Biology AS CIE
-
1-cell-structure10 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS prokaryotic-v-eukaryotic-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS the-vital-role-of-atp
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS animal-and-plant-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS eukaryotic-cell-structures-and-functions
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS calculating-actual-size
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS resolution-and-magnification
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS eyepiece-graticules-and-stage-micrometers
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS magnification-calculations
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
2-biological-molecules19 主题
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
2-4-water AS the-role-of-water-in-living-organisms
-
2-3-proteins AS collagen
-
2-3-proteins AS haemoglobin
-
2-3-proteins AS globular-and-fibrous-proteins
-
2-3-proteins AS protein-shape
-
2-3-proteins AS the-four-levels-of-protein-structure
-
2-3-proteins AS amino-acids-and-the-peptide-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS phospholipids
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS triglycerides
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS cellulose
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS starch-and-glycogen
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS the-glycosidic-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS reducing-and-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS covalent-bonds-in-polymers
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS biological-molecules-key-terms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS testing-for-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS the-benedicts-test
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS biological-molecule-tests
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
3-enzymes13 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-inhibitors
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS vmax-and-the-michaelis-menten-constant
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-inhibitor-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-substrate-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-enzyme-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-ph
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-temperature
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS colorimetry
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS measuring-enzyme-activity
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS how-enzymes-work
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzyme-action
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
4-cell-membranes-and-transport16 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-surface-area
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-diffusion
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS active-transport
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS diffusion
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS cell-signalling
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-cell-surface-membrane
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS components-of-cell-surface-membranes
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-fluid-mosaic-model
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
5-the-mitotic-cell-cycle8 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS the-stages-of-mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS how-tumours-form
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-stem-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-telomeres-
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-cell-cycle
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS chromosome-structure
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
6-nucleic-acids-and-protein-synthesis9 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS transcription
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS constructing-polypeptides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS the-universal-genetic-code
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS from-gene-to-polypeptide
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-rna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS semi-conservative-dna-replication
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-dna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS nucleotides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
7-transport-in-plants11 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS the-sucrose-loading-mechanism
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS movement-in-the-phloem
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS xerophytic-plant-leaf-adaptations
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-the-transpiration-pull
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS transpiration-in-plants
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-mineral-ion-transport-in-plants
