Back to 课程
Biology_A-level_Cie
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies5 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms5 主题
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules3 主题
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids8 主题
-
2-3-proteins6 主题
-
2-4-water2 主题
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes5 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action8 主题
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes4 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells12 主题
-
diffusion
-
osmosis
-
active-transport
-
endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
investigating-diffusion
-
surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
investigating-surface-area
-
estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
osmosis-in-animals
-
comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
diffusion
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells6 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis2 主题
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna4 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis5 主题
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues4 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms7 主题
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system7 主题
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide5 主题
-
8-3-the-heart4 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system6 主题
-
10-1-infectious-diseases3 主题
-
10-2-antibiotics3 主题
-
11-1-the-immune-system4 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination6 主题
-
12-1-energy5 主题
-
12-2-respiration11 主题
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
aerobic-respiration-role-of-nad-and-fad
-
aerobic-respiration-oxidative-phosphorylation
-
anaerobic-respiration
-
energy-yield-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration
-
anaerobic-adaptation-of-rice
-
aerobic-respiration-effect-of-temperature-and-substrate-concentration
-
structure-and-function-of-mitochondria
-
the-four-stages-in-aerobic-respiration
-
aerobic-respiration-glycolysis
-
aerobic-respiration-the-link-reaction
-
aerobic-respiration-the-krebs-cycle
-
13-1-photosynthesis-as-an-energy-transfer-process8 主题
-
13-2-investigation-of-limiting-factors2 主题
-
14-1-homeostasis-in-mammals8 主题
-
14-2-homeostasis-in-plants3 主题
-
15-1-control-and-coordination-in-mammals12 主题
-
the-endocrine-system
-
the-nervous-system
-
neurones
-
sensory-receptor-cells
-
sequence-of-events-resulting-in-an-action-potential
-
transmission-of-nerve-impulses
-
speed-of-conduction-of-impulses
-
the-refractory-period
-
cholinergic-synapses
-
stimulating-contraction-in-striated-muscle
-
ultrastructure-of-striated-muscle
-
sliding-filament-model-of-muscular-contraction
-
the-endocrine-system
-
15-2-control-and-coordination-in-plants3 主题
-
16-1-passage-of-information-from-parents-to-offspring5 主题
-
16-2-the-roles-of-genes-in-determining-the-phenotype7 主题
-
16-3-gene-control3 主题
-
17-1-variation4 主题
-
17-2-natural-and-artificial-selection7 主题
-
17-3-evolution2 主题
-
18-1-classification5 主题
-
18-2-biodiversity7 主题
-
18-3-conservation6 主题
-
19-1-principles-of-genetic-technology11 主题
-
19-2-genetic-technology-applied-to-medicine4 主题
-
19-3-genetically-modified-organisms-in-agriculture2 主题
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids
-
2-3-proteins
-
2-4-water
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna
-
6-2-protein-synthesis
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-3-the-heart
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system
-
10-1-infectious-diseases
-
10-2-antibiotics
-
11-1-the-immune-system
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination
