Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
respiratory-quotient-rq
Respiratory quotient (RQ)
-
The respiratory quotient (RQ) is: the ratio of carbon dioxide molecules produced to oxygen molecules taken in during respiration
RQ values of different respiratory substrates
-
Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins have different typical RQ values
-
This is because the number of carbon-hydrogen bonds differs in each type of biological molecule
-
A higher number of carbon-hydrogen bonds means that more hydrogen atoms can be used to create a proton gradient
-
More hydrogens means that more ATP molecules can be produced by chemiosmosis
-
More oxygen is therefore required to break down the molecule (in the last step of oxidative phosphorylation to form water)
-
-
When glucose is respired aerobically, equal volumes of carbon dioxide are produced and oxygen taken in, meaning it has an RQ value of 1

|
Respiratory substrate |
Typical RQ value |
|---|---|
|
Carbohydrate |
1.0 |
|
Protein |
0.8 – 0.9 |
|
Lipid |
0.7 |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Some questions may ask you to suggest what substrate is being respired during an experiment based on the RQ value—so make yourself familiar with the values in the table.
Calculating RQs
-
The respiratory quotient is calculated from respiration equations
-
It involves comparing the ratios of carbon dioxide given out to oxygen taken in
-
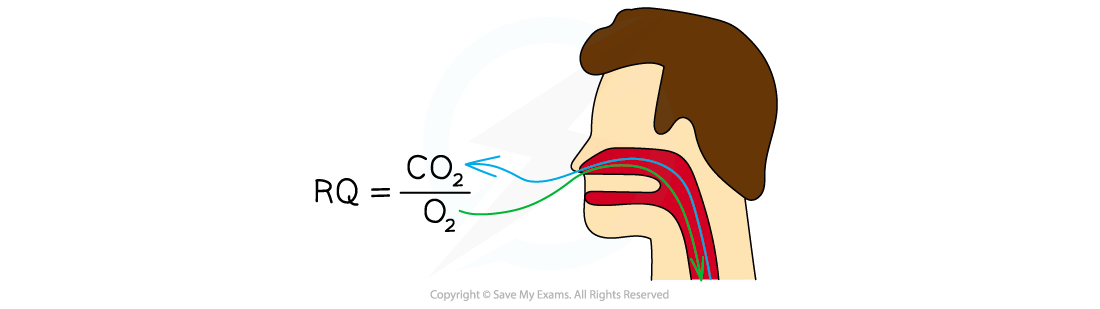
The formula for this is:

Equation to calculate the RQ
-
If you know the molecular formula of the substrate being aerobically respired then you can create a balanced equation to calculate the RQ value
-
In a balanced equation the number before the chemical formula can be taken as the number of molecules/moles of that compound
-
This is because the same number of molecules of any gas take up the same volume e.g. 12 molecules of carbon dioxide take up the same volume as 12 molecules of oxygen
-
-
Glucose has a simple 1:1 ratio and RQ value of 1 but other substrates have more complex ratios leading to different RQ values
Worked Example
RQ for a lipid
Linoleic acid (a fatty acid found in nuts) has the molecular formula C18H32O2
Step 1: Create a respiration equation
C18H32O2 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Step 2: Balance the equation
C × 18 C × 1
H × 32 H × 2
O × 4 O × 3
Step 3: Create the full equation
C18H32O2 + 25O2 → 18CO2 + 16H2O
Step 3: Use the RQ formula
<img alt=”18 over 25 equals 0.72″ data-mathml='<math style=”font-family:Arial” ><semantics><mrow><mfrac><mn>18</mn><mn>25</mn></mfrac><
