Biology AS OCR
-
1-1-practical-skills-written-assessment AS7 主题
-
1-2-practical-skills-endorsement-assessment AS16 主题
-
1-2-1-practical-ethical-use-of-organisms as
-
1-2-2-practical-aseptic-techniques as
-
1-2-3-practical-dissection-of-gas-exchange-surfaces-in-fish-and-insects as
-
1-2-4-drawing-cells-from-blood-smears as
-
1-2-5-practical-investigating-biodiversity-using-sampling as
-
1-2-6-practical-data-loggers-and-computer-modelling as
-
1-2-7-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-diffusion as
-
1-2-8-practical-investigating-water-potential as
-
1-2-9-practical-factors-affecting-membrane-structure-and-permeability as
-
1-2-10-biochemical-tests-reducing-sugars-and-starch as
-
1-2-11-biochemical-tests-lipids as
-
1-2-12-biochemical-tests-proteins as
-
1-2-13-chromatography as
-
1-2-14-serial-dilutions as
-
1-2-15-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-transpiration as
-
1-2-16-practical-using-a-light-microscope as
-
1-2-1-practical-ethical-use-of-organisms as
-
2-1-cell-structure AS9 主题
-
2-1-2-using-a-microscope as
-
2-1-3-drawing-cells as
-
2-1-4-magnification-and-resolution as
-
2-1-5-eukaryotic-cells as
-
2-1-6-eukaryotic-cells-under-the-microscope as
-
2-1-7-organelles-and-the-production-of-proteins as
-
2-1-8-the-cytoskeleton as
-
2-1-9-prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells as
-
2-1-1-studying-cells as
-
2-1-2-using-a-microscope as
-
2-2-biological-molecules AS17 主题
-
2-2-1-properties-of-water as
-
2-2-2-monomers-and-polymers as
-
2-2-3-monosaccharides as
-
2-2-4-the-glycosidic-bond as
-
2-2-5-polysaccharides as
-
2-2-6-biochemical-tests-reducing-sugars-and-starch as
-
2-2-7-lipids-and-ester-bonds as
-
2-2-8-lipids-structure-and-function as
-
2-2-9-biochemical-tests-lipids as
-
2-2-10-amino-acids-and-peptide-bonds as
-
2-2-11-protein-structure as
-
2-2-12-globular-proteins as
-
2-2-13-fibrous-proteins as
-
2-2-14-inorganic-ions as
-
2-2-15-biochemical-tests-proteins as
-
2-2-16-finding-the-concentration-of-a-substance as
-
2-2-17-chromatography as
-
2-2-1-properties-of-water as
-
2-3-nucleotides-and-nucleic-acids AS8 主题
-
2-4-enzymes AS9 主题
-
2-4-1-the-role-of-enzymes as
-
2-4-2-enzyme-action as
-
2-4-3-enzyme-activity-ph as
-
2-4-4-enzyme-activity-temperature as
-
2-4-5-enzyme-activity-enzyme-concentration as
-
2-4-6-enzyme-activity-substrate-concentration as
-
2-4-7-enzyme-activity-enzyme-inhibitors as
-
2-4-8-coenzymes-cofactors-and-prosthetic-groups as
-
2-4-9-practical-measuring-enzyme-activity as
-
2-4-1-the-role-of-enzymes as
-
2-5-biological-membranes AS9 主题
-
2-5-1-the-cell-surface-membrane as
-
2-5-2-membrane-structure-and-permeability as
-
2-5-3-diffusion-and-facilitated-diffusion as
-
2-5-4-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-diffusion as
-
2-5-5-active-transport as
-
2-5-6-endocytosis-and-exocytosis as
-
2-5-7-osmosis as
-
2-5-8-osmosis-in-animal-and-plant-cells as
-
2-5-9-practical-investigating-water-potential as
-
2-5-1-the-cell-surface-membrane as
-
2-6-cell-division-cell-diversity-and-cellular-organisation AS11 主题
-
2-6-1-the-cell-cycle as
-
2-6-2-the-stages-of-mitosis as
-
2-6-3-identifying-mitosis-in-plant-cells as
-
2-6-4-the-significance-of-mitosis as
-
2-6-5-the-stages-of-meiosis as
-
2-6-6-the-significance-of-meiosis as
-
2-6-7-specialised-cells as
-
2-6-8-the-organisation-of-cells as
-
2-6-9-stem-cells as
-
2-6-10-stem-cells-in-animals-and-plants as
-
2-6-11-the-use-of-stem-cells as
-
2-6-1-the-cell-cycle as
-
3-1-exchange-surfaces AS7 主题
-
3-2-transport-in-animals AS12 主题
-
3-2-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-animals as
-
3-2-2-circulatory-systems as
-
3-2-3-blood-vessels as
-
3-2-4-tissue-fluid as
-
3-2-5-the-mammalian-heart as
-
3-2-6-practical-mammalian-heart-dissection as
-
3-2-7-the-cardiac-cycle as
-
