Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
Eukarya
-
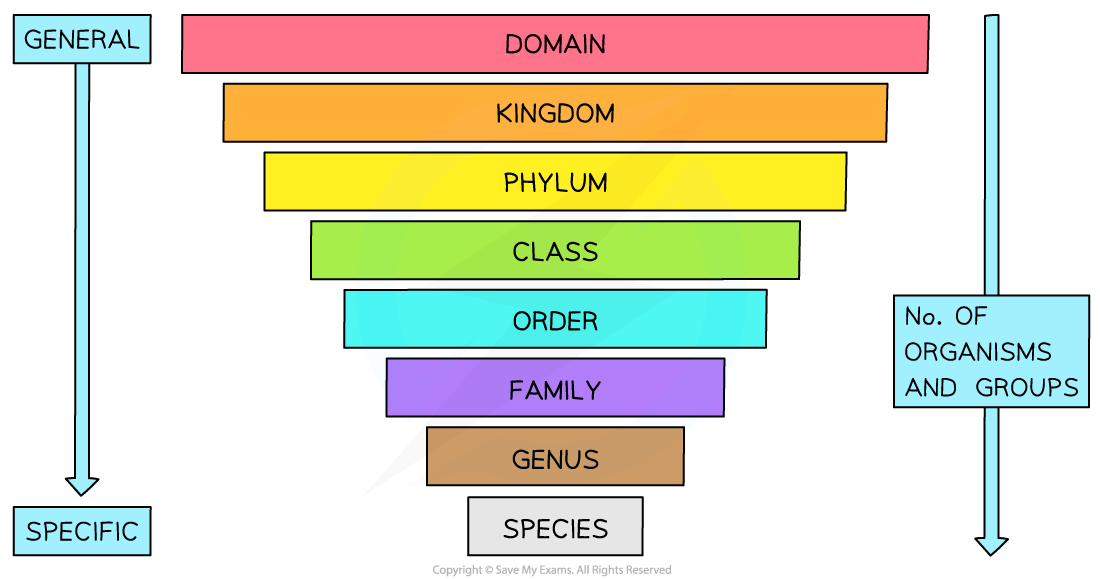
The hierarchical classification system of organisms in biology is used to organise and group similar organisms together so that evolutionary relationships between organisms can be more easily understood
-
There are several taxonomic ranks that exist
-
Species is the lowest taxonomic rank in the system
-
Similar species can be grouped in a genus
-
Similar genuses can be grouped in a family
-
Similar families can be grouped into an order
-
Similar orders can be grouped into a class
-
Similar classes can be grouped into a phylum
-
Similar phyla can be grouped into a kingdom
-
Similar kingdoms can be grouped into a domain
-
-
Domains are the highest taxonomic rank in the system
-
There are a few different mnemonics that exist to help you remember the different ranks in the taxonomic classification system. You can always make up your own but the one below is super helpful!
-
The first letters of all the different ranks below the domains can be remembered as:
-
Kings Play Chess On Fancy Gold Squares
-
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
-
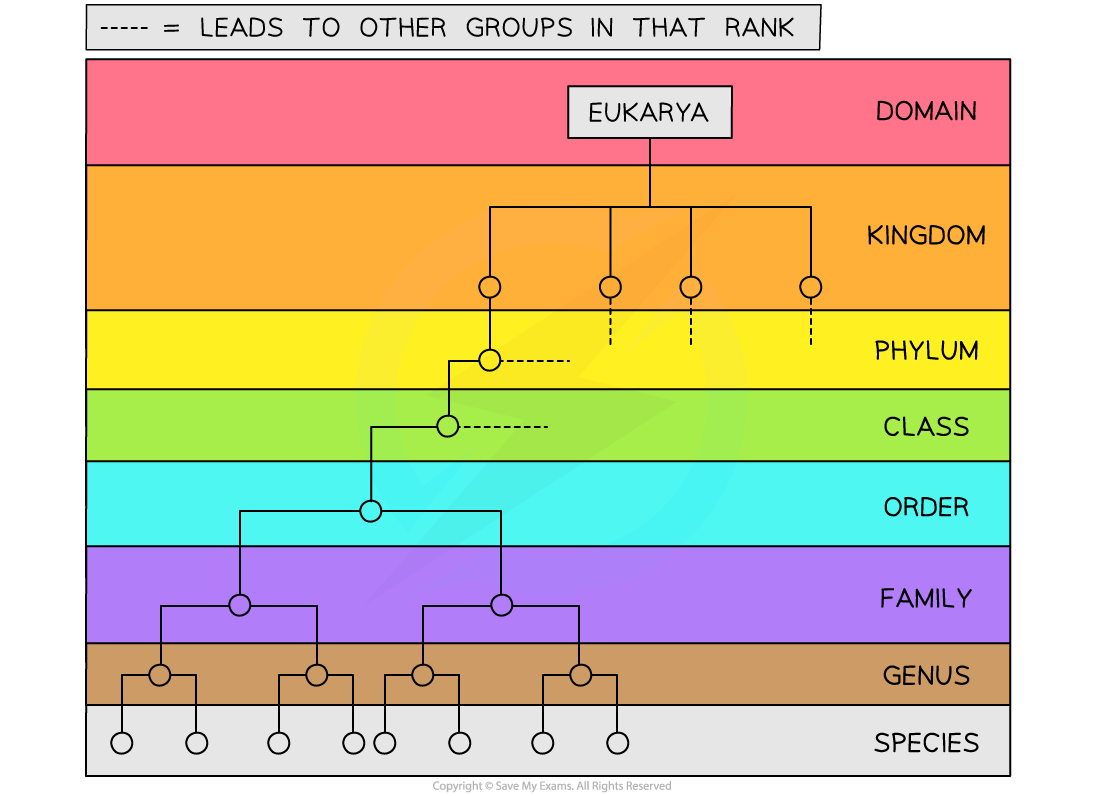
Classification of an organism in the Eukarya domain
-
Just like the other domains, Eukarya contains the taxonomic hierarchy of kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species
-
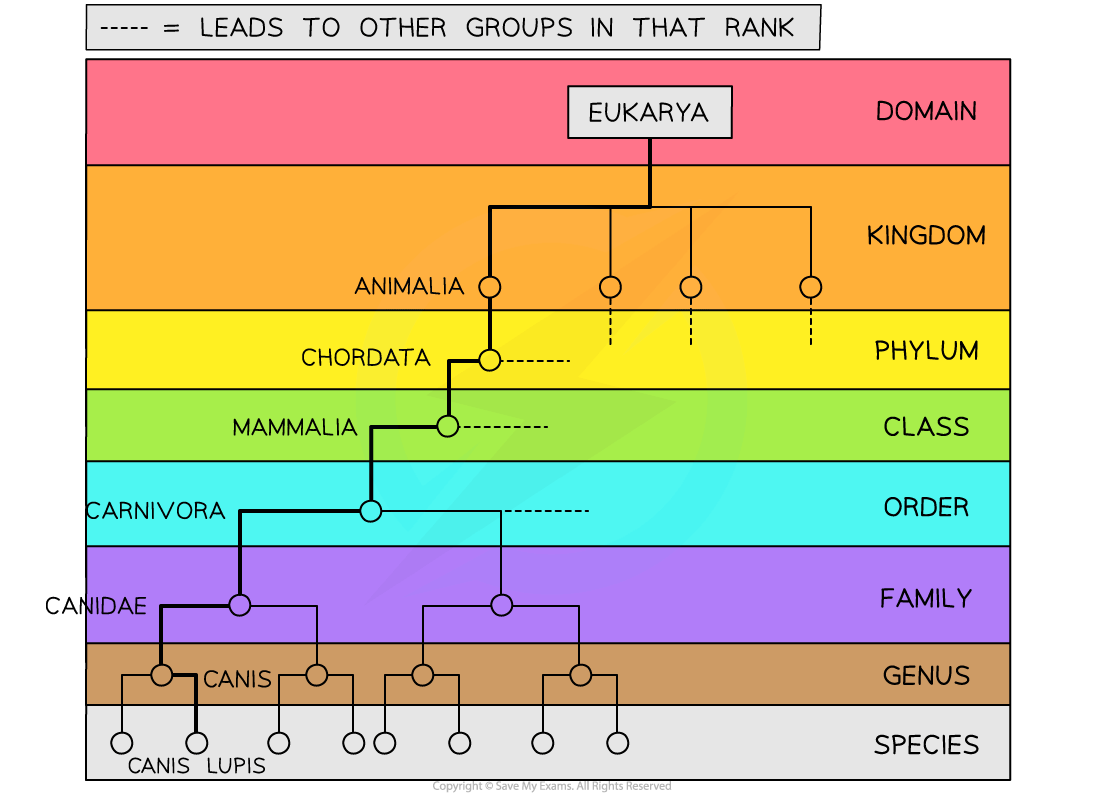
