Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
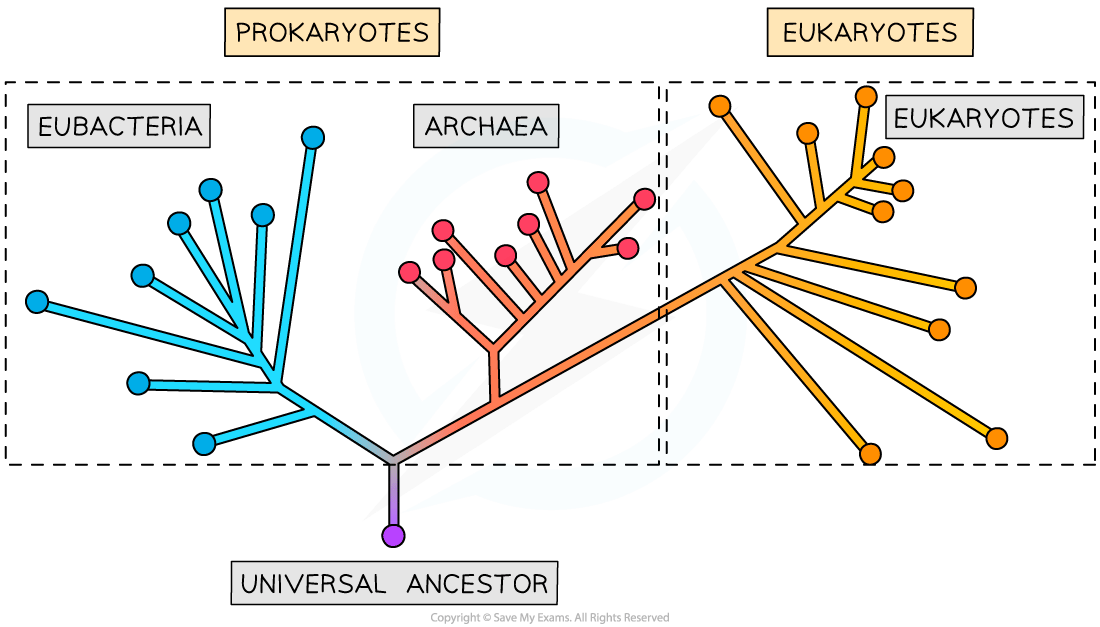
the-three-domains-archaea-bacteria-and-eukarya
The three domains: Archaea, Bacteria & Eukarya
-
Taxonomy is the practice of biological classification
-
It involves placing organisms into a series of categories or taxa
-
By grouping organisms into taxa it can make it easier to see evolutionary relationships between organisms
-
There are several different ranks or levels within the hierarchical classification system used in biology
-
The highest rank is the domain
-
Cell type has a major role in the classification of organisms into the three domains; but do not confuse cell types and domain
-
Prokaryotic cells are easily distinguishable in that they lack a nucleus
-
Eukaryotic cells have compartmentalised structures, with at least their genetic material segregated from the rest of the cell in a nucleus
-
-
Based upon molecular analysis of RNA genes in particular, scientists have realised that using cell type to classify organisms is insufficient, and that prokaryotes could be divided into two separate groups (domains)
-
The three domains are:
-
Archaea (prokaryotes)
-
Bacteria (prokaryotes)
-
Eukarya (eukaryotes)
-
Archaea
-
Archaea are single-celled (unicellular) organisms
-
Organisms within this domain are sometimes referred to as the extremophile prokaryotes
-
Archaea were first discovered living in extreme environments, but not all archaea do
-
-
Archael cells have no nucleus (and so are prokaryotic)
-
They were initially classified as bacteria until several unique properties were discovered that separated them from known bacteria, including:
-
Unique lipids being found in the membranes of their cells
-
No peptidoglycan in their cell walls
-
Ribosomal structure (particularly that of the small subunit) are more similar to the eukaryotic ribosome than that of the bacteria
-
-
Archaea have a similar size range as bacteria (and in many ways metabolism is similar between the two groups)
-
DNA transcription is more similar to that of eukaryotes
-
Example: Halobacterium salinarum are a species of the archaea domain that can be found in environments with high salt concentrations like the Dead Sea
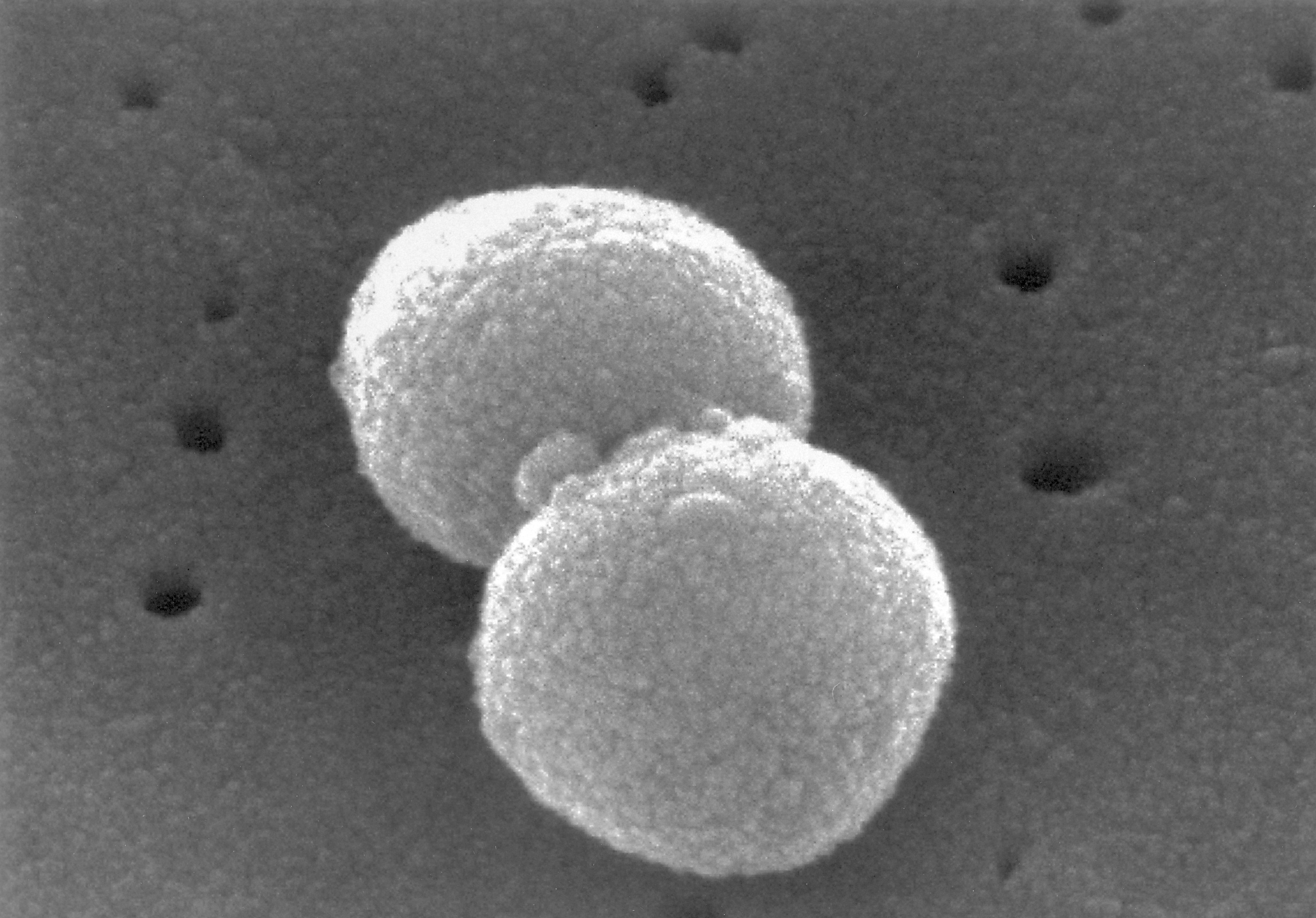
Bacteria
-
Bacteria are single-celled (unicellular) organisms
-
These are organisms that have prokaryotic cells which contain no nucleus
-
They vary in size over a wide range: the smallest are bigger than the largest known-viruses and the largest are smaller that the smallest known single-celled eukaryotes
-
Bacterial cells divide by binary fission
-
Example: Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacterial species that causes pneumonia
Eukarya
-
Organisms that have eukaryotic cells with nuclei and membrane-bound organelles are placed in this domain
-
