Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
semi-conservative-dna-replication
Semi-conservative DNA replication
-
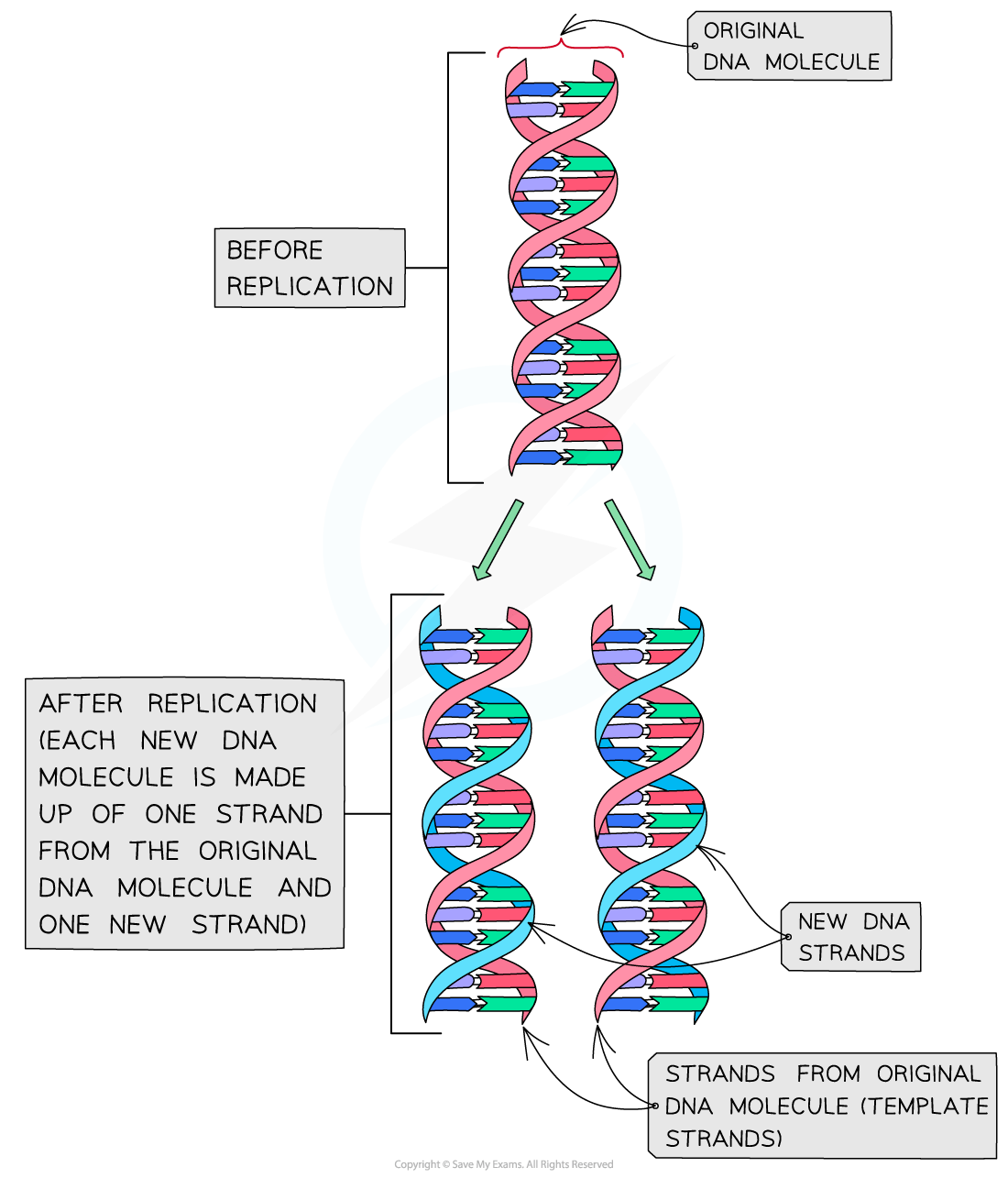
DNA replication occurs in preparation for mitosis when a parent cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells
-
This is because each daughter cell needs to contain the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell
-
Therefore the number of DNA molecules in the parent cell must be doubled before mitosis takes place
-
-
DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle
-
This occurs during interphase when a cell is not dividing
-
-
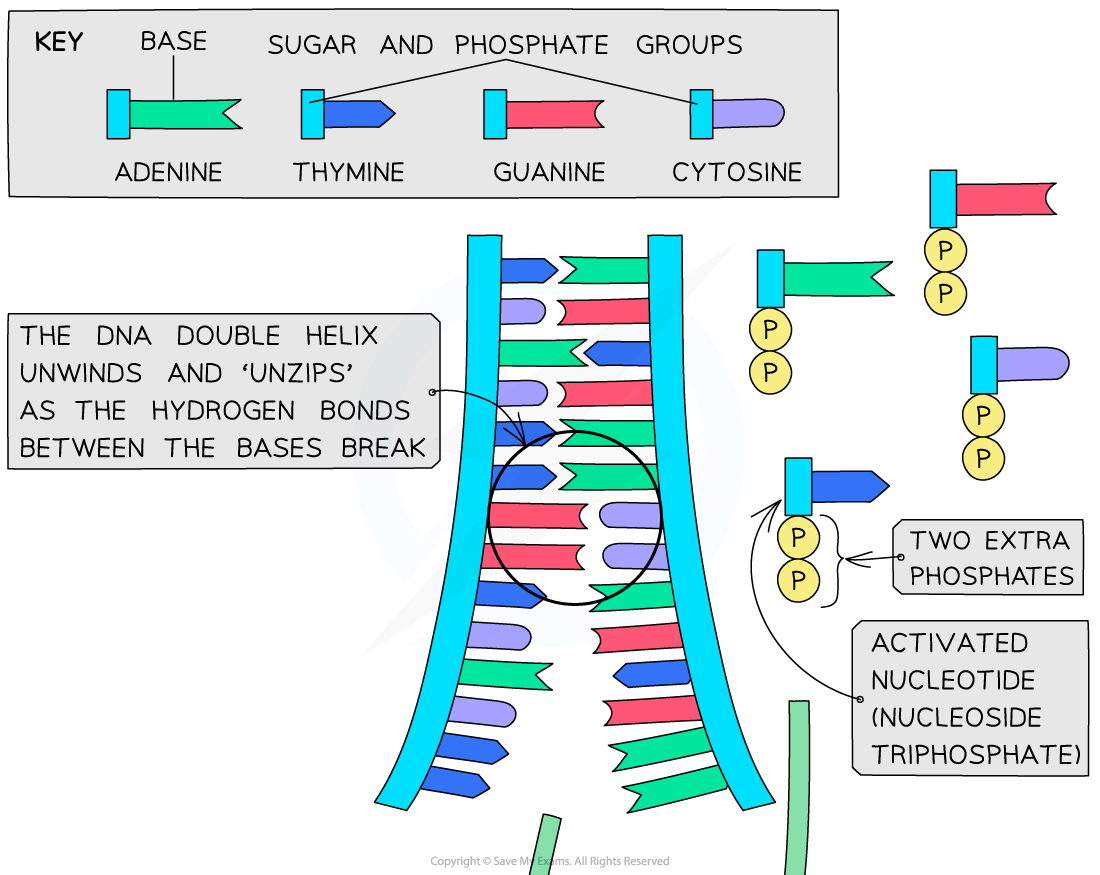
The hydrogen bonds between the base pairs on the two antiparallel polynucleotide DNA strands are broken
-
This ‘unzips’ or unwinds the DNA double helix to form two single polynucleotide DNA strands
-
-
