Biology AS CIE
-
1-cell-structure10 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS prokaryotic-v-eukaryotic-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS the-vital-role-of-atp
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS animal-and-plant-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS eukaryotic-cell-structures-and-functions
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS calculating-actual-size
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS resolution-and-magnification
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS eyepiece-graticules-and-stage-micrometers
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS magnification-calculations
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
2-biological-molecules19 主题
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
2-4-water AS the-role-of-water-in-living-organisms
-
2-3-proteins AS collagen
-
2-3-proteins AS haemoglobin
-
2-3-proteins AS globular-and-fibrous-proteins
-
2-3-proteins AS protein-shape
-
2-3-proteins AS the-four-levels-of-protein-structure
-
2-3-proteins AS amino-acids-and-the-peptide-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS phospholipids
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS triglycerides
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS cellulose
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS starch-and-glycogen
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS the-glycosidic-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS reducing-and-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS covalent-bonds-in-polymers
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS biological-molecules-key-terms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS testing-for-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS the-benedicts-test
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS biological-molecule-tests
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
3-enzymes13 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-inhibitors
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS vmax-and-the-michaelis-menten-constant
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-inhibitor-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-substrate-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-enzyme-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-ph
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-temperature
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS colorimetry
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS measuring-enzyme-activity
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS how-enzymes-work
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzyme-action
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
4-cell-membranes-and-transport16 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-surface-area
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-diffusion
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS active-transport
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS diffusion
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS cell-signalling
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-cell-surface-membrane
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS components-of-cell-surface-membranes
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-fluid-mosaic-model
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
5-the-mitotic-cell-cycle8 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS the-stages-of-mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS how-tumours-form
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-stem-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-telomeres-
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-cell-cycle
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS chromosome-structure
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
6-nucleic-acids-and-protein-synthesis9 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS transcription
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS constructing-polypeptides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS the-universal-genetic-code
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS from-gene-to-polypeptide
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-rna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS semi-conservative-dna-replication
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-dna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS nucleotides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
7-transport-in-plants11 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS the-sucrose-loading-mechanism
