Biology AS Edexcel Snab Revision
-
lifestyle-health-and-risk as19 主题
-
diet-and-health interpreting-data-on-risk-factors
-
diet-and-health treatment-of-cvd
-
diet-and-health energy-budgets-and-diet
-
diet-and-health monosaccharides
-
diet-and-health the-glycosidic-bond
-
diet-and-health disaccharides
-
diet-and-health polysaccharides
-
diet-and-health lipids-and-ester-bonds
-
diet-and-health reducing-risk-factors-of-cvd
-
diet-and-health practical-vitamin-c-content
-
the-circulatory-system the-need-for-a-circulatory-system
-
the-circulatory-system the-importance-of-water-in-transport
-
the-circulatory-system mammalian-heart-structure-and-function
-
the-circulatory-system blood-vessels-structure-and-function
-
the-circulatory-system cardiac-cycle
-
the-circulatory-system investigating-heart-rate
-
the-circulatory-system atherosclerosis
-
the-circulatory-system blood-clotting
-
diet-and-health cardiovascular-disease
-
diet-and-health interpreting-data-on-risk-factors
-
genes-and-health as28 主题
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport properties-of-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport ficks-law-of-diffusion
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport the-mammalian-lung
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport cell-membranes
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport practical-investigating-membrane-permeability
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport diffusion-and-facilitated-diffusion
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport active-transport
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport osmosis
-
nucleic-acids nucleotides-and-phosphodiester-bonds
-
nucleic-acids dna-structure
-
nucleic-acids rna-structure
-
proteins transcription
-
proteins translation
-
proteins nature-of-the-genetic-code
-
proteins amino-acids-and-peptide-bonds
-
proteins levels-of-protein-structure
-
proteins globular-proteins-structure-and-function
-
proteins fibrous-proteins-structure-and-function
-
proteins the-role-of-enzymes
-
proteins mode-of-enzyme-action
-
proteins enzyme-and-substrate-concentrations
-
inheritance dna-replication
-
inheritance mutations
-
inheritance inheritance-key-terms
-
inheritance pedigree-diagrams
-
inheritance monohybrid-crosses
-
inheritance chi-squared-test
-
inheritance genetic-screening
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport properties-of-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
voice-of-the-genome as19 主题
-
cell-structure-and-organisation cell-theory
-
cell-structure-and-organisation eukaryotic-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation prokaryotic-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation organisation-of-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation microscopy
-
cell-structure-and-organisation magnification-calculations
-
cell-structure-and-organisation recognising-organelles
-
cell-division the-cell-cycle
-
cell-division mitosis
-
cell-division practical-identifying-mitosis-in-plant-cells
-
reproduction-and-inheritance mammalian-gametes
-
reproduction-and-inheritance fertilisation-in-mammals
-
reproduction-and-inheritance genes-and-linkage
-
reproduction-and-inheritance meiosis-source-of-genetic-variation
-
differentiation-and-variation stem-cells
-
differentiation-and-variation stem-cells-in-medicine
-
differentiation-and-variation cell-differentiation
-
differentiation-and-variation epigenetics
-
differentiation-and-variation phenotypes-and-variation
-
cell-structure-and-organisation cell-theory
