Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
natural-selection-types-of-selection
Natural selection: types of selection
-
Environmental factors that affect the chance of survival of an organism are selection pressures
-
For example, there could be high competition for food between lions if there is not plentiful prey available
-
This environmental factor ‘selects’ for faster, more powerful lions that are better hunters
-
-
These selection pressures can have different effects on the allele frequencies of a population through natural selection
-
There are three types of selection:
-
Stabilising
-
Disruptive
-
Directional
-
Stabilising selection
-
Stabilising selection is natural selection that keeps allele frequencies relatively constant over generations
-
This means that allele frequencies stay constant unless there is a change in the environment
-
-
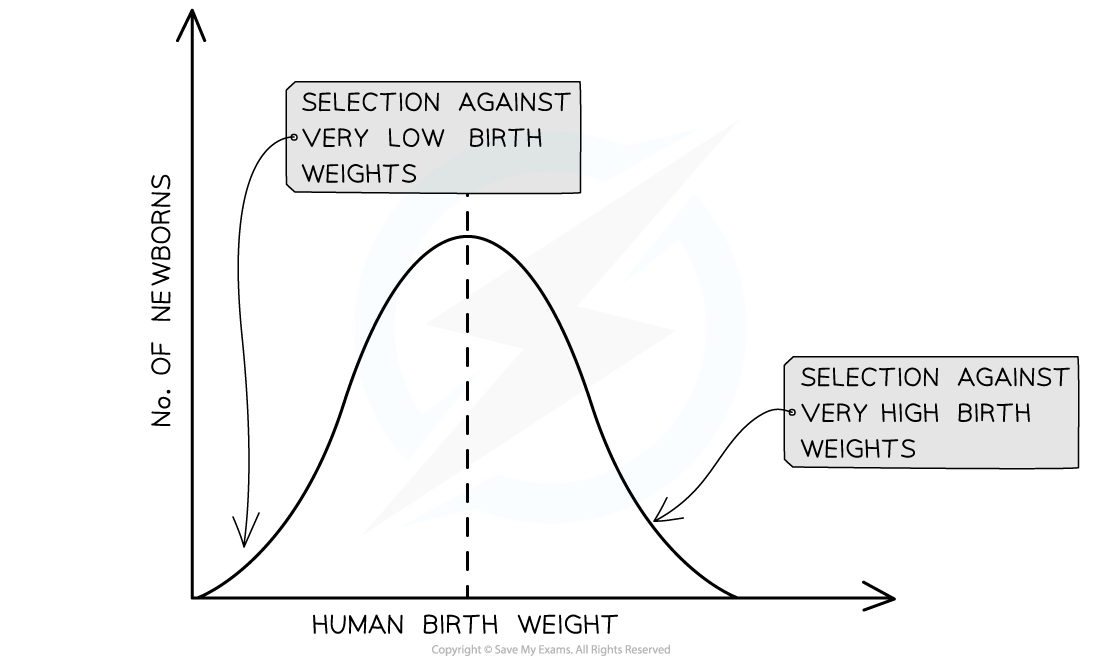
A classic example of stabilising selection can be seen in human birth weights
-
Very low and very high birth weights are selected against leading to the maintenance of intermediate birth weights
-
It is disadvantageous to have a very low birth weight because it increases the risk of health complications for the baby
-
It is disadvantageous to have a very high birth weight as this increases the risk of birth complications
-
-
Directional selection
-
Directional selection is natural selection that produces a gradual change in allele frequencies over several generations
-
This usually happens when there is a change in the environment or new selection pressures which leads to a certain allele becoming advantageous
-
For example, a recent finding has shown that climate change is having an effect on fish size in certain habitats; the increase in temperature is selecting for a smaller body size and against a larger body size
-
Warmer seas cause fish metabolism to speed up and so increase their need for oxygen; oxygen levels are lower in warmer seas
-
Larger fish have greater metabolic needs than smaller fish, so they feel the effect of increased temperatures more strongly
-
Organisms are sensitive to changes in temperature primarily because of the effect that temperature can have on enzyme activity
-
Fish with a smaller body size are therefore fitter and better adapted to living in seas experiencing increased temperatures
-
Fish body size is determined by both genetic and environmental factors
-
Fish of a smaller size are more likely to reproduce and pass on their alleles to offspring
-
Over generations, this leads to an increase in the frequency of alleles that code for a small body size and a decrease in the frequency of alleles that code for a larger body size
-

Disruptive selection
-
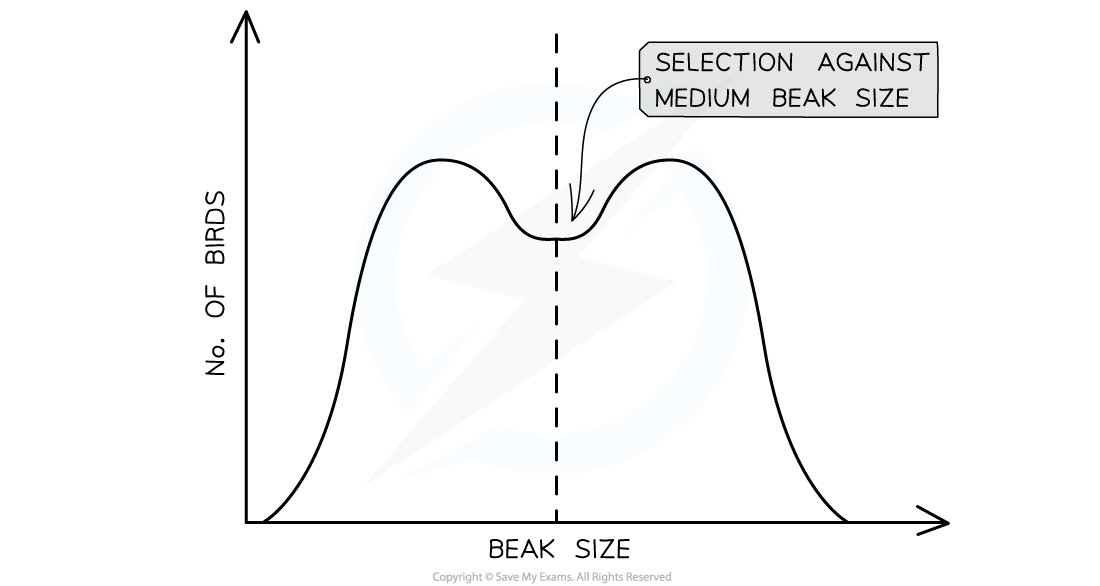
Disruptive selection is natural selection that maintains high frequencies of two different sets of alleles
-
In other words, individuals with intermediate phenotypes or alleles are selected against
-
-
Disruptive selection maintains polymorphism; the continued existence of two or more distinct phenotypes in species
-
This can occur in an environment that shows variation
-
For example, birds that live on the Galapagos Islands use their beaks to forage for different-sized seeds
-
Different sizes of seed are more efficiently foraged by a shorter or longer beak than by a medium-sized beak
-
The size of the bird’s beaks are either small or large with the intermediate, medium-sized beak selected against
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Become familiar with the shapes of the graphs above. They can help you answer questions about the type of selection that is occurring in a population.
