Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
predicting-inheritance-test-crosses
Predicting inheritance: test crosses
-
A test cross can be used to deduce the genotype of an unknown individual that is expressing a dominant phenotype
-
The individual in question is crossed with an individual that is expressing the recessive phenotype
-
This is because an individual with a recessive phenotype has a known genotype
-
The resulting phenotypes of the offspring provides sufficient information to suggest the genotype of the unknown individual
Results
-
For a monohybrid test cross:
-
If no offspring exhibit the recessive phenotype then the unknown genotype is homozygous dominant
-
If at least one of the offspring exhibit the recessive phenotype then the unknown genotype is heterozygous
-
-
For a dihybrid test cross:
-
If no offspring exhibit the recessive phenotype for either gene then the unknown genotype is homozygous dominant for both genes
-
If at least one of the offspring exhibit the recessive phenotype for one gene but not the other, then the unknown genotype is heterozygous for one gene and homozygous dominant for the other
-
If at least one of the offspring exhibit the recessive phenotype for both genes then the unknown genotype is heterozygous for both genes
-
Worked example: test crosses
-
Rabbits have a single gene for ear length that has two alleles:
-
D, a dominant allele that produces long ears
-
d, a recessive allele that produces shorter ears
-
-
A breeder has a rabbit with long ears and they want to know the genotype of the rabbit
-
There are two possibilities: DD or Dd
-
-
The breeder crosses the long-eared rabbit with a short-eared rabbit
-
A rabbit displaying the recessive short ear phenotype has to have the genotype dd
-
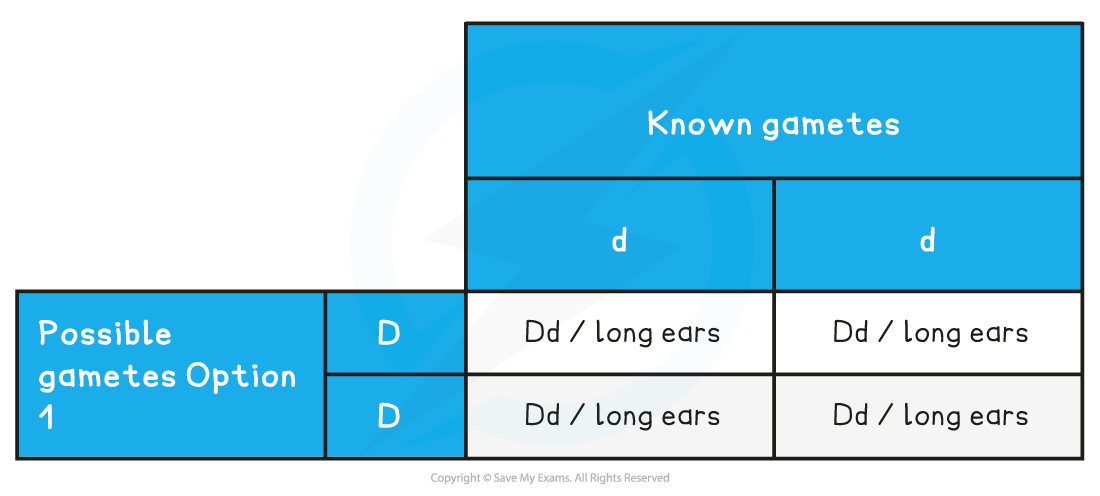
Predicted ratio of phenotypes of offspring – 1 long ears
Predicted ratio of genotypes of offspring – 1 Dd
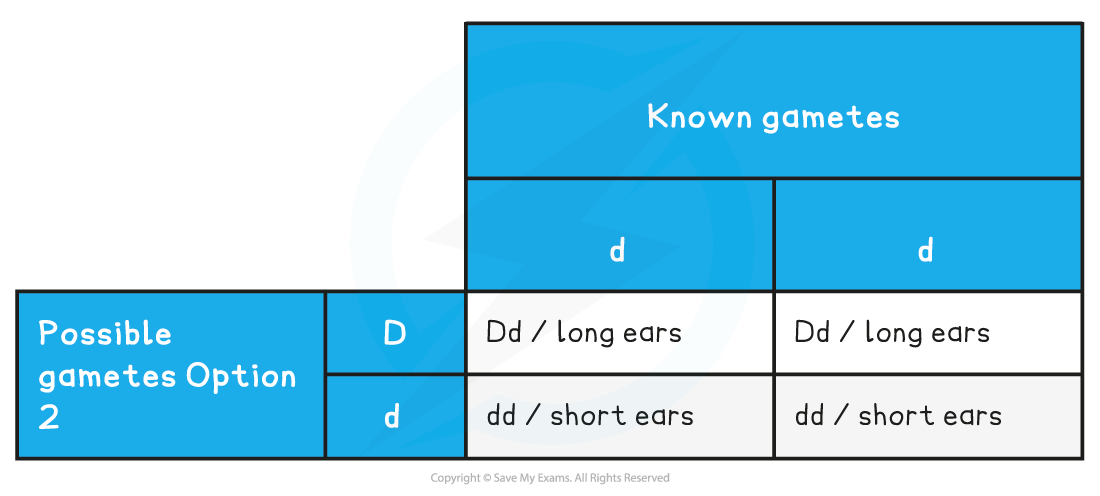
Predicted ratio of phenotypes of offspring – 1 long ears : 1 short ears
Predicted ratio of genotypes of offspring – 1 Dd : 1 dd
-
The breeder identifies the different phenotypes present in the offspring
-
There is at least one offspring with the short ear phenotype
-
This tells the breeder that their rabbit has the genotype Dd
-
If the rabbit was genotype DD none of the offspring would have short ears
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure before you start a test cross you think about the following: how many genes are there, how many alleles of each gene are there, which is the dominant allele, what type of dominance is it and is there linkage or epistasis between genes?