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS movement-in-the-phloem
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS xerophytic-plant-leaf-adaptations
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-the-transpiration-pull
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS transpiration-in-plants
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-mineral-ion-transport-in-plants
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS phloem-sieve-tube-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-vessels-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-and-phloem-distribution
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS plant-transverse-sections
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
8-transport-in-mammals16 主题
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-cardiac-cycle
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-walls-of-the-heart
-
8-3-the-heart AS structure-of-the-heart
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-bohr-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-oxygen-dissociation-curve
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS plasma-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-chloride-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS red-blood-cells-haemoglobin-and-oxygen
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-tissue-fluid-and-lymph
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-role-of-water-in-circulation
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS cells-of-the-blood
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-vessels-structures-and-functions
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS observing-and-drawing-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-main-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS circulatory-systems
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
9-gas-exchange6 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS structures-and-functions-of-the-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-structures
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS distribution-of-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
10-infectious-diseases6 主题
-
11-immunity10 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS how-vaccines-work
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS types-of-immunity
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS uses-of-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS making-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS antibodies
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS memory-cells-and-immunity
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS primary-immune-response
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS antigens
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS phagocytes
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS xerophytic-plant-leaf-adaptations
Exam code:9700
Xerophytic plant leaf adaptations
-
Xerophytes (from the Greek xero for ‘dry’) are plants that are adapted to dry and arid conditions
-
Xerophytes have physiological and structural (xeromorphic) adaptations to maximise water conservation
|
Xerophytic Adaptations of Leaves |
Effect of Adaptation |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Fleshy succulent leaves |
Store of water for times of low availability |
Bryophyllum |
|
“Hinge cells” shrink when flaccid |
Causes leaves to roll, exposing thick cuticle to the air and creating a humid space in the middle of the rolled leaf |
Marram Grass (Ammophila arenaria) |
|
Leaves reduced to scales, spines, needles. Leaves curled, rolled or folded when flaccid |
Reduced transpiration due to reduced surface area exposed |
Cactus (Opuntia) Marram Grass (Ammophila arenaria) |
|
Stomata closed during daylight Stomata open during night |
Daytime water loss minimised Carbon dioxide fixed at night |
Pineapple, Yucca, American Aloe |
|
Sunken stomata and leaf surface covered in fine hairs |
Water loss minimised as moist air is trapped and diffusion gradient reduced |
Pine, Nerium |
|
Reduced numbers of stomata |
Less water loss as fewer pores |
Nerium, Prickly pear |
|
Thick waxy cuticles |
Water loss reduced via cuticle distance |
Pine, Prickly pear |
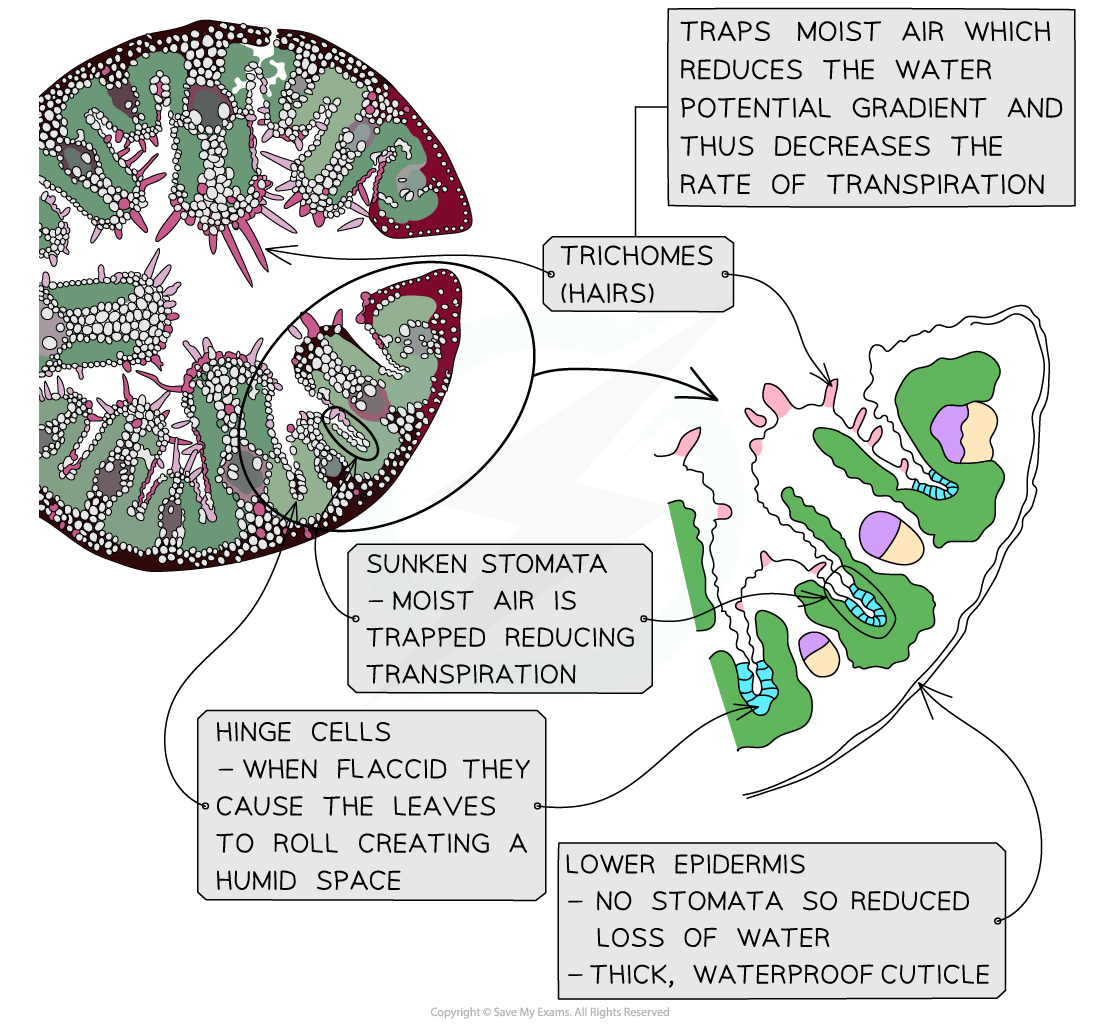
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will be expected to make annotated drawings of transverse sections of leaves from xerophytic plants to explain how they are adapted.
Remember not all leaves will have every feature listed above so if you are looking at an unfamiliar image consider whether the adaptations you can see will help reduce water being lost from the leaf.

Responses