Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
gene-control-transcription-factors
Gene control: transcription factors
-
Prokaryotes use operons to control the expression of genes in cells
-
Eukaryotes also use transcription factors to control gene expression
-
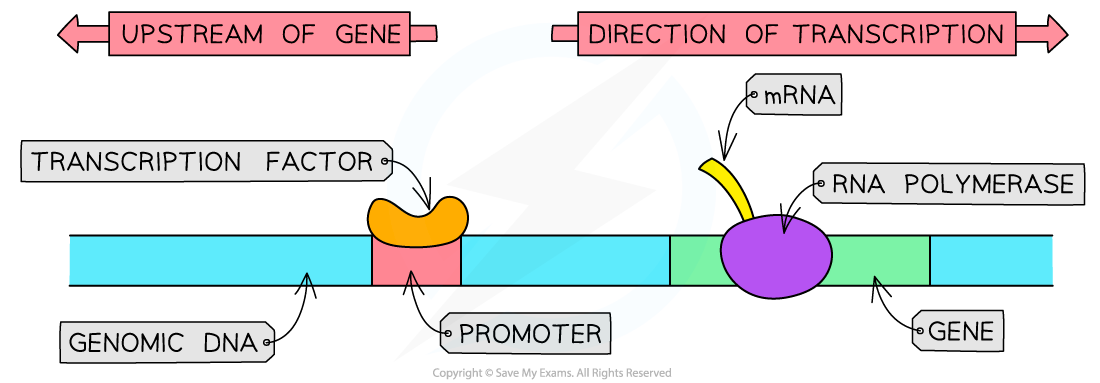
A transcription factor is a protein that controls the transcription of genes by binding to a specific region of DNA
-
They ensure that genes are being expressed in the correct cells, at the correct time and to the right level
-
It is estimated that ~10% of human genes code for transcription factors
-
There are several types of transcription factors that have varying effects on gene expression
-
This is still a relatively young area of research and scientists are working hard to understand how all the different transcription factors function
-
Transcription factors allow organisms to respond to their environment
-
Some hormones achieve their effect via transcription factors
-
How transcription factors work
-
Some transcription factors bind to the promoter region of a gene
-
This binding can either allow or prevent the transcription of the gene from taking place
-
-
The presence of a transcription factor will either increase or decrease the rate of transcription of a gene
-
For example, PIF is a transcription factor found in plants that activates the transcription of the amylase gene
Gene control: gibberellin
-
Plant cells use transcription factors in a similar way to animal cells
-
Gibberellin is a hormone found in plants (e.g. wheat and barley) that controls seed germination by stimulating the synthesis of the enzyme amylase
-
It does this by influencing transcription of the amylase gene
-
When gibberellin is applied to a germinating seed there is an increased amount of the mRNA for amylase present
-
Mechanism for gene control by gibberellin
-
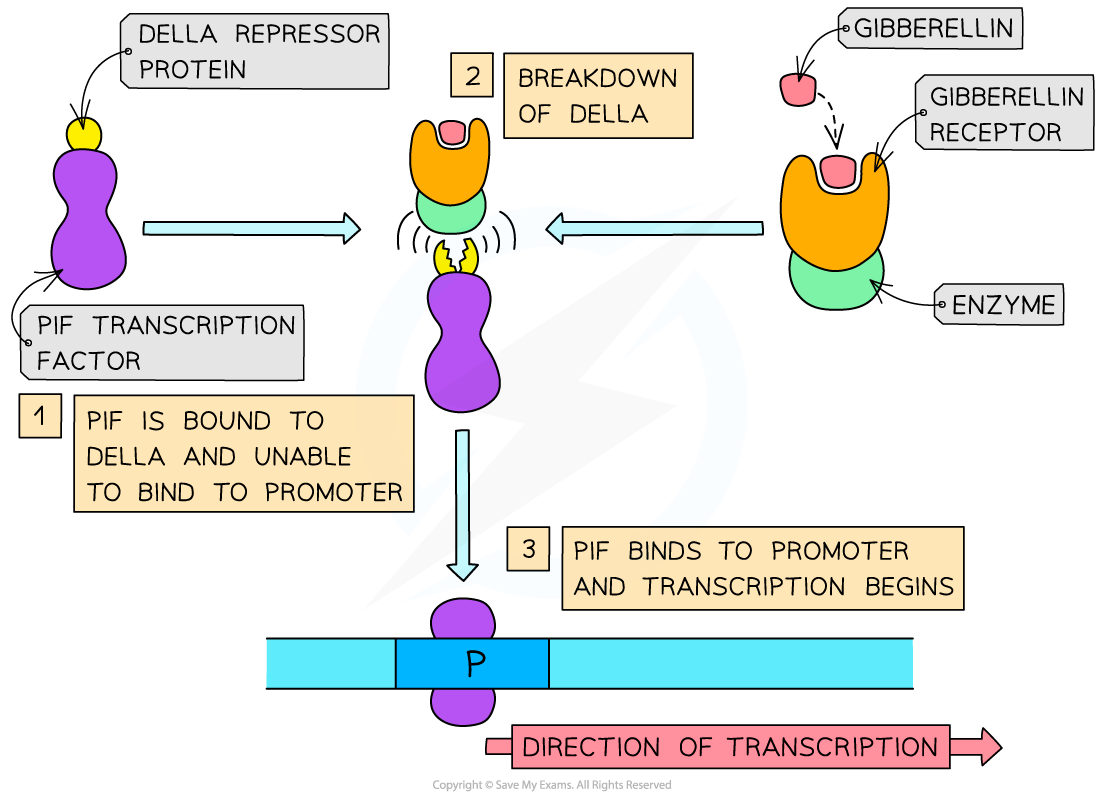
The breakdown of DELLA protein by gibberellin is necessary for the synthesis of amylase
-
The following components are involved:
-
Repressor protein DELLA
-
Transcription factor PIF
-
Promoter of amylase gene
-
Amylase gene
-
Gibberellin
-
Gibberellin receptor and enzyme
-
-
The process occurs as follows:
-
DELLA protein is bound to PIF, preventing it from binding to the promoter of the amylase gene so no transcription can occur
-
Gibberellin binds to a gibberellin receptor and enzyme which starts the breakdown of DELLA
-
PIF is no longer bound to DELLA protein and so it binds to the promoter of the amylase gene
-
Transcription of amylase gene begins
-
Amylase is produced
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In your exam you may be asked to explain why RNA analysis is important with regards to gene expression. From the outside most cells look almost identical with the same DNA in their nucleus. However we know that they are most likely expressing different genes.
When a cell expresses a gene, RNA is produced by transcription. This RNA present in a cell can be analysed. Scientists can match the RNA present in a cell to specific genes and work out which genes are being expressed in that specific cell.
