Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
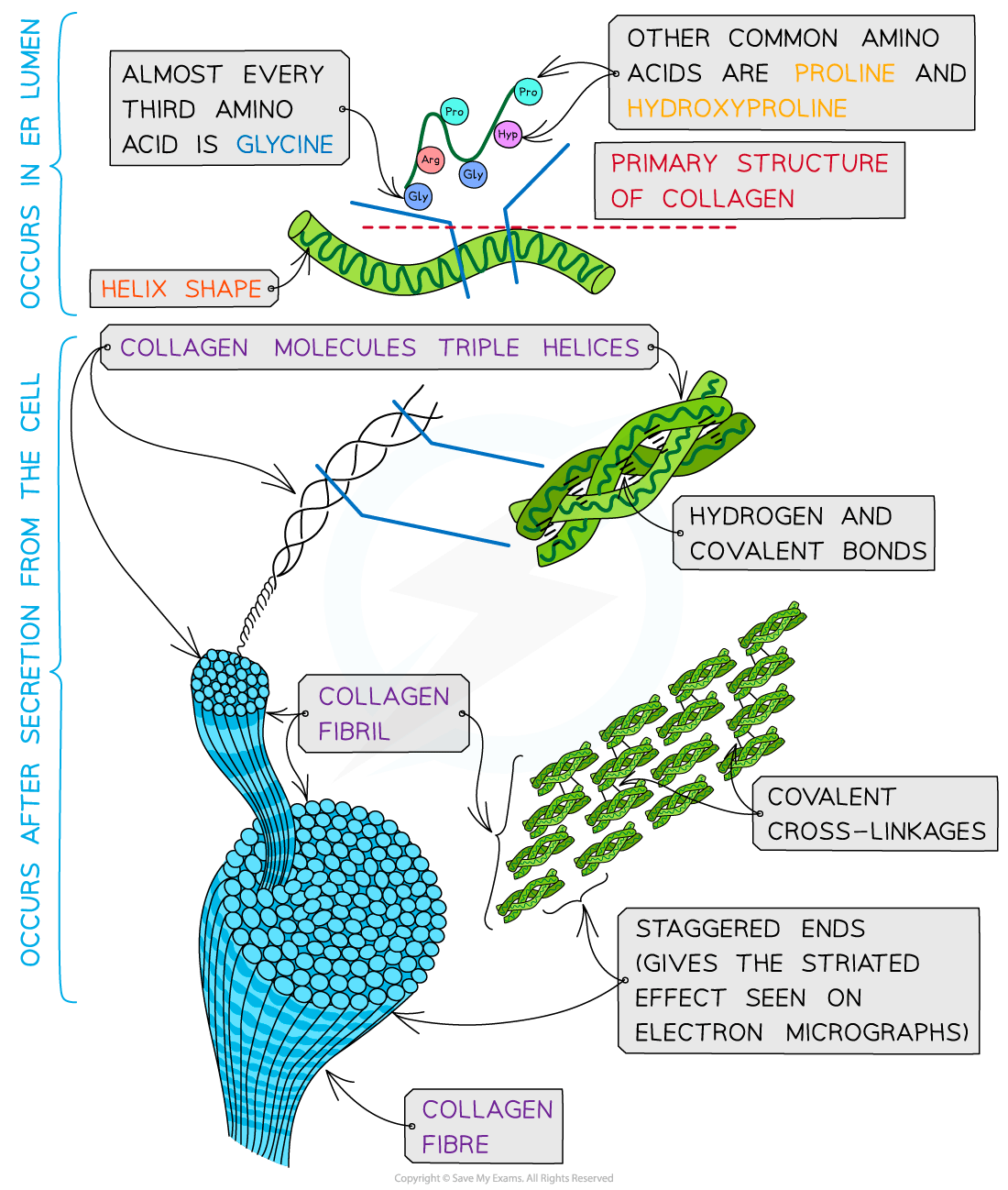
The molecular structure of collagen
-
Collagen is the most common structural protein found in vertebrates
-
In vertebrates it is the component of connective tissue which forms:
-
Tendons
-
Cartilage
-
Ligaments
-
Bones
-
Teeth
-
Skin
-
Walls of blood vessels
-
Cornea of the eye
-
-
Collagen is an insoluble fibrous protein
Structure
-
Collagen is formed from three polypeptide chains closely held together by hydrogen bonds to form a triple helix (known as tropocollagen)
-
Each polypeptide chain:
-
Is a helix shape (but not α-helix as the chain is not as tightly wound)
-
Contains about 1000 amino acids with glycine, proline and hydroxyproline being the most common
-
-
In the primary structure of collagen almost every third amino acid is glycine
-
This is the smallest amino acid with a R group that contains a single hydrogen atom
-
Glycine tends to be found on the inside of the polypeptide chains allowing the three chains to be arranged closely together forming a tight triple helix structure
-
-
Along with hydrogen bonds forming between the three chains there are also covalent bonds present
-
Covalent bonds also form cross-links between R groups of amino acids in interacting triple helices when they are arranged parallel to each other
-
The cross-links hold the collagen molecules together to form fibrils
-
-
The collagen molecules are positioned in the fibrils so that there are staggered ends
-
This gives the striated effect seen in electron micrographs
-
-
When many fibrils are arranged together they form collagen fibres
-
Collagen fibres are positioned so that they are lined up with the forces they are withstanding
Function
-
Collagen is a flexible structural protein forming connective tissues
-
The presence of the many hydrogen bonds within the triple helix structure of collagen results in great tensile strength
-
This enables collagen to be able to withstand large pulling forces without stretching or breaking
-
-
The staggered ends of the collagen molecules within the fibrils provide strength
-
Collagen is a stable protein due to the high proportion of proline and hydroxyproline amino acids
-
This results in more stability as their R groups repel each other
-
-
The length of collagen molecules means they take too long to dissolve in water, so collagen is therefore insoluble in water
|
Feature |
Collagen |
Haemoglobin |
|---|---|---|
|
Number of polypeptide chains |
3 (triple helix) |
4 (two alpha globin, two beta globin) |
|
Outline (shape) |
Long, thin |
Spherical |
|
Type of protein |
Fibrous |
Globular |
|
Main function |
Structural (forms connective tissue) |
Functional (transports oxygen) |
|
Amino acid variation |
Repetitive |
Variable |
|
Prosthetic group |
No |
Yes (haem group) |
|
Solubility |
Insoluble in water |
Soluble in water |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Use the acronym NOT MAPS (number, outline, type etc.) to help you revise how the function relates to the structure of collagen and know the difference between collagen and haemoglobin.
