Biology AS CIE
-
1-cell-structure10 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS prokaryotic-v-eukaryotic-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS the-vital-role-of-atp
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS animal-and-plant-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS eukaryotic-cell-structures-and-functions
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS calculating-actual-size
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS resolution-and-magnification
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS eyepiece-graticules-and-stage-micrometers
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS magnification-calculations
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
2-biological-molecules19 主题
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
2-4-water AS the-role-of-water-in-living-organisms
-
2-3-proteins AS collagen
-
2-3-proteins AS haemoglobin
-
2-3-proteins AS globular-and-fibrous-proteins
-
2-3-proteins AS protein-shape
-
2-3-proteins AS the-four-levels-of-protein-structure
-
2-3-proteins AS amino-acids-and-the-peptide-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS phospholipids
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS triglycerides
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS cellulose
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS starch-and-glycogen
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS the-glycosidic-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS reducing-and-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS covalent-bonds-in-polymers
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS biological-molecules-key-terms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS testing-for-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS the-benedicts-test
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS biological-molecule-tests
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
3-enzymes13 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-inhibitors
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS vmax-and-the-michaelis-menten-constant
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-inhibitor-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-substrate-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-enzyme-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-ph
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-temperature
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS colorimetry
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS measuring-enzyme-activity
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS how-enzymes-work
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzyme-action
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
4-cell-membranes-and-transport16 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-surface-area
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-diffusion
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS active-transport
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS diffusion
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS cell-signalling
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-cell-surface-membrane
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS components-of-cell-surface-membranes
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-fluid-mosaic-model
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
5-the-mitotic-cell-cycle8 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS the-stages-of-mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS how-tumours-form
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-stem-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-telomeres-
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-cell-cycle
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS chromosome-structure
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
6-nucleic-acids-and-protein-synthesis9 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS transcription
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS constructing-polypeptides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS the-universal-genetic-code
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS from-gene-to-polypeptide
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-rna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS semi-conservative-dna-replication
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-dna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS nucleotides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
7-transport-in-plants11 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS the-sucrose-loading-mechanism
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS movement-in-the-phloem
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS xerophytic-plant-leaf-adaptations
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-the-transpiration-pull
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS transpiration-in-plants
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-mineral-ion-transport-in-plants
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS phloem-sieve-tube-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-vessels-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-and-phloem-distribution
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS plant-transverse-sections
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
8-transport-in-mammals16 主题
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-cardiac-cycle
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-walls-of-the-heart
-
8-3-the-heart AS structure-of-the-heart
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-bohr-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-oxygen-dissociation-curve
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS plasma-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-chloride-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS red-blood-cells-haemoglobin-and-oxygen
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-tissue-fluid-and-lymph
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-role-of-water-in-circulation
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS cells-of-the-blood
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-vessels-structures-and-functions
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS observing-and-drawing-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-main-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS circulatory-systems
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
9-gas-exchange6 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS structures-and-functions-of-the-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-structures
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS distribution-of-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
10-infectious-diseases6 主题
-
11-immunity10 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS how-vaccines-work
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS types-of-immunity
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS uses-of-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS making-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS antibodies
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS memory-cells-and-immunity
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS primary-immune-response
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS antigens
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS phagocytes
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS plasma-and-carbon-dioxide
Exam code:9700
Plasma & carbon dioxide
-
Waste carbon dioxide produced during respiration diffuses from the tissues into the blood
-
This waste carbon dioxide is transported around the body in different ways:
-
Around 5 % of carbon dioxide dissolves directly in the blood plasma
-
Around 10 % of carbon dioxide is bound to haemoglobin as carbaminohaemoglobin
-
Around 85 % of carbon dioxide is found in the blood plasma in the form of hydrogen carbonate ions (HCO3–)
-
Carbon dioxide in the plasma
-
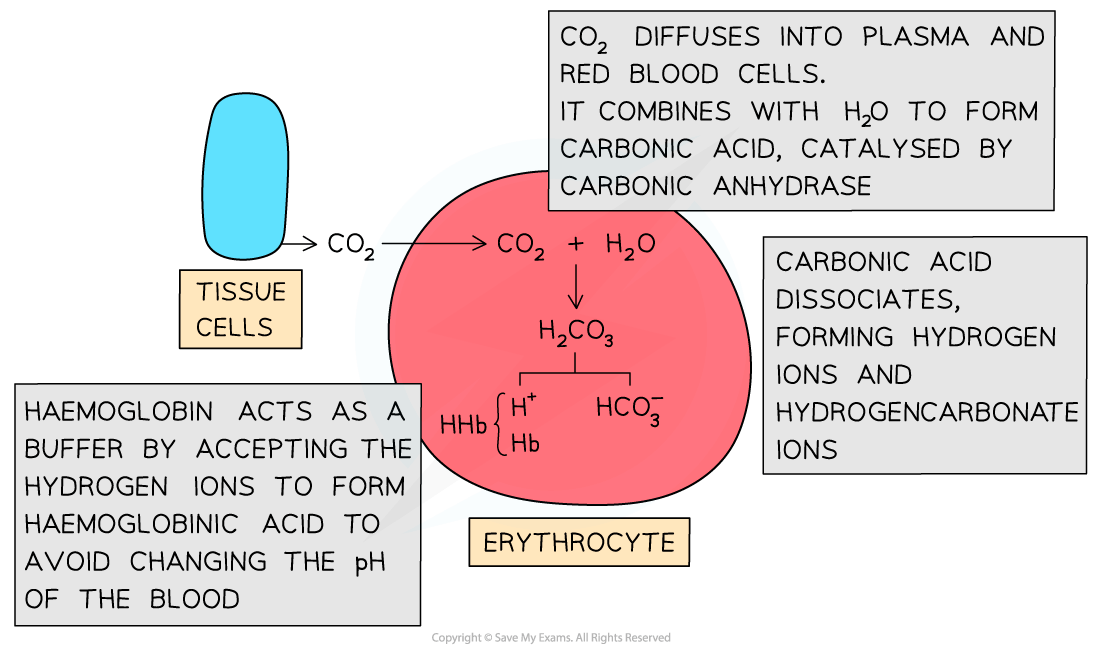
Carbon dioxide released as a waste product from respiring cells diffuses into the cytoplasm of red blood cells
-
Inside red blood cells, carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3)
CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2CO3
-
Red blood cells contain the enzyme carbonic anhydrase which catalyses the reaction between carbon dioxide and water
-
Without carbonic anhydrase this reaction proceeds very slowly
-
-
The plasma contains very little carbonic anhydrase hence H2CO3 forms more slowly in plasma than in the cytoplasm of red blood cells
-
Carbonic acid dissociates readily into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydrogen carbonate ions (HCO3–)
H2CO3 ⇌ HCO3– + H+
-
Hydrogen ions can combine with haemoglobin, forming haemoglobinic acid and preventing the H+ ions from lowering the pH of the red blood cell
-
Haemoglobin is said to act as a buffer in this situation
-
-
The hydrogen carbonate ions diffuse out of the red blood cells into the plasma to be transported in solution
Worked Example
Explain how carbon dioxide is transported in the form of hydrogen carbonate ions.
-
Carbon dioxide diffuses down a concentration gradient from respiring cells into the plasma, and diffuses again into red blood cells
-
In the red blood cells some carbon dioxide combines with water to form carbonic acid, in a reaction catalysed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase
-
Carbonic acid dissociates to form hydrogen carbonate ions and hydrogen ions
-
The hydrogen carbonate ions diffuse out of the red blood cells into the plasma, where they are transported to the lungs

Responses