3-2-8-cardiac-output as
-
3-2-9-heart-action-initiation-and-control as
-
3-2-10-electrocardiograms-ecgs as
-
3-2-11-the-role-of-haemoglobin as
-
3-2-12-adult-and-fetal-haemoglobin as
-
3-2-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-animals as
-
3-3-transport-in-plants AS11 主题
-
3-3-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-plants as
-
3-3-2-the-xylem-and-phloem as
-
3-3-3-the-xylem as
-
3-3-4-the-phloem as
-
3-3-5-transverse-sections-stems-roots-and-leaves as
-
3-3-6-the-process-of-transpiration as
-
3-3-7-transpiration-in-plants as
-
3-3-8-practical-investigating-the-rate-of-transpiration as
-
3-3-9-translocation as
-
3-3-10-the-mass-flow-hypothesis as
-
3-3-11-the-adaptations-of-xerophytic-and-hydrophytic-plants as
-
3-3-1-the-need-for-transport-systems-in-plants as
-
4-1-communicable-diseases-disease-prevention-and-the-immune-system AS16 主题
-
4-1-1-common-pathogens-and-communicable-diseases as
-
4-1-2-transmission-of-communicable-pathogens as
-
4-1-3-plant-defences-against-pathogens as
-
4-1-4-non-specific-immune-responses as
-
4-1-5-phagocytes as
-
4-1-6-blood-cells as
-
4-1-7-the-t-lymphocyte-response as
-
4-1-8-the-b-lymphocyte-response as
-
4-1-9-primary-and-secondary-immune-responses as
-
4-1-10-antibodies as
-
4-1-11-opsonins-agglutinins-and-anti-toxins as
-
4-1-12-types-of-immunity as
-
4-1-13-autoimmune-diseases as
-
4-1-14-principles-of-vaccination as
-
4-1-15-sources-of-medicine as
-
4-1-16-antibiotics as
-
4-1-1-common-pathogens-and-communicable-diseases as
-
4-2-biodiversity AS10 主题
-
4-2-1-biodiversity as
-
4-2-2-sampling-to-determine-biodiversity as
-
4-2-3-practical-investigating-biodiversity-using-sampling as
-
4-2-4-measuring-species-richness-and-species-evenness as
-
4-2-5-simpsons-index as
-
4-2-6-genetic-diversity as
-
4-2-7-factors-affecting-biodiversity as
-
4-2-8-reasons-for-maintaining-biodiversity as
-
4-2-9-methods-of-maintaining-biodiversity as
-
4-2-10-conservation-agreements as
-
4-2-1-biodiversity as
-
4-3-classification-and-evolution AS15 主题
-
4-3-1-classification-of-species as
-
4-3-2-binomial-system as
-
4-3-3-classification-of-the-three-domains as
-
4-3-4-classification-of-the-five-kingdoms as
-
4-3-5-classification-and-phylogeny as
-
4-3-6-evidence-of-evolution as
-
4-3-7-types-of-variation as
-
4-3-8-standard-deviation as
-
4-3-9-variation-t-test-method as
-
4-3-10-variation-t-test-worked-example as
-
4-3-11-spearmans-rank-correlation as
-
4-3-12-adaptation as
-
4-3-13-natural-selection as
-
4-3-14-evolution-of-resistance as
-
4-3-15-consequences-of-resistance as
-
4-3-1-classification-of-species as
4-2-5-simpsons-index as
Exam code:H020
Simpson’s Index of Diversity
-
Once the abundance of different species in an area has been recorded the results can be used to calculate the species diversity or biodiversity for that area
-
Species diversity looks at the number of different species in an area (species richness) but also the evenness of abundance across the different species in that area (species evenness)
-
Simpson’s index of diversity (D) can be used to quantify the biodiversity of an area
Simpson’s index
-
The formula is:

-
Where:
-
n = total no. of organisms for a single species
-
N = total no. of organisms for all species
-
-
-
To calculate Simpson’s Index:
-
Step 1: First calculate n / N for each species
-
Step 2: Square each of these values
-
Step 3: Add them together and subtract the total from 1
-
-
To understand what the value of D means you need to know the following:
-
The value of D can fall between 0 and 1
-
Values near 1 indicate high levels of biodiversity
-
Values near 0 indicate low levels of biodiversity
-
-
Worked Example
Samples of different insect species in a back garden were collected using sweep nets and identification keys. Use the data to calculate Simpson’s Index.