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS phloem-sieve-tube-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-vessels-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-and-phloem-distribution
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS plant-transverse-sections
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
8-transport-in-mammals16 主题
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-cardiac-cycle
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-walls-of-the-heart
-
8-3-the-heart AS structure-of-the-heart
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-bohr-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-oxygen-dissociation-curve
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS plasma-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-chloride-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS red-blood-cells-haemoglobin-and-oxygen
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-tissue-fluid-and-lymph
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-role-of-water-in-circulation
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS cells-of-the-blood
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-vessels-structures-and-functions
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS observing-and-drawing-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-main-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS circulatory-systems
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
9-gas-exchange6 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS structures-and-functions-of-the-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-structures
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS distribution-of-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
10-infectious-diseases6 主题
-
11-immunity10 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS how-vaccines-work
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS types-of-immunity
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS uses-of-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS making-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS antibodies
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS memory-cells-and-immunity
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS primary-immune-response
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS antigens
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS phagocytes
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS distribution-of-tissues
Exam code:9700
Distribution of tissues in the gas exchange system
Cartilage
-
Cartilage is a strong and flexible tissue found in various places around the body
-
Cartilage forms ‘c’ shaped rings that are arranged along the trachea, called tracheal rings
-
These rings help to support the trachea and ensure it stays open, while allowing it to move and flex while we breathe
-
-
Cartilage also supports the bronchi, though it does not form c-shaped rings here
-
Cartilage is not found in the bronchioles
-
Ciliated epithelium
-
Ciliated epithelium is a specialised tissue which lines all of the tubes of the airways
-
Each cell has small projections of cilia
-
The cilia sweep mucus, dust and bacteria upwards and away from the lungs and the epithelium itself
-
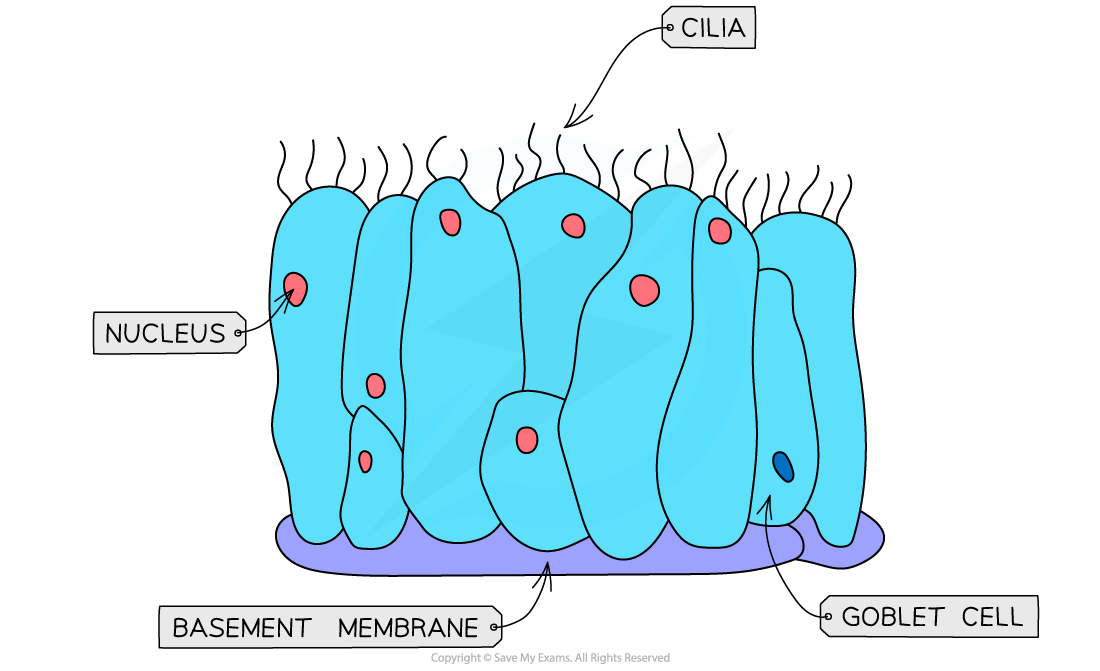
Goblet cells
-
Goblet cells can be found scattered throughout the ciliated epithelium in the trachea, and also in the bronchi, though usually not in the bronchioles
-
They are mucus-producing cells that secrete viscous mucus
-
This mucus traps dust, bacteria and other microorganisms and prevents them from reaching the lungs
-
The mucus is then swept along by the cilia of the ciliated epithelium upwards and is swallowed
-
The mucus and any microorganisms will then be destroyed by the acid in the stomach
-
Squamous epithelium of alveoli
-
The alveoli have a lining of thin squamous epithelium, that allows for gas exchange
-
The squamous epithelium forms the structure of the alveolar wall and is very thin and permeable for the easy diffusion of gases
-
Smooth muscle
-
Smooth muscle can be found in the walls of the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles
-
It helps to regulate the flow of air into the lungs by relaxing when more air is needed and constricting when less air is needed
-
Capillaries
-
Each alveolus is surrounded by an extensive network of capillaries
-
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillaries and into the alveoli to be exhaled, while oxygen diffuses the other way from alveoli and into the capillaries to be carried around the body
-
These capillaries have a diameter of around 3-4 µm, which is only wide enough for one red blood cell to travel through at any one time
-
This ensures that there is sufficient time and opportunity for gas exchange to occur
-
-
Worked Example
Explain how the lining of the trachea, bronchus and bronchioles provide protection against pathogens
-
Cilia beat to move mucus away from the lungs and up towards the mouth
-
Mucus is produced by goblet cells and acts as a barrier to pathogens from entering the ciliated epithelium
-
The mucus also traps bacteria and microorganisms, while blood vessels bring macrophages to engulf any pathogens in phagocytosis

Responses