Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
variation-discontinuous-and-continuous
Variation: discontinuous & continuous
-
The term variation refers to the differences that exist between at least two things (be it a level, presence, quantity or feature of something)
-
Concerning natural selection, variation refers to the differences that exist between individuals of a species
-
This may also be referred to as intraspecific variation
-
-
The variation observed in the phenotypes of organisms can be due to qualitative or quantitative differences
Discontinuous variation
-
Qualitative differences in the phenotypes of individuals within a population give rise to discontinuous variation
-
Qualitative differences fall into discrete and distinguishable categories, usually with no intermediates (a feature can’t fall in between categories)
-
For example, there are four possible ABO blood groups in humans; a person can only have one of them
-
-
It is easy to identify discontinuous variation when it is present in a table or graph due to the distinct categories that exist when data is plotted for particular characteristics

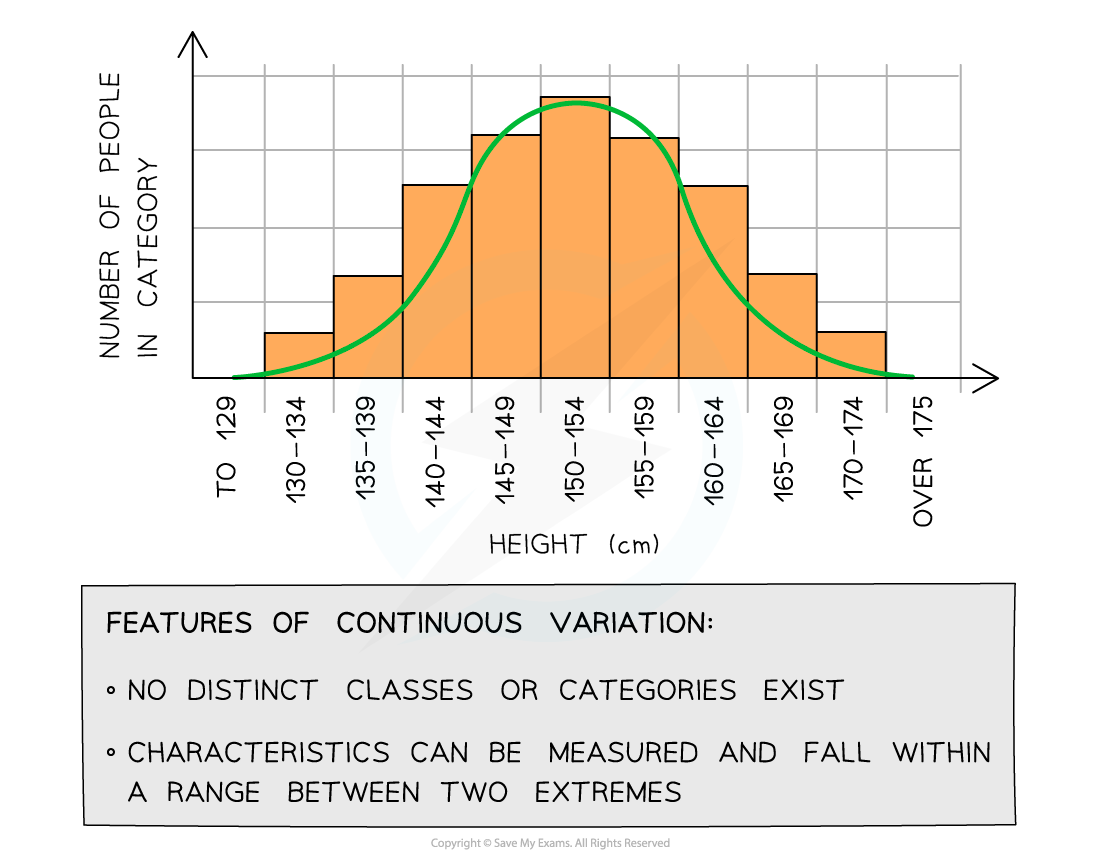
Continuous variation
-
Continuous variation occurs when there are quantitative differences in the phenotypes of individuals within a population for particular characteristics
-
Quantitative differences do not fall into discrete categories like in discontinuous variation
-
Instead, for these features, a range of values exists between two extremes within which the phenotype will fall
-
For example, the mass or height of a human is an example of continuous variation
-
-
The lack of categories and the presence of a range of values can be used to identify continuous variation when it is presented in a table or graph
The genetic basis of variation
-
Discontinuous variation refers to the differences between individuals of a species where the differences are qualitative (categoric)
-
Continuous variation is the differences between individuals of a species where the differences are quantitative (measurable)
-
Each type of variation can be explained by genetic and/or environmental factors
Genetic basis of discontinuous variation
-
This type of variation occurs solely due to genetic factors
-
The environment has no direct effect
-
At the genetic level:
-
Different genes have different effects on the phenotype
-
Different alleles at a single gene locus have a large effect on the phenotype
-
Remember diploid organisms will inherit two alleles of each gene; these alleles can be the same or different
-
-
A good example of this is the F8 gene that codes for the blood-clotting protein Factor VIII
-
The different alleles at the F8 gene locus dictate whether or not normal Factor VIII is produced and whether the individual has the condition haemophilia
-
Genetic basis of continuous variation
-
This type of variation is caused by an interaction between genetics and the environment
-
Phenotype = genotype + environment
-
At the genetic level:
-
Different alleles at a single locus have a small effect on the phenotype
-
Different genes can have the same effect on the phenotype and these add together to have an additive effect
-
If a large number of genes have a combined effect on the phenotype they are known as polygenes
-
The additive effect of genes
-
The height of a plant is controlled by two unlinked genes H / h and T / t
-
The two genes have an additive effect
-
The recessive alleles h and t contribute x cm to the plant’s height
-
The dominant alleles H and T contribute 2x cm to the plant’s height
-
The following genotypes will have the following phenotypes:
-
h h t t : x + x + x + x = 4x cm
-
H H T T : 2x + 2x + 2x + 2x = 8x cm
-
H h T t : 2x + x + 2x + x = 6x cm
-
H H T t : 2x + 2x + 2x + x = 7x cm
-
H h T T : 2x + x + 2x + 2x = 7x cm
-
h h T t : x + x + 2x + x = 5x cm
-
H h t t : 2x + x + x + x = 5x cm
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful when answering questions that involve polygenes or genes with an additive effect. It is not a given that each gene will have the same effect on the phenotype as in the example above so make sure to double check the information you have been given in the question.
