Biology_A-level_Cie
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
transmission-of-disease
Transmission of common diseases
Transmission of cholera
-
Cholera is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae
-
The disease is water-borne and food-borne
-
Infected people egest large numbers of the pathogenic bacteria in their faeces and water becomes contaminated
-
Cholera can then be transmitted when individuals:
-
Wash in contaminated water
-
Drink contaminated water
-
Eat food exposed to contaminated water
-
-
This means the disease occurs where people do not have access to proper sanitation and uncontaminated food
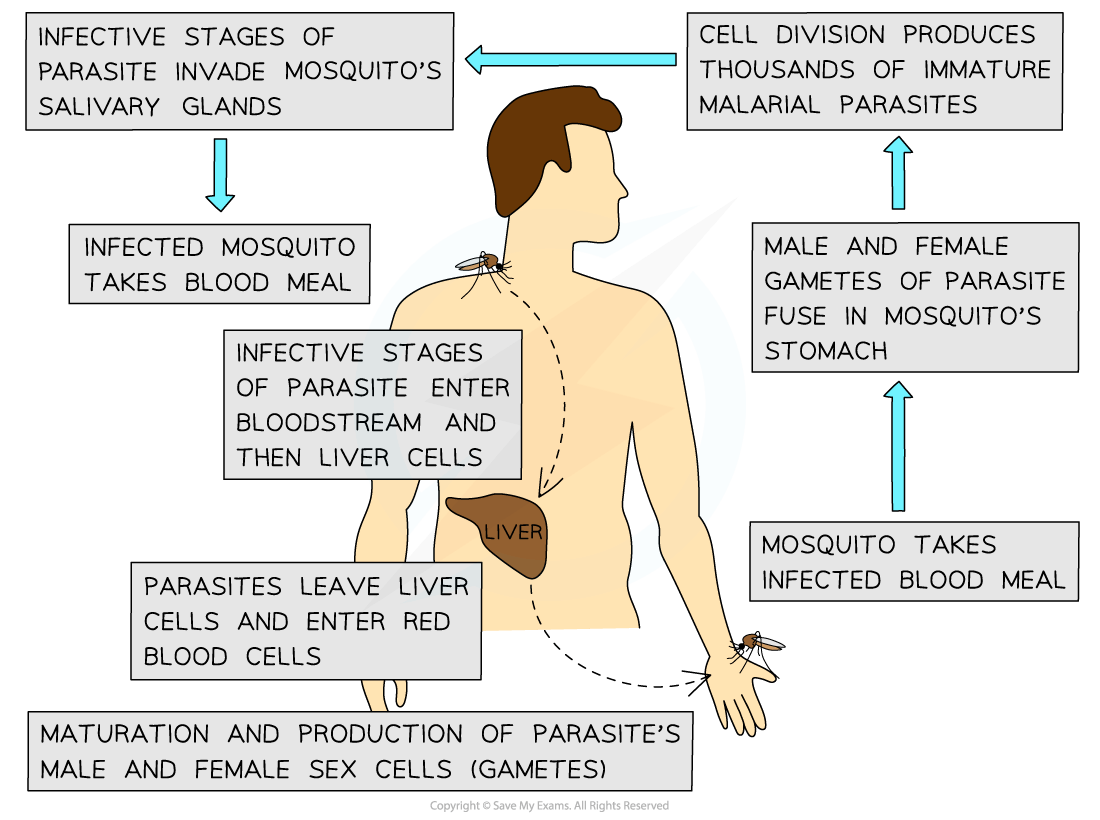
Transmission of malaria
-
Malaria is caused by one of four species of the protoctist Plasmodium
-
These protoctists are transmitted to humans by an insect vector as follows:
-
Female Anopheles mosquitoes feed on human blood to obtain the protein they need to develop their eggs
-
If the person they bite is infected with Plasmodium, the mosquito will take up some of the pathogen with the blood meal
-
When feeding on the next human, Plasmodium pass from the mosquito to the new human’s blood
-
-
Malaria may also be transmitted:
-
During blood transfusion
-
When unsterile needles are re-used
-
-
Plasmodium can also pass from mother to child across the placenta
Transmission of tuberculosis (TB)
-
TB is cause by the bacterial pathogens Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis
-
Human to human transmission occurs by droplet infection as follows:
-
When infected people with the active form of the disease cough or sneeze, M. tuberculosis bacteria enter the air in tiny droplets of liquid
-
TB is transmitted when uninfected people inhale these droplets
-
TB therefore spreads more quickly among people living in overcrowded conditions
-
-
The form of TB caused by M. bovis occurs in cattle but can spread to humans through:
-
Contaminated meat
-
Unpasteurised milk
-
-
Very few people in developed countries now acquire TB in this way, although meat and milk can still be a source of infection in some developing countries
Transmission of HIV/AIDS
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) can infect human cells and eventually lead to AIDS
-
The virus is spread by intimate human contact and can only be transmitted by direct exchange of body fluids
-
This means HIV can be transmitted in the following ways:
-
Sexual intercourse
-
Blood donation
-
Sharing of needles used by intravenous drug users
-
From mother to child across the placenta
-
Mixing of blood between mother and child during birth
-
From mother to child through breast milk
-
|
Disease |
Pathogen |
Transmission |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cholera |
Vibrio cholerae |
Contaminated water or food |
Diarrhoea and dehydration |
|
Malaria |
Plasmodium falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovale, P. vivax |
Female Anopheles mosquito |
Fever, headaches and muscle pain |
|
TB |
Mycobacterium tuberlulosis, M. bovis |
Airborne droplets |
Cough, chest pain, fever and weight loss |
|
HIV/AIDS |
Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
Exchange of body fluids |
Initial flu-like symptoms, and eventually a loss of immune function (AIDS) |