Answer:
The results and working out are seen in the table below. The figures have been rounded to three decimal places for columns 3 and 4
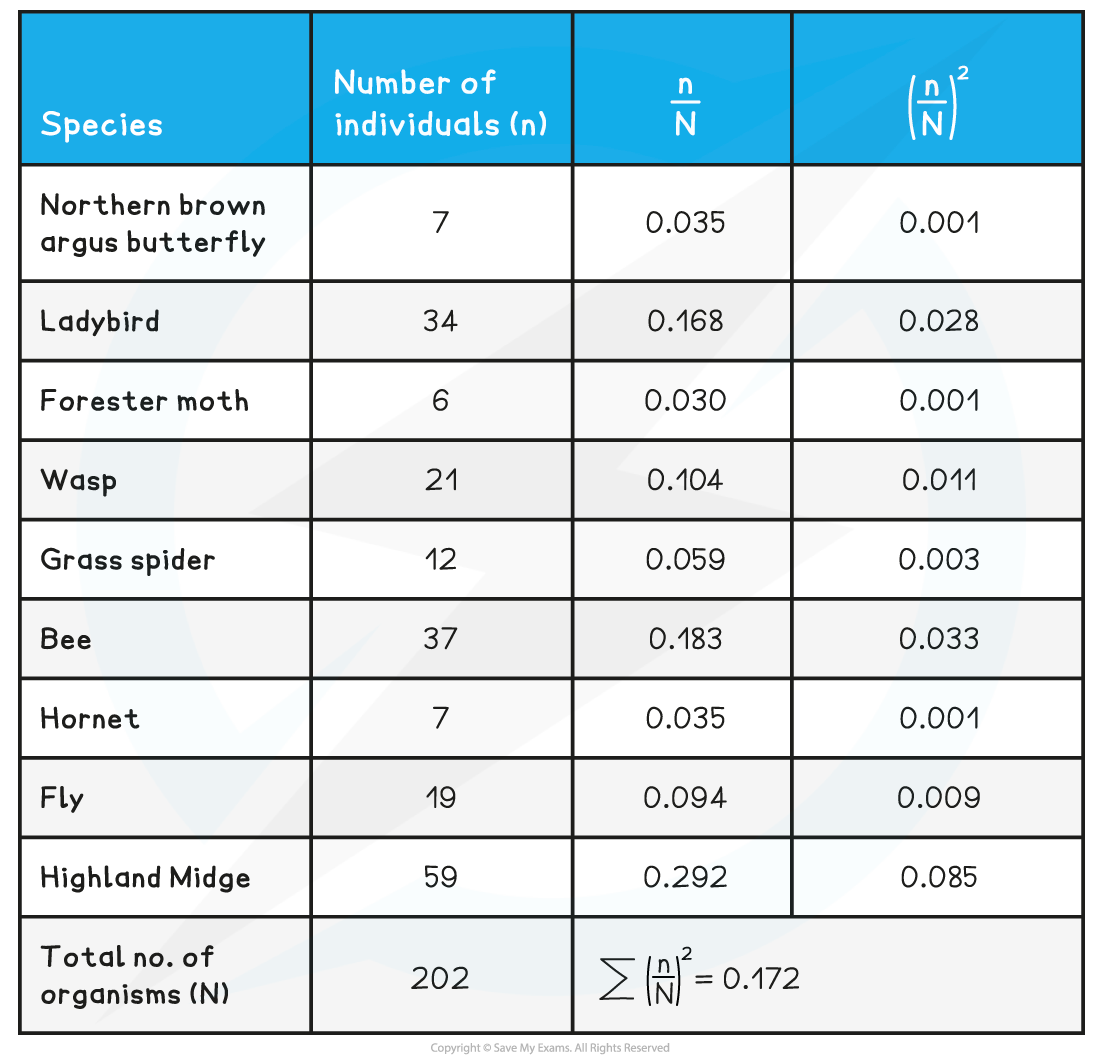
D = 1 – 0.172 = 0.828
As the value of D is much closer to 1 than 0, it can be said that this is a relatively high value for biodiversity.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember, you will be provided with the formula for Simpson’s Index in the exam so you do not need to recall this.

Responses