Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
starch-and-glycogen
Starch & glycogen: structures & functions
-
Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides
-
Polysaccharides are polymers formed from many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds to form chains; these chains may be:
-
Branched or unbranched
-
Folded
-
Straight or coiled
-
-
Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides because they are:
-
Compact
-
Many molecules fit into a small space, so large volumes can be stored inside cells
-
-
Insoluble
-
They do not dissolve in the cell cytoplasm, so have no osmotic effect on cells; soluble molecules like glucose would lower the water potential of cell cytoplasm, drawing water into cells by osmosis
-
-
Starch
-
Starch is the storage polysaccharide of plants. It is stored as granules in plastids (e.g. chloroplasts)
-
Due to the many monomers in a starch molecule, it takes longer to digest than glucose
-
Starch is constructed from two different polysaccharides:
-
Amylose (10 – 30% of starch)
-
Unbranched helix-shaped chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose molecules
-
The helix shape enables it to be more compact and thus it is more resistant to digestion
-
-
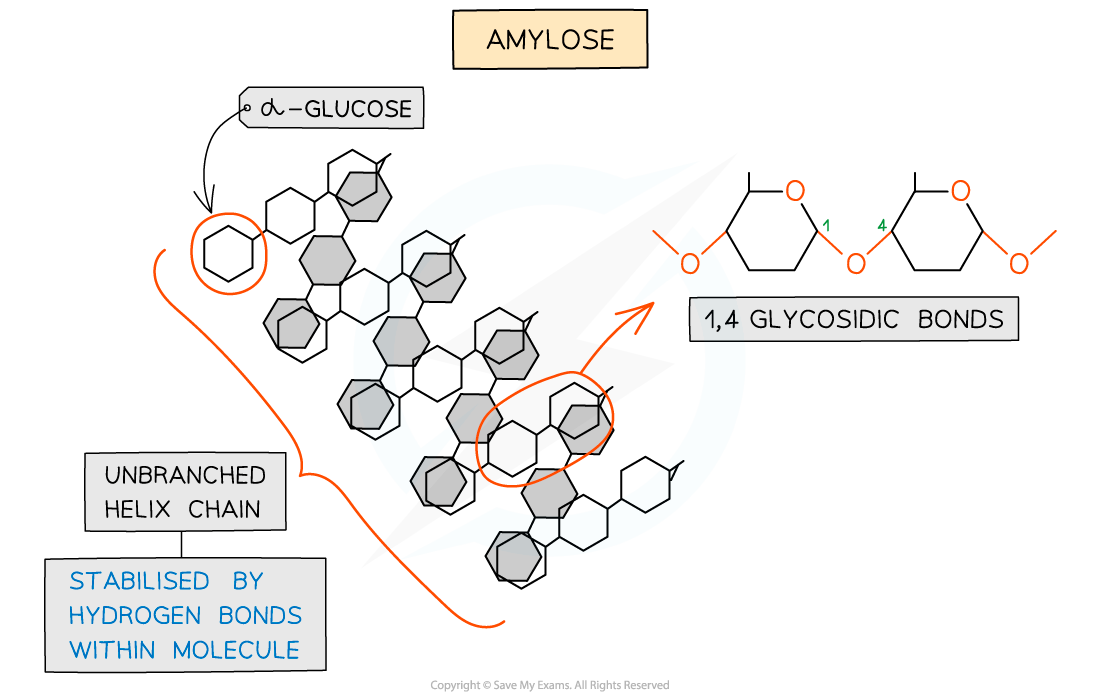
-
Amylopectin (70 – 90% of starch)
-
1,4 glycosidic bonds between α-glucose molecules but also 1,6 glycosidic bonds form between glucose molecules creating a branched molecule