课 1,
主题 1
In Progress
the-microscope-in-cell-studies
课 Progress
0% Complete
Microscope slide preparation
Preparing a microscope slide
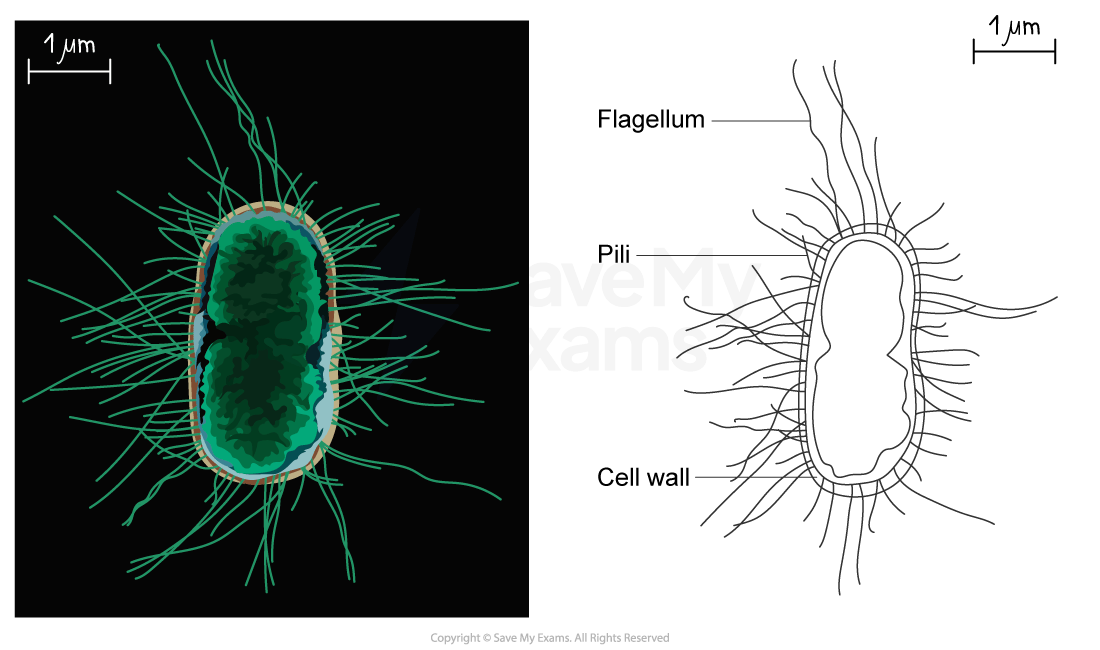
- Specimens can be viewed under a light microscope; this allows some details of cellular material to be observed
- Pre-prepared permanent slides can be viewed
- Such slides are produced by cutting very thin layers of tissue which are stained and permanently mounted on a glass slide for repeated use
- Different methods will be used to view different types of specimen, e.g. temporary slide preparations can be produced in the school laboratory as described below
Preparing a slide using a liquid specimen
- Add a few drops containing the liquid sample to a clean slide using a pipette
- Lower a coverslip over the specimen and gently press down to remove air bubbles
- Coverslips protect the microscope lens from liquids and help to prevent drying out
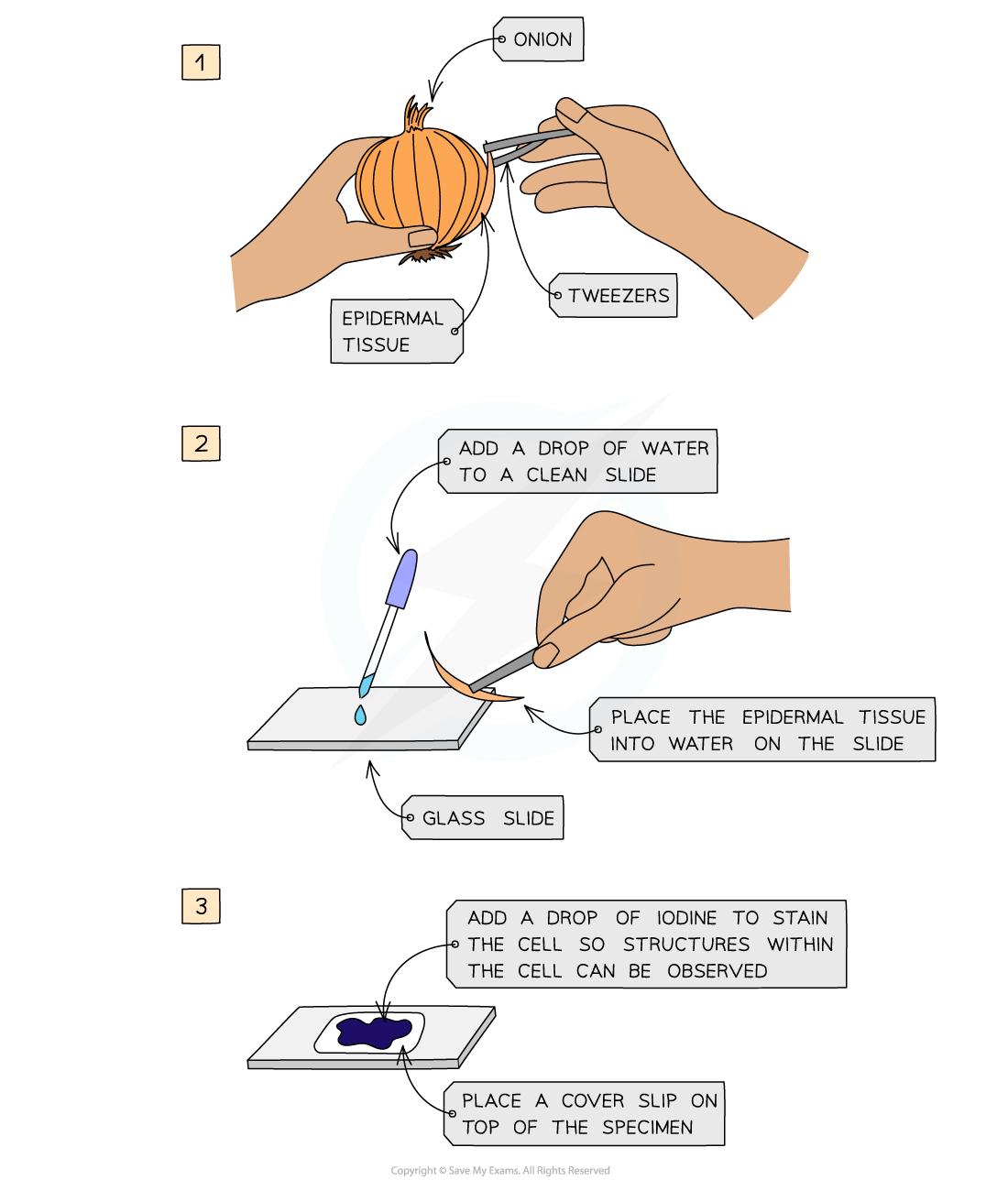
Preparing a microscope slide using a solid specimen
- Use scissors or a scalpel to cut a small sample of tissue, and peel away or cut a very thin layer of cells from the tissue sample
- The preparation method always needs to ensure that samples are thin enough to allow light to pass through
- Place the sample onto a slide
- A drop of water may be added at this point
- Apply iodine stain
- Gently lower a coverslip over the specimen and press down to remove any air bubbles
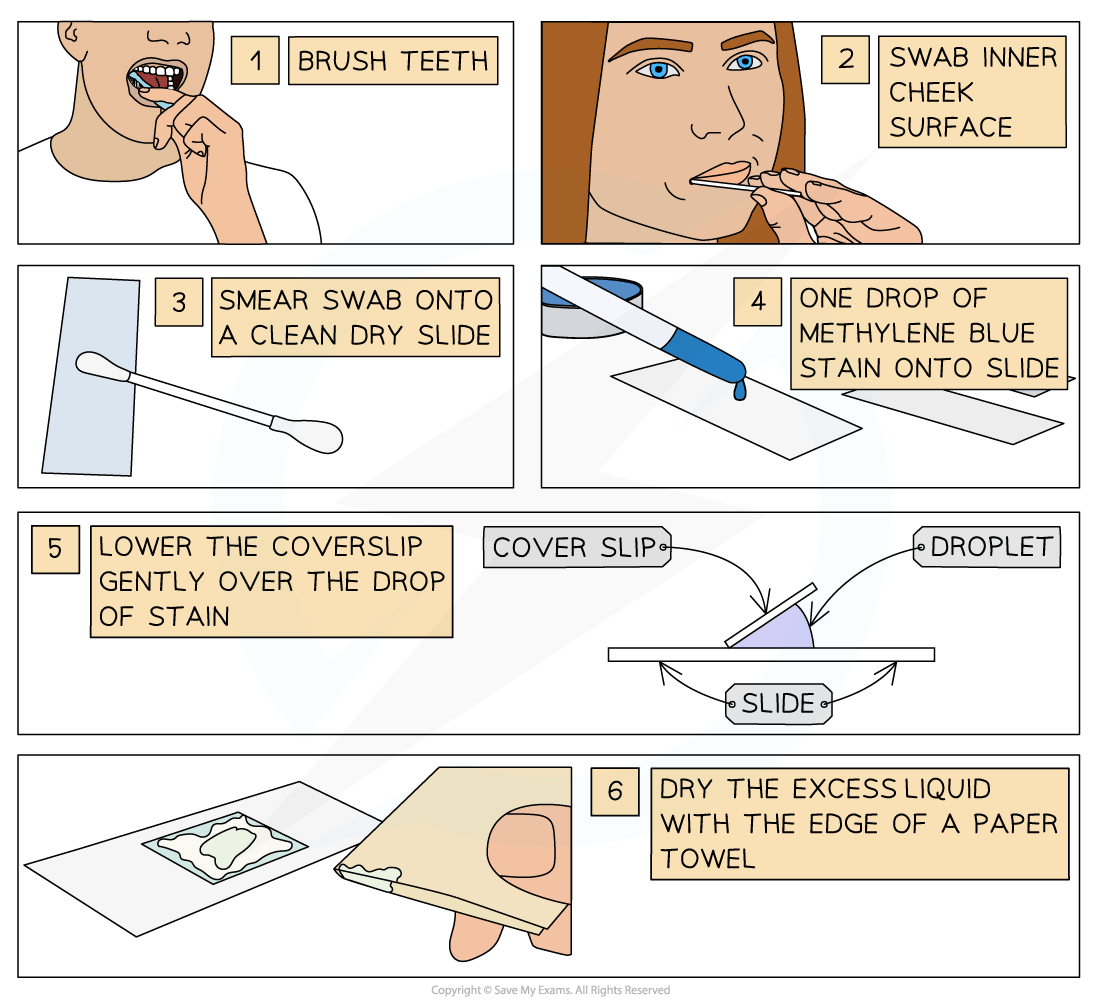
Preparing a slide using human cells
- Brush teeth thoroughly with normal toothbrush and toothpaste
- This removes bacteria from teeth so they don’t obscure the view of the cheek cells
- Take a sterile cotton swab and gently scrape the inside cheek surface of the mouth for 5-10 seconds
- Smear the cotton swab on the centre of the microscope slide for 2-3 seconds
