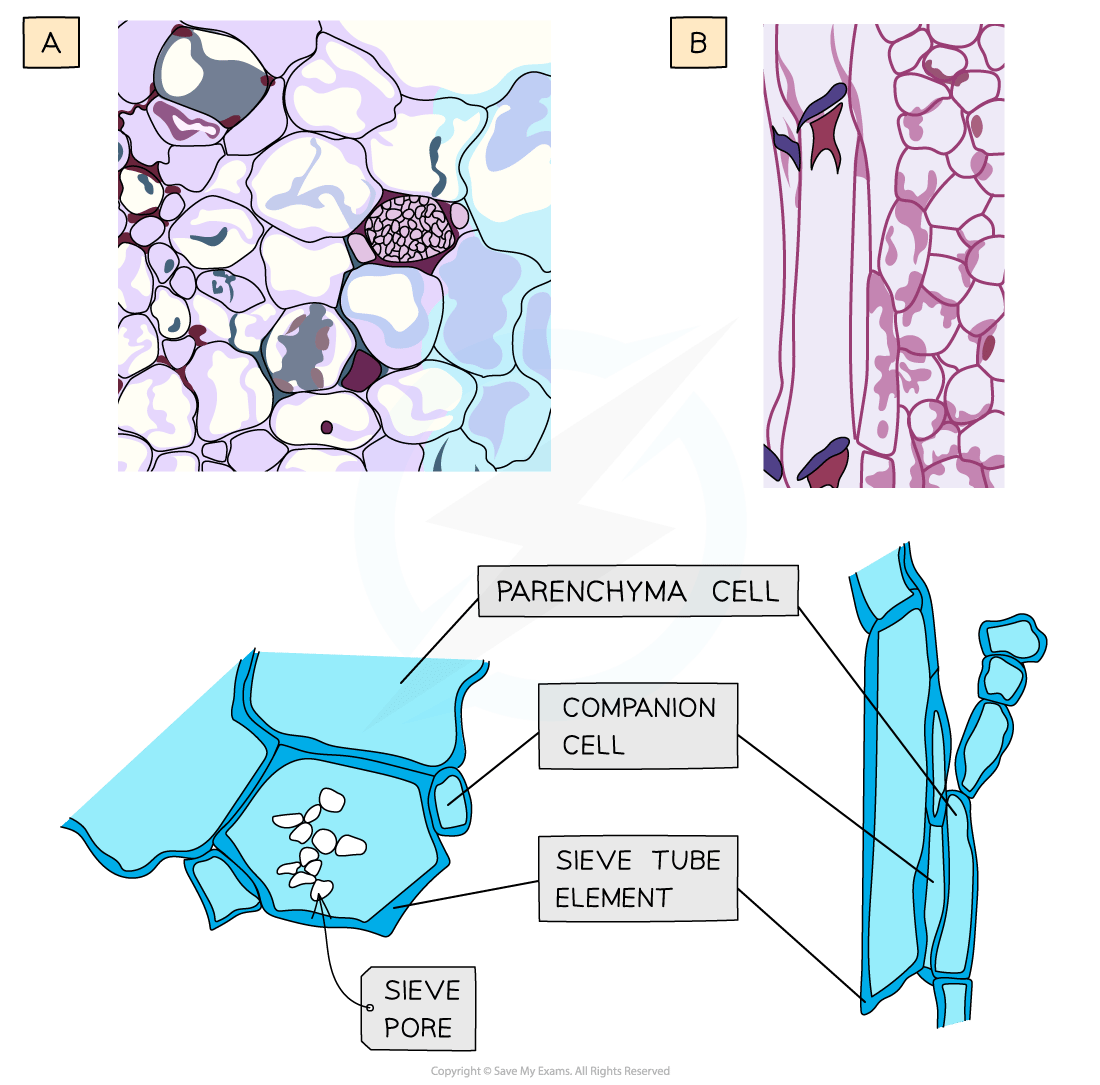
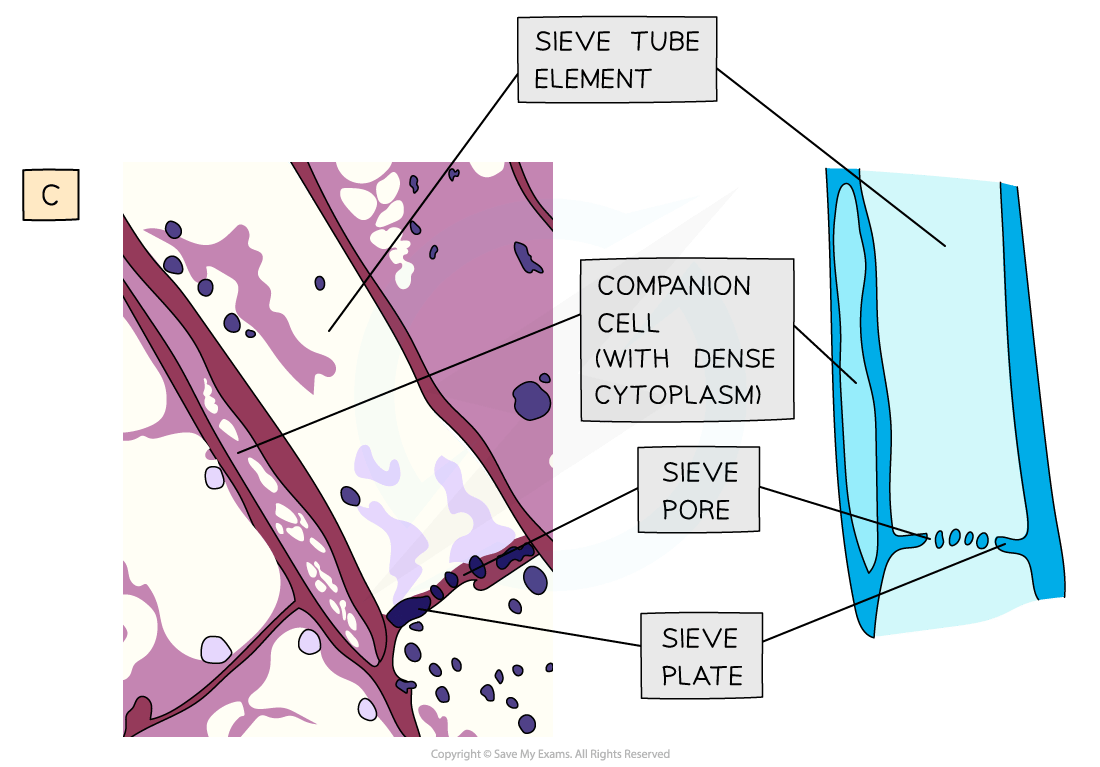
Sieve tube elements
-
Sieve tube elements line up end to end to form a continuous tube
-
They transport sugars and nutrients up and down the plants in sieve cells
|
Structure |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Sieve plates with sieve pores |
Allows for continuous movement of organic substances |
|
Cellulose cell wall |
Strengthens the wall to withstand the hydrostatic pressures that move assimilates |
|
No nucleus, ribosomes or vacuole in mature cells |
Maximises space for movement of assimilates |
|
Thin cytoplasm |
Reduces friction to facilitate movement of assimilates |
Companion cells
-
Each sieve tube element has a companion cell associated with it as companion cells control the metabolism of their associated sieve tube member
-
They also play a role in loading and unloading of sugars into the phloem
|
Structure |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Nucleus and other organelles present |
Provides metabolic support to sieve tube elements and helps with loading and unloading of assimilates |
|
Transport proteins in plasma membranes |
Moves assimilates into and out of sieve tube elements |
|
Large numbers of mitochondria |
Provides ATP for the active transport of assimilates |
|
Plasmodesmata (channels in cell wall) |
The link to sieve tube elements, allowing organic compounds to move from the companion cells into the sieve tube elements |
Comparing xylem and phloem
-
Xylem and phloem are similar in some ways but there are key differences that ensure they can carry out their separate functions in transport around the plant
|
|
Xylem |
Phloem |
|---|---|---|
|
Living cells |
No (hollow cells) |
Yes (companion cells) |
|
Substances transported |
Water and mineral ions |
Organic compounds/assimilates |
|
Process of transportation |
Transpiration |
Active translocation |
|
Direction of flow |
One way / upwards (roots to leaves) |
Two ways / up and down (source to sink) |
|
Presence of end walls |
No |
Yes (sieve plates) |
|
Cell wall material |
Lignin and cellulose |
Cellulose |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Understand the difference between sieve tube elements and companion cells, and how they are different to xylem tissue.
Remember that mature xylem tissue is dead, so there is no evidence of organelles, and they have lignified cell walls, whereas sieve tube elements have no lignin, do have sieve plates, and their companion cells contain nuclei and dense cytoplasm.
