Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
meiosis-sources-of-genetic-variation
Meiosis: sources of genetic variation
-
Having genetically different offspring can be advantageous for natural selection
-
Meiosis has several mechanisms that increase the genetic diversity of gametes produced
-
Both crossing over and independent assortment (random orientation) result in different combinations of alleles in gametes
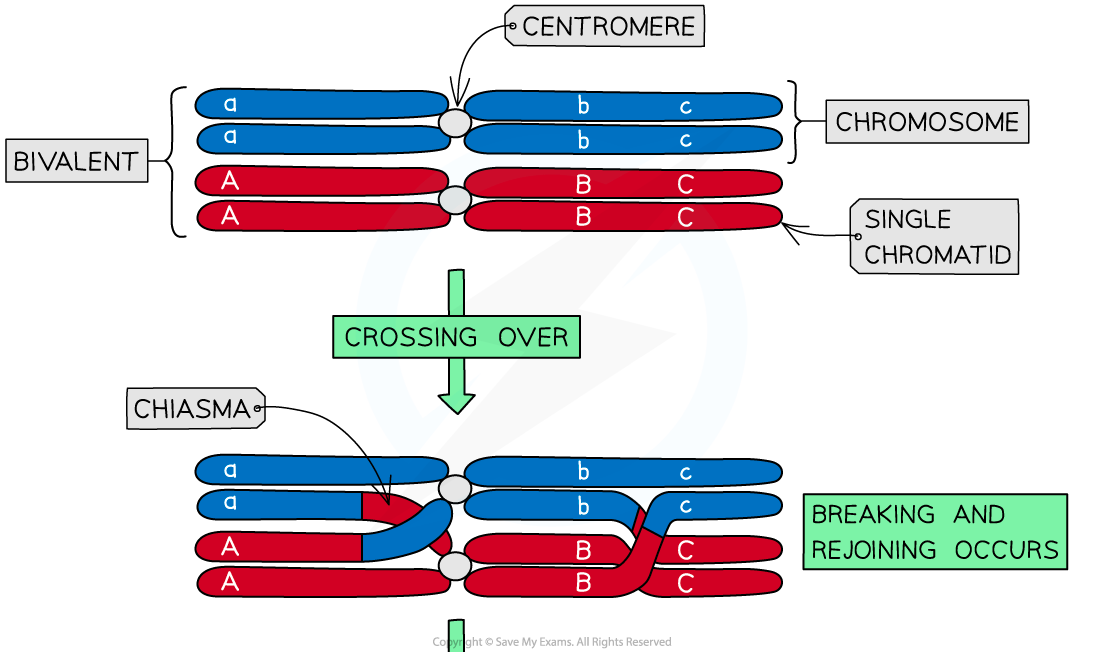
Crossing over
-
Crossing over is the process by which non-sister chromatids exchange alleles
-
Process:
-
During meiosis I homologous chromosomes pair up and are in very close proximity to each other
-
The non-sister chromatids can cross over and get entangled
-
These crossing points are called chiasmata
-
The entanglement places stress on the DNA molecules
-
As a result of this, a section of chromatid from one chromosome may break and rejoin with the chromatid from the other chromosome
-
-
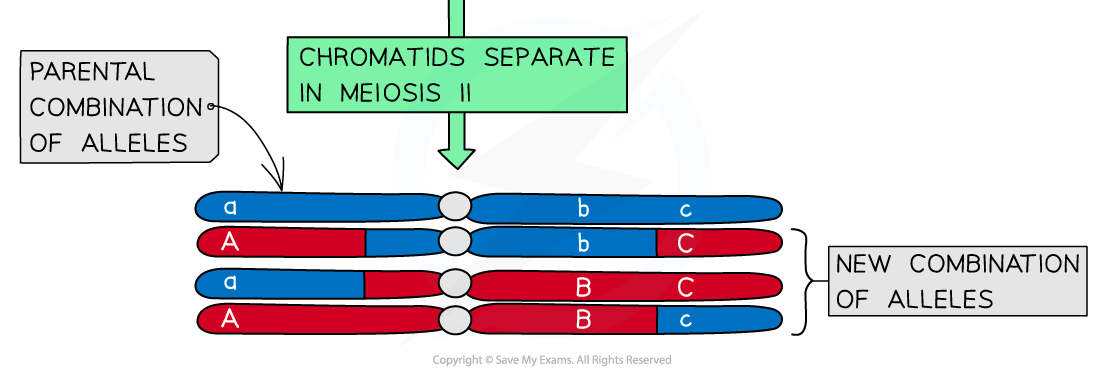
This swapping of alleles is significant as it can result in a new combination of alleles on the two chromosomes
-
There is usually at least one, if not more, chiasmata present in each bivalent during meiosis
-
Crossing over is more likely to occur further down the chromosome away from the centromere
Independent assortment
-
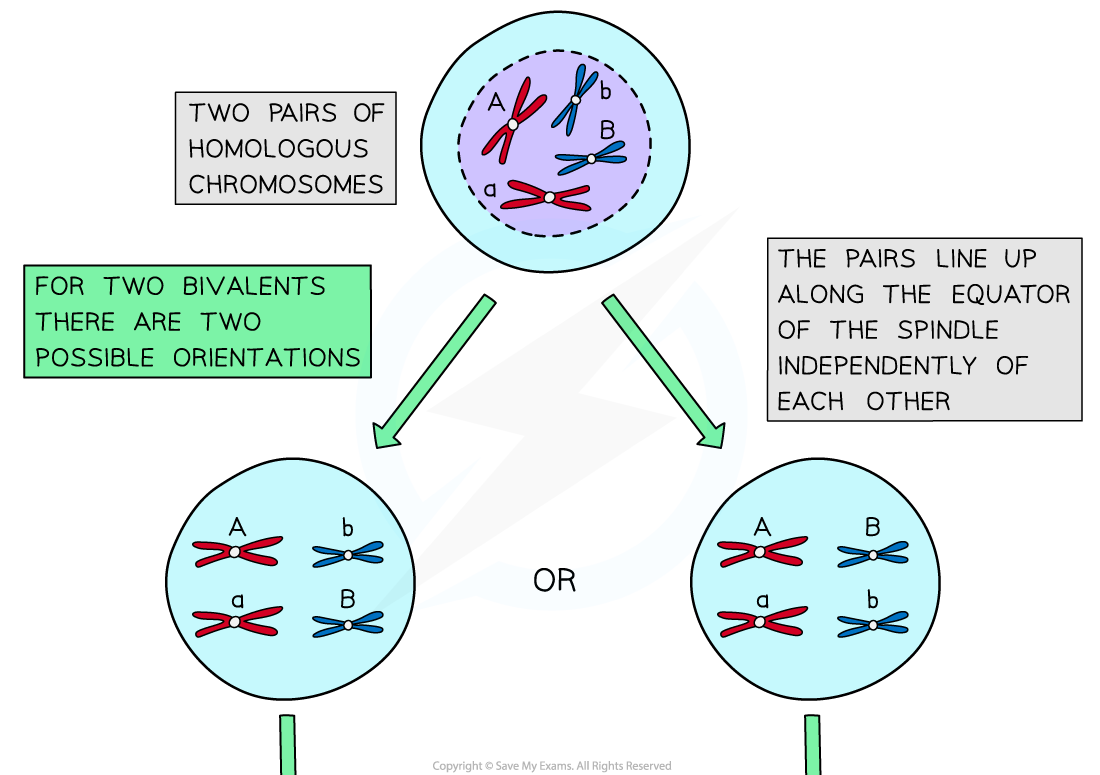