A wolf is an example of an organism in the Eukarya domain
-
It can be classified further into its kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus and species
-
A wolf belongs to the following taxonomic groups:
-
Domain: Eukarya
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Mammalia
-
Order: Carnivora
-
Family: Canidae
-
Genus: Canis
-
Species: lupus
-
-
The Hibiscus rosa-sinensis is another example of of an organism in the Eukarya domain
-
It is a colourful flowering plant
-
It belongs to the following taxonomic groups:
-
Domain: Eukarya
-
Kingdom: Plantae
-
Phylum: Angiospermae
-
Class: Dicotyledonae
-
Order: Malvales
-
Family: Malvaceae
-
Genus: Hibiscus
-
Species: rosa-sinensis
-
|
Taxonomic rank |
Wolf |
Hibiscus |
|---|---|---|
|
Domain |
Eukarya |
Eukarya |
|
Kingdom |
Animalia |
Plantae |
|
Phylum |
Chordata |
Angiospermae |
|
Class |
Mammalia |
Dicotyledonae |
|
Order |
Carnivora |
Malvales |
|
Family |
Canidae |
Malvaceae |
|
Genus |
Canis |
Hibiscus |
|
Species |
lupus |
rosa-sinensis |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The Latinised name of a species always consists of two words: the genus and species. This means when provided with the Latin name of a species you are automatically provided with information about the last two taxonomic ranks that the organism belongs to. Remember this when being asked to show or explain the classification of an organism in the exam.
