Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
gene-mutations
Gene mutations & their effect on polypeptides
-
A gene mutation is a change in the sequence of base pairs in a DNA molecule that may result in an altered polypeptide
-
As the DNA base sequence determines the sequence of amino acids that make up a protein, mutations in a gene can sometimes lead to a change in the polypeptide that the gene codes for
-
Most mutations do not alter the polypeptide or only alter it slightly so that its structure or function is not changed
-
This is because the genetic code is degenerate
-
-
There are different ways that a mutation in the DNA base sequence can occur:
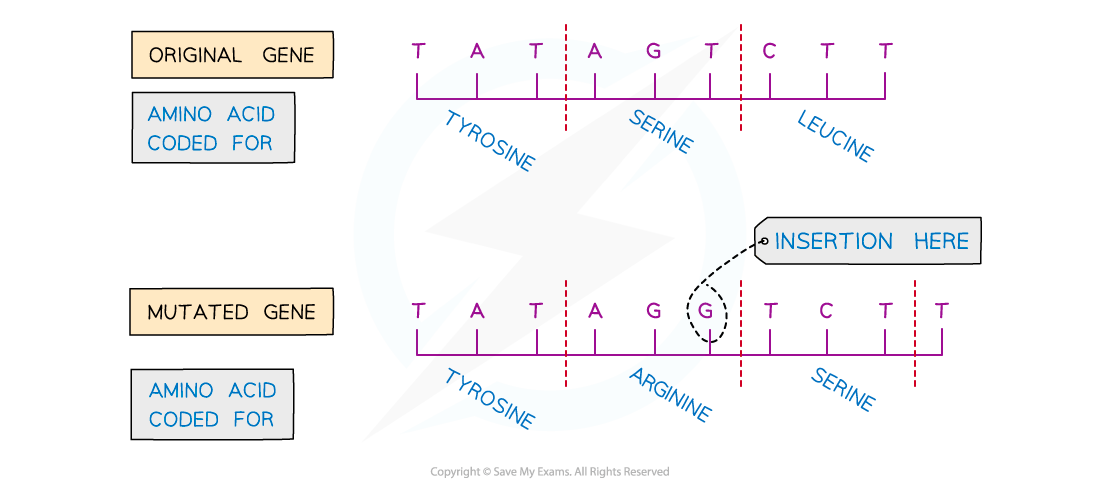
Insertion of nucleotides
-
A mutation that occurs when a nucleotide (with a new base) is randomly inserted into the DNA sequence is known as an insertion mutation
-
An insertion mutation changes the amino acid that would have been coded for by the original base triplet, as it creates a new, different triplet of bases
-
An insertion mutation also has a knock-on effect by changing the triplets (groups of three bases) further on in the DNA sequence
-
This is sometimes known as a frameshift mutation
-
-
This may dramatically change the amino acid sequence produced from this gene and therefore the ability of the polypeptide to function
Deletion of nucleotides
-
A mutation that occurs when a nucleotide (and therefore its base) is randomly deleted from the DNA sequence
-
Like an insertion mutation, a deletion mutation:
-
Changes the amino acid that would have been coded for
-
Has a knock-on effect by changing the groups of three bases further on in the DNA sequence
-
This is another type of frameshift mutation
-
-
-
This may dramatically change the amino acid sequence produced from this gene and therefore the ability of the polypeptide to function
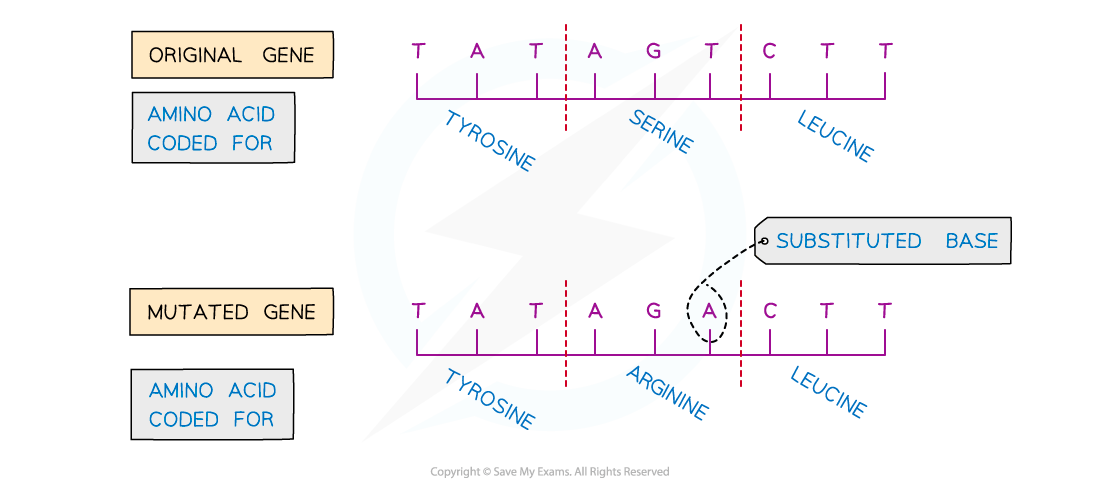
Substitution of nucleotides
-
A mutation that occurs when a base in the DNA sequence is randomly swapped for a different base
-
Unlike an insertion or deletion mutation, a substitution mutation will only change the amino acid for the triplet (a group of three bases) in which the mutation occurs
-
It will not have a knock-on effect (it is not a frameshift mutation)
-
The effect of gene mutations on polypeptides
-
Most mutations do not alter the polypeptide or only alter it slightly so that its appearance or function is not changed
-
However, a small number of mutations code for a significantly altered polypeptide with a different shape
-
This may affect the ability of the protein to perform its function
-
For example:
-
If the shape of the active site on an enzyme changes, the substrate may no longer be able to bind to the active site
-
A structural protein (like collagen) may lose its strength if its shape changes
-
-
