Biology AS Edexcel Snab Revision
-
lifestyle-health-and-risk as19 主题
-
diet-and-health interpreting-data-on-risk-factors
-
diet-and-health treatment-of-cvd
-
diet-and-health energy-budgets-and-diet
-
diet-and-health monosaccharides
-
diet-and-health the-glycosidic-bond
-
diet-and-health disaccharides
-
diet-and-health polysaccharides
-
diet-and-health lipids-and-ester-bonds
-
diet-and-health reducing-risk-factors-of-cvd
-
diet-and-health practical-vitamin-c-content
-
the-circulatory-system the-need-for-a-circulatory-system
-
the-circulatory-system the-importance-of-water-in-transport
-
the-circulatory-system mammalian-heart-structure-and-function
-
the-circulatory-system blood-vessels-structure-and-function
-
the-circulatory-system cardiac-cycle
-
the-circulatory-system investigating-heart-rate
-
the-circulatory-system atherosclerosis
-
the-circulatory-system blood-clotting
-
diet-and-health cardiovascular-disease
-
diet-and-health interpreting-data-on-risk-factors
-
genes-and-health as28 主题
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport properties-of-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport ficks-law-of-diffusion
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport the-mammalian-lung
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport cell-membranes
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport practical-investigating-membrane-permeability
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport diffusion-and-facilitated-diffusion
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport active-transport
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport osmosis
-
nucleic-acids nucleotides-and-phosphodiester-bonds
-
nucleic-acids dna-structure
-
nucleic-acids rna-structure
-
proteins transcription
-
proteins translation
-
proteins nature-of-the-genetic-code
-
proteins amino-acids-and-peptide-bonds
-
proteins levels-of-protein-structure
-
proteins globular-proteins-structure-and-function
-
proteins fibrous-proteins-structure-and-function
-
proteins the-role-of-enzymes
-
proteins mode-of-enzyme-action
-
proteins enzyme-and-substrate-concentrations
-
inheritance dna-replication
-
inheritance mutations
-
inheritance inheritance-key-terms
-
inheritance pedigree-diagrams
-
inheritance monohybrid-crosses
-
inheritance chi-squared-test
-
inheritance genetic-screening
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport properties-of-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
voice-of-the-genome as19 主题
-
cell-structure-and-organisation cell-theory
-
cell-structure-and-organisation eukaryotic-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation prokaryotic-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation organisation-of-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation microscopy
-
cell-structure-and-organisation magnification-calculations
-
cell-structure-and-organisation recognising-organelles
-
cell-division the-cell-cycle
-
cell-division mitosis
-
cell-division practical-identifying-mitosis-in-plant-cells
-
reproduction-and-inheritance mammalian-gametes
-
reproduction-and-inheritance fertilisation-in-mammals
-
reproduction-and-inheritance genes-and-linkage
-
reproduction-and-inheritance meiosis-source-of-genetic-variation
-
differentiation-and-variation stem-cells
-
differentiation-and-variation stem-cells-in-medicine
-
differentiation-and-variation cell-differentiation
-
differentiation-and-variation epigenetics
-
differentiation-and-variation phenotypes-and-variation
-
cell-structure-and-organisation cell-theory
-
biodiversity-and-natural-resources as19 主题
-
biodiversity the-variety-of-life
-
biodiversity measuring-biodiversity-within-a-habitat
-
biodiversity comparing-biodiversity-between-habitats
-
biodiversity ecological-niches-and-adaptations
-
biodiversity natural-selection
-
biodiversity hardy-weinberg-equation
-
biodiversity reproductive-isolation
-
biodiversity classification
-