Each of these single polynucleotide DNA strands acts as a template for the formation of a new strand
-
The original strand and the new strand then join together to form a new DNA molecule
-
-
This method of replicating DNA is known as semi-conservative replication because half of the original DNA molecule is kept (conserved) in each of the two new DNA molecules
DNA polymerase
-
In the nucleus, there are free nucleotides to which two extra phosphates have been added
-
These free nucleotides with three phosphate groups are known as nucleoside triphosphates or ‘activated nucleotides’
-
-
The extra phosphates activate the nucleotides, enabling them to take part in DNA replication
-
The bases of the free nucleoside triphosphates align with their complementary bases on each of the template DNA strands
-
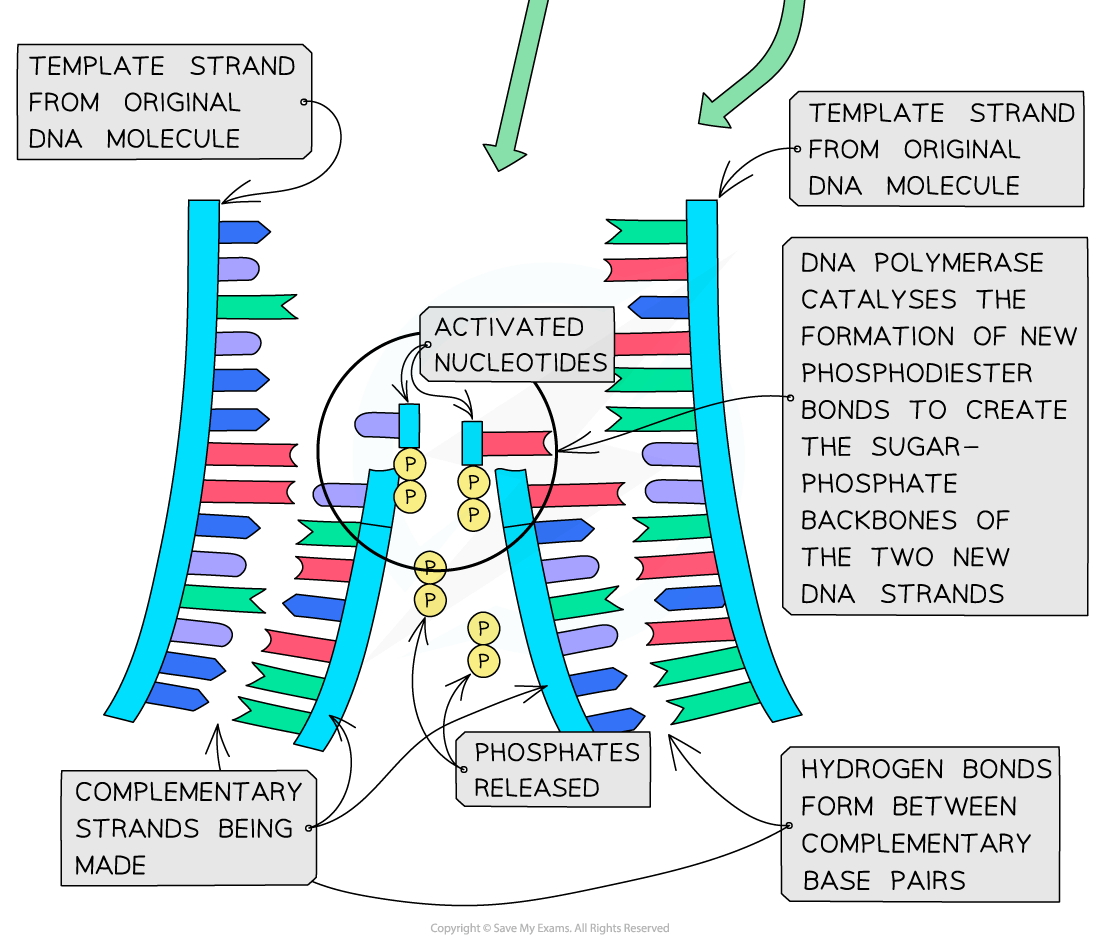