They vary massively in size from single-celled organisms several micrometres across to large multicellular organisms many-metres in size, such as blue whales
-
Eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis
-
Eukaryotes can reproduce sexually or asexually
-
Example: Canis lupus also known as wolves
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It might be worth refreshing your knowledge on the defining features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells before tackling this new topic!
Differences between Archaea & Bacteria
-
Domains are the highest taxonomic rank that exist within the hierarchical classification system of organisms
-
Initially, all organisms within the Archaea domain were classified as Bacteria
-
Then several unique features possessed by Archaea were discovered that separated them from both Bacteria and Eukarya
-
The main differences between Archaea and Bacteria are seen in:
-
Membrane lipids
-
Ribosomal RNA
-
Cell wall composition
-
Membrane lipids
-
The membrane lipids found in the cells of Archaea organisms are completely unique
-
They are not found in any bacterial or eukaryotic cells
-
The membrane lipids of Archaea consist of branched hydrocarbon chains bonded to glycerol by ether linkages
-
The membrane lipids of Bacteria consist of unbranched hydrocarbon chains bonded to glycerol by ester linkages
Ribosomal RNA
-
Both Archaea and Bacteria possess 70S ribosomes
-
The 70S ribosomes in Archaea possess a smaller subunit that is more similar to the subunit found in Eukaryotic ribosomes than subunits in Bacterial ribosomes
-
The base sequences of ribosomal RNA in Archaea show more similarity to the rRNA of Eukarya than Bacteria
-
The primary structure of ribosome proteins in Archaea show more similarity to the ribosome proteins in Eukarya than Bacteria
-
Composition of cell walls
-
Organisms from the Bacteria domain have cells that always possess cell walls with peptidoglycan
-
Organisms from the Archaea domain also have cells that always possess cell walls, however these do not contain peptidoglycan
|
Archaea |
Bacteria |
Eukaryotes |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cell type |
Prokaryotic |
Prokaryotic |
Eukaryotic |
|
Chromosome |
Circular |
Circular |
Linear chromosomes + circular mtDNA and cpDNA |
|
Cell membrane lipids |
Glycerol – ether lipids |
Glycerol – ester lipids |
Glycerol – ester lipids |
|
Ribosomes |
70S ribosomes but small subunit is more similar to eukaryotic ribosomes |
70S ribosomes |
Large 80S ribosomes in the cytosol and 70S ribosomes in mitochondria and chloroplasts |
|
Cell walls |
Always present (without peptidoglycan) |
Always present (with peptidoglycan) |
Sometimes present (without peptidoglycan) |
|
Histones |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Introns |
Sometimes |
Rarely |
Yes |