- Add a drop of methylene blue solution
- Methylene blue stains negatively charged molecules in the cell, including DNA and RNA
- This causes the nucleus and mitochondria to appear darker than their surroundings
- Place a coverslip on top
- Lay the coverslip down at one edge and then gently lower the other edge until it is flat
- This reduces bubble formation under the coverslip
- Absorb any excess solution by allowing a paper towel to touch one side of the coverslip
Drawing cells
- To record the observations seen under a microscope, a labelled biological drawing is often made
- Biological drawings are line drawings which show specific features that have been observed when the specimen was viewed
- There are a number of rules/conventions that are followed when making a biological drawing
- The drawing must have a title
- The magnification under which the observations shown by the drawing are made should be recorded if possible
- A scale bar may be used
- A sharp pencil should be used
- Drawings should be on plain white paper
- Lines should be clear, single lines without sketching
- No shading should be used
- The drawing should take up as much of the space on the page as possible
- Well-defined structures should be drawn
- Only visible structures should be drawn, and the drawing should look like the specimen
- The drawing should be made with proper proportions
- Structures should be clearly labelled with label lines that:
- Do not cross
- Do not have arrowheads
- Connect directly to the part of the drawing being labelled
- Are on one side of the drawing
- Are drawn with a ruler
- Drawings of cells are typically made when visualizing cells at a higher magnification power, whereas plan drawings are typically made of tissues viewed under lower magnifications (individual cells are never drawn in a plan diagram)