biodiversity conservation-of-biodiversity
-
resources-from-plants plant-cell-structure
-
resources-from-plants plant-stems
-
resources-from-plants importance-of-water-and-inorganic-ions-to-plants
-
resources-from-plants starch-and-cellulose-structure-and-function
-
resources-from-plants plant-fibres
-
resources-from-plants practical-identifying-tissue-types-within-stems
-
resources-from-plants tensile-strength-plant-fibres
-
resources-from-plants development-of-drug-testing
-
resources-from-plants antimicrobial-properties-of-plants
-
resources-from-plants sustainability-and-plant-materials
-
biodiversity the-variety-of-life
inheritance pedigree-diagrams
Exam code:8BN0
Pedigree Diagrams
-
Family pedigree diagrams can be used to trace the pattern of inheritance of a specific trait, e.g. a genetic disorder, through generations of a family
-
Pedigree diagrams can provide information such as
-
Whether a trait is caused by a dominant or recessive allele
-
Whether a trait is more likely to be inherited by males or females
-
The genotypes of individuals in the family
-
The probability that an individual in the family will inherit a trait
-
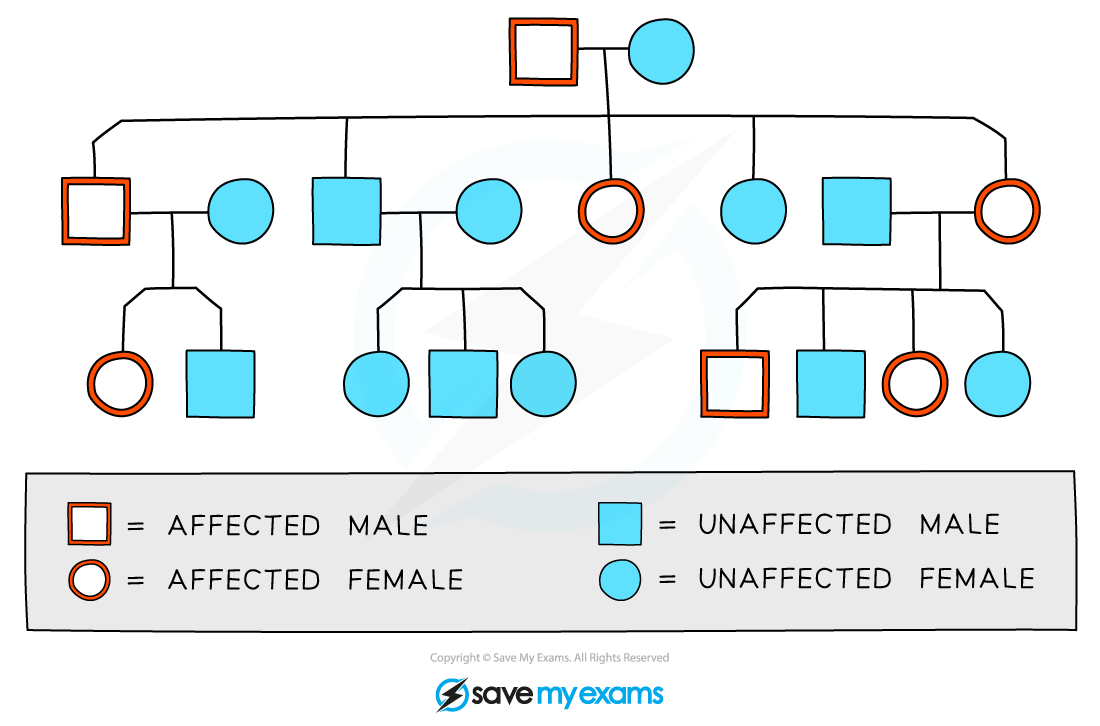
Pedigree diagrams can be used to show the pattern of inheritance of a genetic trait
-
Males are indicated by the square shape and females are represented by circles
-
Affected and unaffected individuals can be indicated using colour, shading, or cross-hatching
-
Horizontal lines between males and females show that they have produced children
-
Vertical lines show the relationship between parent and child
-
Roman numerals may be used to indicate generations
-
For each generation the eldest child is on the left and each individual is numbered
-
The family pedigree above shows the following
-
Both males and females are affected by the trait in question
-
Every generation has affected individuals
-
The eldest son in the second generation is affected
-
There is one family group that has no affected parents or children
-
-
The diagram above does not contain enough information to show
-
Whether the trait is caused by a dominant or recessive allele
-
The genotypes of the individuals involved
-
Worked Example
The pedigree diagram below traces the inheritance of albinism through several generations. Albinism affects the production of the pigment melanin leading to lighter hair, skin and eyes.

Using the pedigree chart, deduce and explain the following:
-
The type of allele that causes albinism
-
The genotype of individuals 9 and 7
-
The possible genotypes of 10 and 11
Answer:
Question 1
Albinism is caused by a recessive allele
Person number 9 is an affected individual despite parents 6 and 7 being unaffected; 6 and 7 must both be carriers of the recessive allele and 9 has inherited one recessive allele from each parent
Question 2
The genotype of person 9 must be homozygous recessive (aa) and the genotype of 7 must be heterozygous (Aa)
Person 9 is an affected individual with albinism; as this is determined by the recessive allele they must have two copies of the albinism allele
Person 7 must be heterozygous as he does not have albinism but has passed on the recessive allele to person 9
Question 3
The possible genotypes of 10 and 11 are heterozygous (Aa) or homozygous dominant (AA)
They are both unaffected individuals so must possess at least one dominant allele (A), however, it is possible that they each might have inherited a recessive allele (a) from one parent (both parents must have a copy of the recessive allele in order for person 9 to have albinism)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When answering questions about pedigree charts for genetic diseases, it is always useful to remember which phenotype is caused by the homozygous recessive genotype. You can write these genotypes onto your chart and it will give you a good starting point for working out the possible genotypes of the rest of the individuals in the chart.

Responses