Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
the-calvin-cycle
Stages of the Calvin cycle
-
Energy from ATP and hydrogen from reduced NADP are passed from the light-dependent stage to the light-independent stage of photosynthesis
-
The energy and hydrogen are used during the light-independent reactions (known collectively as the Calvin cycle) to produce complex organic molecules, including (but not limited to) carbohydrates, such as:
-
Starch (for storage)
-
Sucrose (for translocation around the plant)
-
Cellulose (for making cell walls)
-
-
This stage of photosynthesis does not, in itself, require energy from light (hence light-independent) and can therefore take place in light or darkness
-
However, as it requires inputs of ATP and reduced NADP from the light-dependent stage, the Calvin cycle cannot continue indefinitely in darkness, as these inputs will run out
-
There are three main steps within the Calvin cycle:
-
Rubisco catalyses the fixation of carbon dioxide by combination with a molecule of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), a 5-carbon compound, to yield two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP), a 3-carbon compound
-
GP is reduced to triose phosphate (TP) in a reaction involving reduced NADP and ATP
-
RuBP is regenerated from TP in reactions that use ATP
-
Carbon fixation
-
Carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon (5C) sugar known as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
-
An enzyme called rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase) catalyses this reaction
-
The resulting six-carbon (6C) compound is unstable and splits in two
-
This gives two molecules of a three-carbon (3C) compound known as glycerate 3-phosphate (GP)
-
The carbon dioxide has been ‘fixed’ (it has been removed from the external environment and has become part of the organic matter of the plant cell)
-
Glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) is not a carbohydrate but the next step in the Calvin cycle converts it into one
Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
-
Energy from ATP and hydrogen from reduced NADP – both produced during the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis – are used to reduce glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) to a phosphorylated three-carbon (3C) sugar known as triose phosphate (TP)
-
One-sixth of the triose phosphate (TP) molecules are used to produce useful organic molecules needed by the plant:
-
Triose phosphates can condense to become hexose phosphates (6C), which can be used to produce starch, sucrose or cellulose
-
Triose phosphates can be converted to glycerol and glycerate 3-phosphates to fatty acids, which join to form lipids for cell membranes
-
Triose phosphates can be used in the production of amino acids for protein synthesis
-
Regeneration of ribulose bisphosphate
-
Five-sixths of the triose phosphate (TP) molecules are used to regenerate ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
-
This process requires ATP
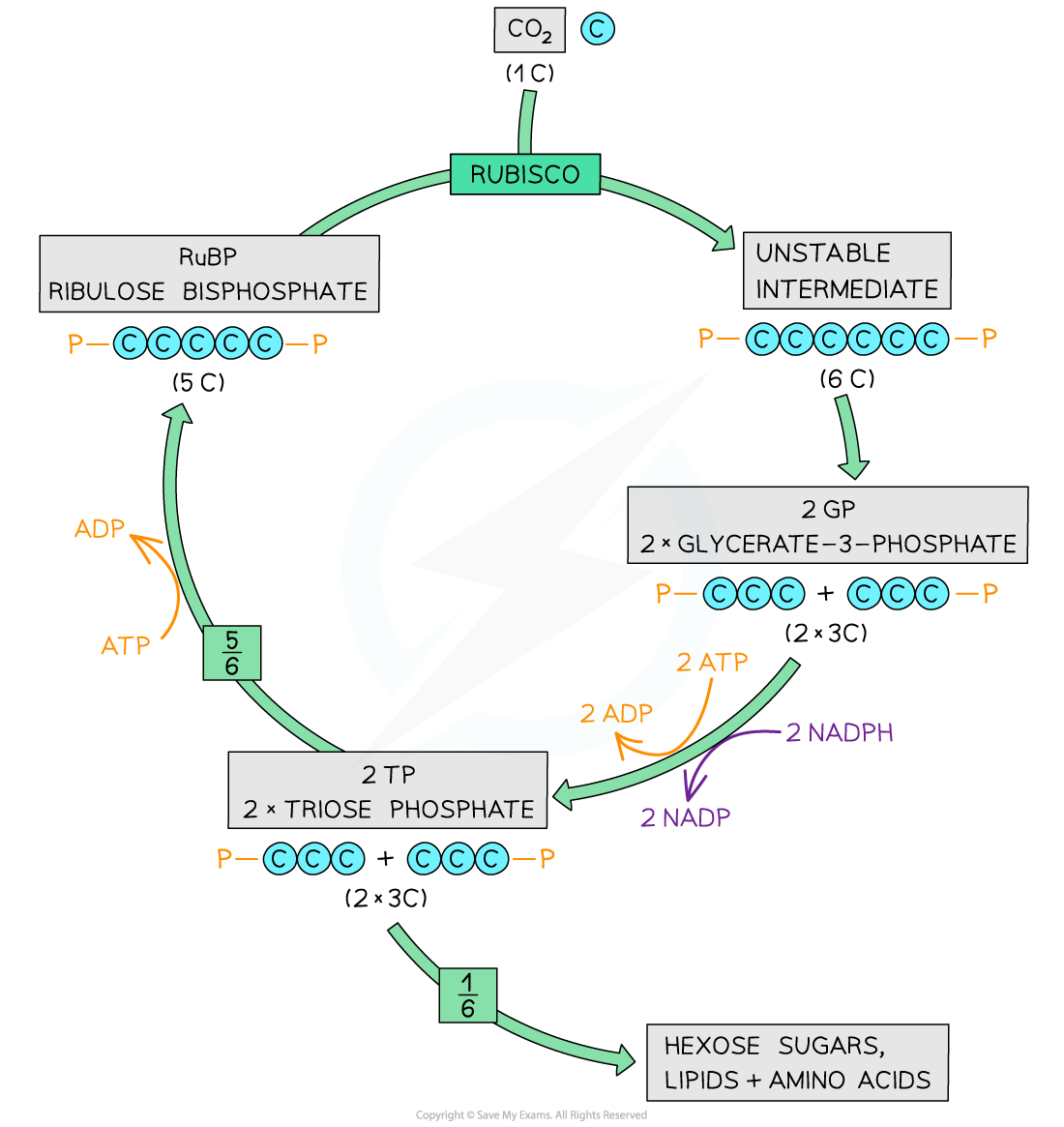
Calvin cycle intermediates
-
Intermediate molecules of the Calvin cycle (such as glycerate 3-phosphate and triose phosphate) are used to produce other molecules
-
Glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) is used to produce some amino acids
-
Triose phosphate (TP) is used to produce:
-
Hexose phosphates (6C), which can be used to produce starch, sucrose or cellulose
-
Lipids for cell membranes
-
Amino acids for protein synthesis
-