Independent assortment is the production of different combinations of alleles in daughter cells due to the random alignment of homologous pairs along the equator of the spindle during metaphase I
-
The different combinations of chromosomes in daughter cells increases genetic variation between gametes
-
In prophase I homologous chromosomes pair up and in metaphase I they are pulled towards the equator of the spindle
-
Each pair can be arranged with either chromosome on top, this is completely random
-
The orientation of one homologous pair is independent (unaffected by the orientation of any other pair)
-
-
The homologous chromosomes are then separated and pulled apart to different poles
-
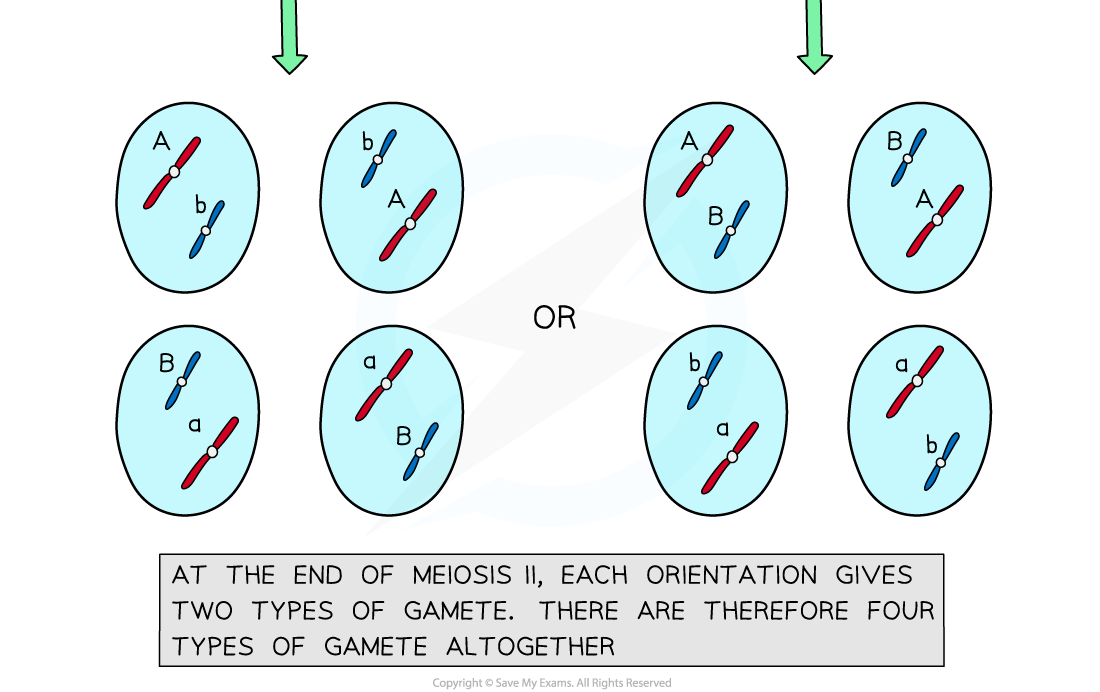
The combination of alleles that end up in each daughter cell depends on how the pairs of homologous chromosomes were lined up
-
To work out the number of different possible chromosome combinations the formula 2n can be used, where n corresponds to the number of chromosomes in a haploid cell
-
For humans this is 223 which calculates as 8 388 608 different combinations
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Several sources of genetic variation have been outlined above. It is also worth remembering that genetic variation can occur on an even smaller scale than chromosomes: mutations can occur within genes. A random mutation that takes place during DNA replication can lead to the production of new alleles and increased genetic variation.