-
biodiversity-and-natural-resources as19 主题
-
biodiversity the-variety-of-life
-
biodiversity measuring-biodiversity-within-a-habitat
-
biodiversity comparing-biodiversity-between-habitats
-
biodiversity ecological-niches-and-adaptations
-
biodiversity natural-selection
-
biodiversity hardy-weinberg-equation
-
biodiversity reproductive-isolation
-
biodiversity classification
-
biodiversity conservation-of-biodiversity
-
resources-from-plants plant-cell-structure
-
resources-from-plants plant-stems
-
resources-from-plants importance-of-water-and-inorganic-ions-to-plants
-
resources-from-plants starch-and-cellulose-structure-and-function
-
resources-from-plants plant-fibres
-
resources-from-plants practical-identifying-tissue-types-within-stems
-
resources-from-plants tensile-strength-plant-fibres
-
resources-from-plants development-of-drug-testing
-
resources-from-plants antimicrobial-properties-of-plants
-
resources-from-plants sustainability-and-plant-materials
-
biodiversity the-variety-of-life
proteins amino-acids-and-peptide-bonds
Exam code:8BN0
Amino Acid: Structure
Proteins
-
Proteins are polymers (and macromolecules) made of monomers called amino acids
-
The sequence, type and number of the amino acids within a protein determines its shape and therefore its function
-
Proteins are extremely important in cells because they form all of the following:
-
Enzymes
-
Cell membrane proteins (eg. carrier)
-
Hormones
-
Immunoproteins (eg. immunoglobulins)
-
Transport proteins (eg. haemoglobin)
-
Structural proteins (eg. keratin, collagen)
-
Contractile proteins (eg. myosin)
-
Amino acids
-
Amino acids are the monomers of polypeptides
-
There are 20 amino acids found in proteins common to all living organisms
-
The general structure of all amino acids is a central carbon atom bonded to:
-
An amine (also called amino) group -NH2
-
A carboxylic acid group -COOH
-
A hydrogen atom
-
An R group (which is how each amino acid differs and why amino acid properties differ e.g. whether they are acidic or basic or whether they are polar or non-polar)
-
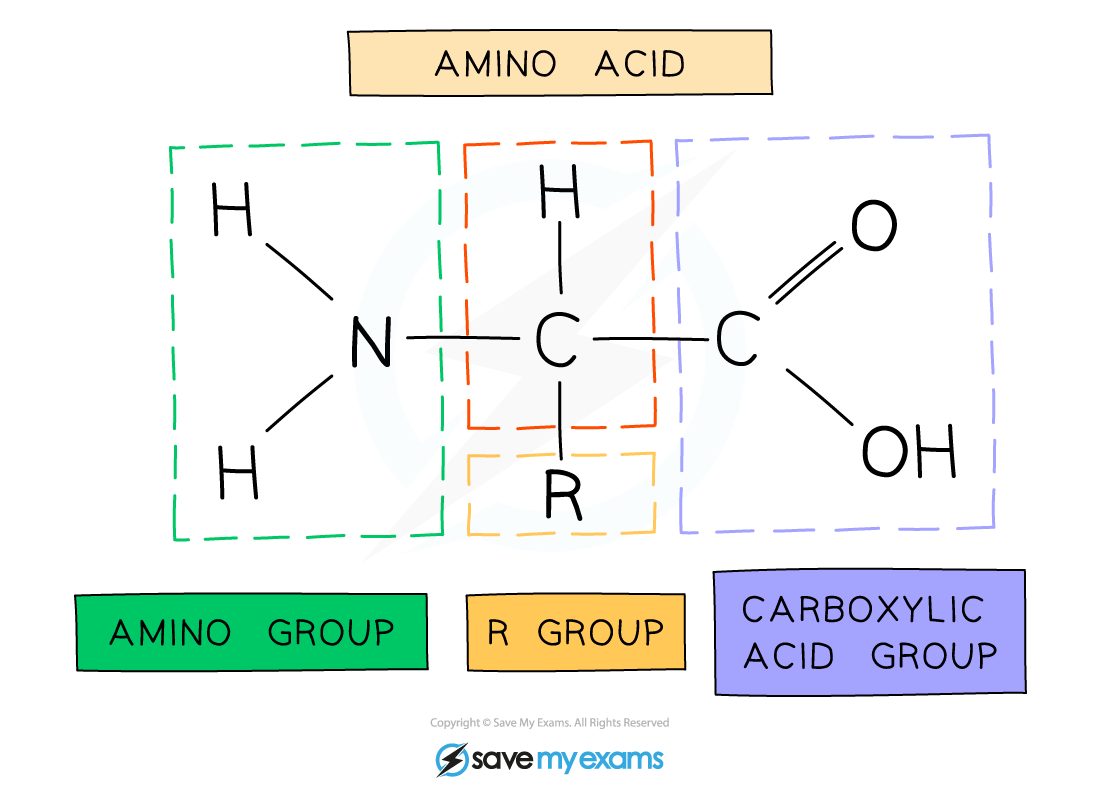
The general structure of an amino acid
The Peptide Bond
-
Peptide bonds form between amino acids
-
Peptide bonds are covalent bonds and so involve the sharing of electrons
-
In order to form a peptide bond :
-
A hydroxyl (-OH) is lost from the carboxylic group of one amino acid
-
A hydrogen atom is lost from the amine group of another amino acid
-
-
The remaining carbon atom (with the double-bonded oxygen) from the first amino acid bonds to the nitrogen atom of the second amino acid
-
This is a condensation reaction so water is released
-
Dipeptides are formed by the condensation of two amino acids
-
Polypeptides are formed by the condensation of many (3 or more) amino acids
-
A protein may have only one polypeptide chain or it may have multiple chains interacting with each other
-
During hydrolysis reactions, the addition of water breaks the peptide bonds resulting in polypeptides being broken down to amino acids
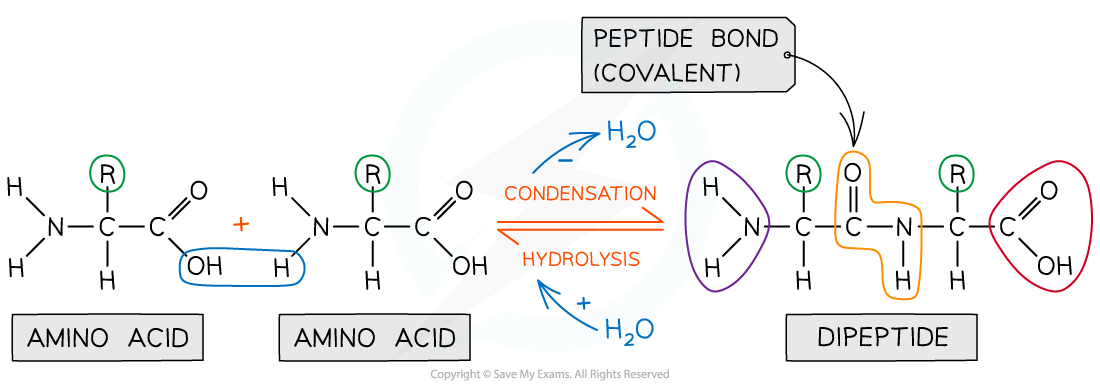
Peptide bonds are formed by condensation reactions (releasing a molecule of water) and broken by hydrolysis reactions (adding a molecule of water)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When asked to identify the location of the peptide bond, look for where nitrogen is bonded to a carbon which has a double bond with an oxygen atom, note the R group is not involved in the formation of a peptide bond.
Structures of specific amino acids are not required.

Responses