The enzyme DNA polymerase synthesises new DNA strands from the two template strands
-
It does this by catalysing condensation reactions between the deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups of adjacent nucleotides within the new strands
-
This creates the sugar-phosphate backbone of the new DNA strands
-
-
DNA polymerase cleaves (breaks off) the two extra phosphates and uses the energy released to create the phosphodiester bonds (between adjacent nucleotides)
-
Hydrogen bonds then form between the complementary base pairs of the template and new DNA strands
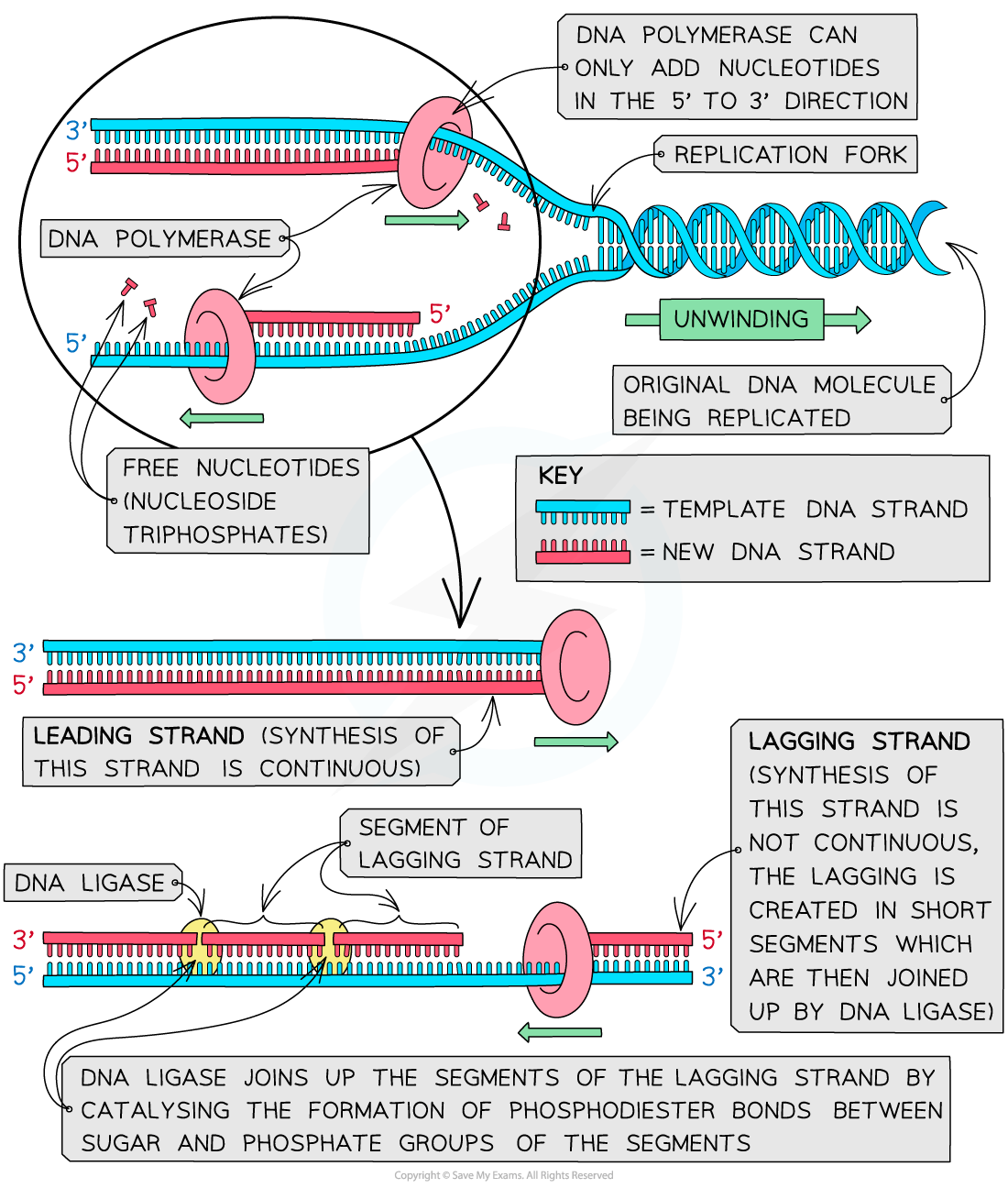
Leading and lagging strands
-
DNA polymerase can only add new DNA nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction, so the new DNA strand is built from its 5′ end towards its 3′ end
-
This is because DNA polymerase is an enzyme with a specific active site, so can only attach to the 3’ end of the original strand and move towards its 5′ end
-
-
On one of the DNA template strands the DNA polymerase enzyme can move continuously towards the replication fork as the DNA molecule is unzipped, so the new strand will be produced in one long piece
-
The strand that DNA polymerase synthesises continuously in this way is known as the leading strand
-
-
On the other strand, which is antiparallel to the strand described above, DNA polymerase moves away from the replication fork, meaning that the new DNA is synthesised in short segments as the new sections of the template strand are exposed
-
The strand in which DNA is synthesised in short segments is known as the lagging strand
-
The short segments are known as Okazaki fragments
-
A second enzyme, DNA ligase, is needed to join these short segments together to form a continuous new DNA strand
-