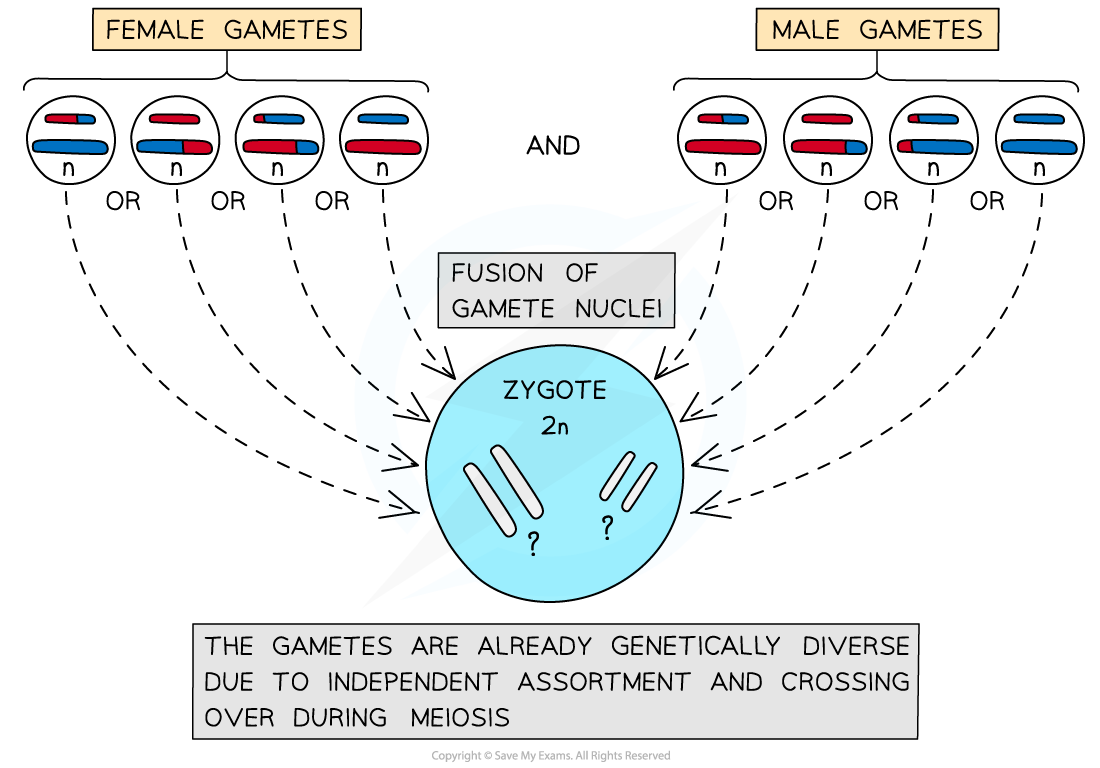
Fusion of gametes
-
Meiosis creates genetic variation between the gametes produced by an individual through crossing over and independent assortment
-
This means each gamete carries substantially different alleles
-
During fertilisation any male gamete can fuse with any female gamete to form a zygote
-
This random fusion of gametes at fertilisation creates genetic variation between zygotes as each will have a unique combination of alleles
-
There is an almost zero chance of individual organisms resulting from successive sexual reproduction being genetically identical
Examiner Tips and Tricks
These sources of genetic variation explain why relatives can differ so much from each other. Even with the same parents, individuals can be genetically unique due to the processes outlined above.