-
The branches result in many terminal glucose molecules that can be easily hydrolysed for use during cellular respiration or added to for storage
-
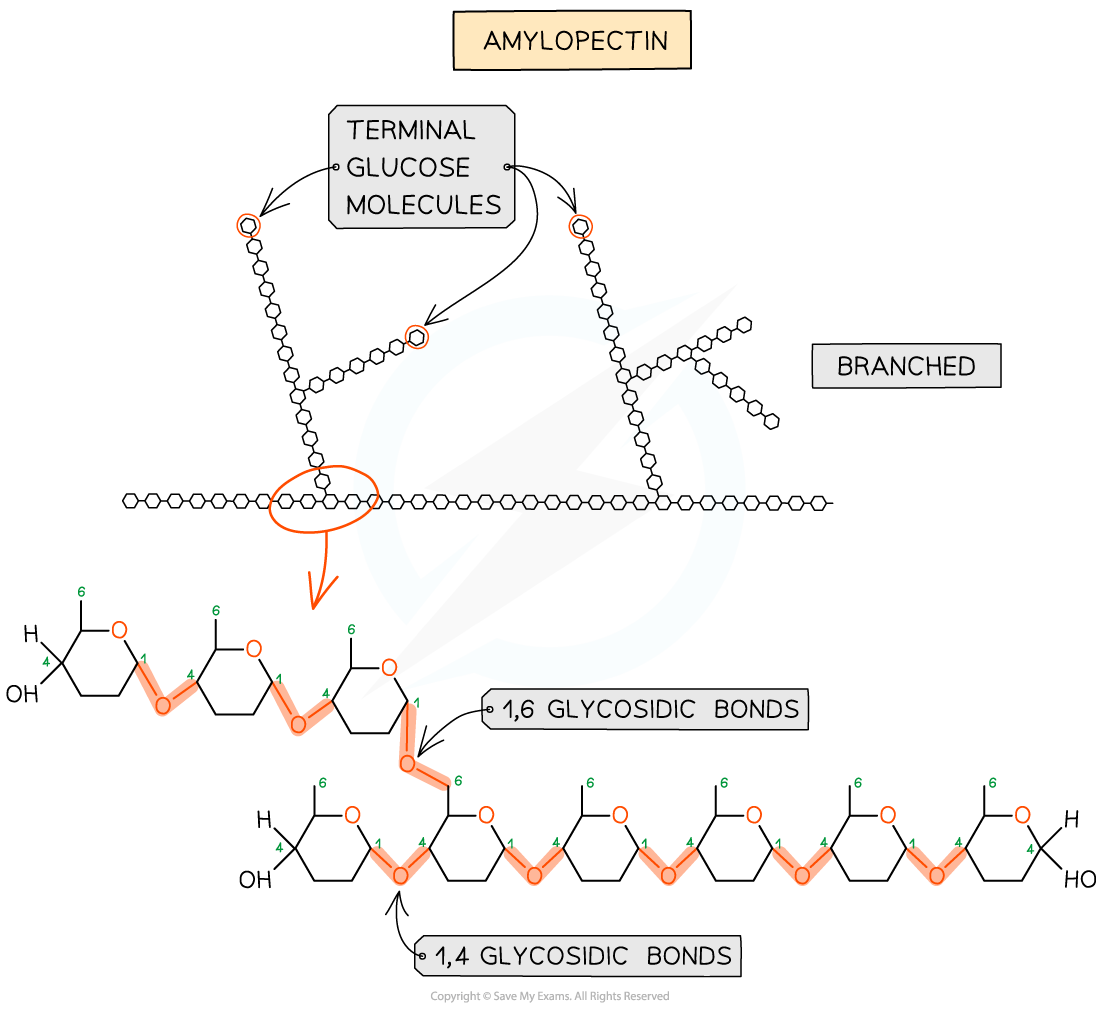
Glycogen
-
Glycogen is the storage polysaccharide of animals and fungi, it is highly branched and not coiled
-
Liver and muscles cells have a high concentration of glycogen, present as visible granules, as the cellular respiration rate is high in these cells (due to animals being mobile)
-
Glycogen is more branched than amylopectin making it more compact which helps animals store more
-
The branching enables more free ends where glucose molecules can either be added or removed allowing for condensation and hydrolysis reactions to occur more rapidly – thus the storage or release of glucose can suit the demands of the cell
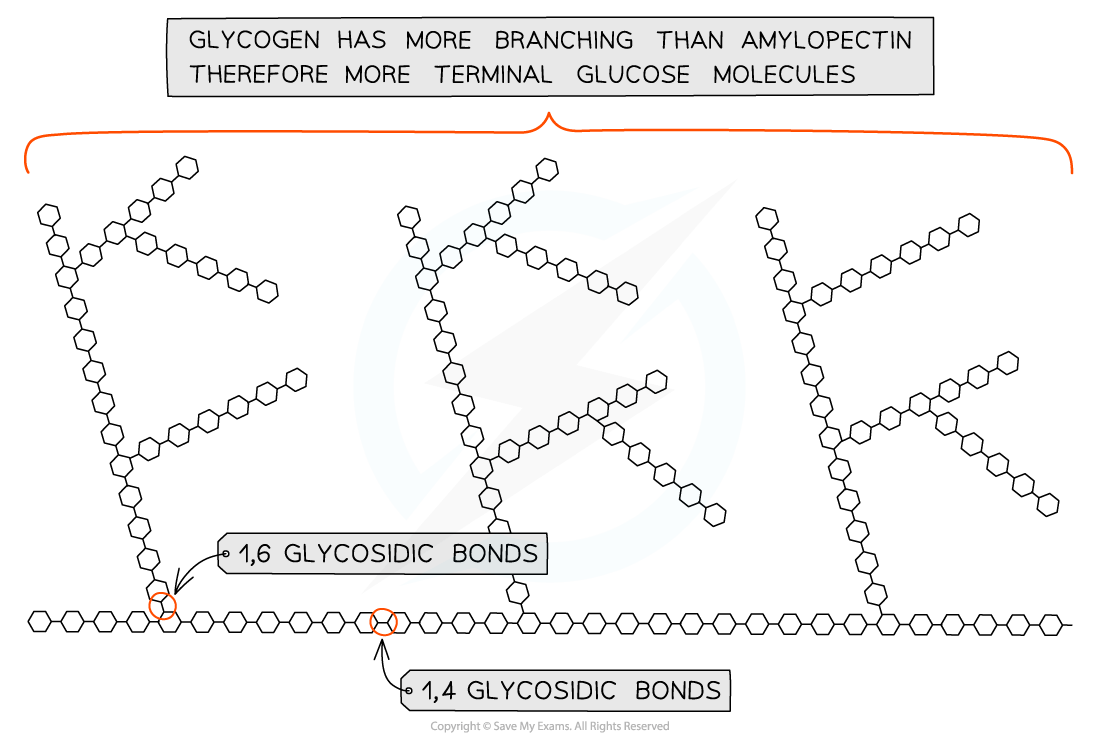
|
Feature |
Starch |
Glycogen |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Amylose |
Amylopectin |
||
|
Monomer |
α-glucose |
α-glucose |
α-glucose |
|
Branched |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Helix shape |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Glycosidic Bond Present |
1,4 |
1,4 and 1,6 |
1,4 and 1,6 |
|
Source |
Plants |
Plants |
Animals |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be clear about the differences between starch (amylose and amylopectin) and glycogen.
