Biology AS CIE
-
1-cell-structure10 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS prokaryotic-v-eukaryotic-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS the-vital-role-of-atp
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS animal-and-plant-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS eukaryotic-cell-structures-and-functions
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS calculating-actual-size
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS resolution-and-magnification
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS eyepiece-graticules-and-stage-micrometers
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS magnification-calculations
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
2-biological-molecules19 主题
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
2-4-water AS the-role-of-water-in-living-organisms
-
2-3-proteins AS collagen
-
2-3-proteins AS haemoglobin
-
2-3-proteins AS globular-and-fibrous-proteins
-
2-3-proteins AS protein-shape
-
2-3-proteins AS the-four-levels-of-protein-structure
-
2-3-proteins AS amino-acids-and-the-peptide-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS phospholipids
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS triglycerides
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS cellulose
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS starch-and-glycogen
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS the-glycosidic-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS reducing-and-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS covalent-bonds-in-polymers
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS biological-molecules-key-terms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS testing-for-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS the-benedicts-test
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS biological-molecule-tests
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
3-enzymes13 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-inhibitors
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS vmax-and-the-michaelis-menten-constant
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-inhibitor-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-substrate-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-enzyme-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-ph
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-temperature
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS colorimetry
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS measuring-enzyme-activity
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS how-enzymes-work
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzyme-action
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
4-cell-membranes-and-transport16 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-surface-area
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-diffusion
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS active-transport
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS diffusion
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS cell-signalling
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-cell-surface-membrane
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS components-of-cell-surface-membranes
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-fluid-mosaic-model
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
5-the-mitotic-cell-cycle8 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS the-stages-of-mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS how-tumours-form
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-stem-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-telomeres-
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-cell-cycle
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS chromosome-structure
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
6-nucleic-acids-and-protein-synthesis9 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS transcription
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS constructing-polypeptides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS the-universal-genetic-code
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS from-gene-to-polypeptide
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-rna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS semi-conservative-dna-replication
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-dna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS nucleotides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
7-transport-in-plants11 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS the-sucrose-loading-mechanism
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS movement-in-the-phloem
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS xerophytic-plant-leaf-adaptations
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-the-transpiration-pull
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS transpiration-in-plants
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-mineral-ion-transport-in-plants
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS phloem-sieve-tube-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-vessels-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-and-phloem-distribution
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS plant-transverse-sections
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
8-transport-in-mammals16 主题
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-cardiac-cycle
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-walls-of-the-heart
-
8-3-the-heart AS structure-of-the-heart
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-bohr-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-oxygen-dissociation-curve
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS plasma-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-chloride-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS red-blood-cells-haemoglobin-and-oxygen
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-tissue-fluid-and-lymph
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-role-of-water-in-circulation
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS cells-of-the-blood
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-vessels-structures-and-functions
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS observing-and-drawing-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-main-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS circulatory-systems
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
9-gas-exchange6 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS structures-and-functions-of-the-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-structures
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS distribution-of-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
10-infectious-diseases6 主题
-
11-immunity10 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS how-vaccines-work
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS types-of-immunity
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS uses-of-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS making-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS antibodies
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS memory-cells-and-immunity
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS primary-immune-response
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS antigens
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS phagocytes
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
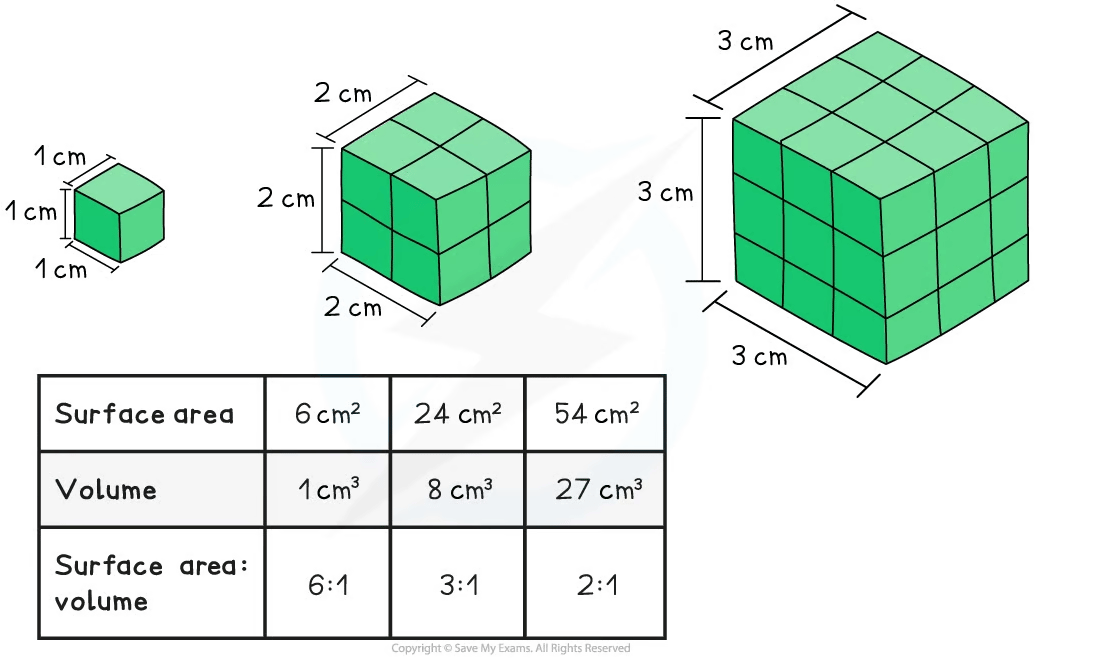
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS surface-area-to-volume-ratios
Exam code:9700
Principles of SA:V
-
Surface area and volume are both very important factors in the exchange of materials in organisms
-
As the surface area and volume of an organism increase (and therefore the overall ‘size’ of the organism increases), the surface area : volume ratio decreases
-
This is because volume increases more rapidly than surface area as size increases
Importance of a high surface area to volume ratio
-
Having a high surface area to volume ratio increases the ability of a biological system to perform the following important functions
-
Obtaining necessary resources eg, oxygen, glucose, amino acids
-
Eliminating waste products eg. carbon dioxide, urea
-
Acquiring or dissipating thermal energy (heat)
-
Otherwise exchanging chemicals and energy with the surroundings eg. absorbing hormones at the cell surface in the hormone’s target organ
-
|
|
Cube |
Cuboid |
Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Diagram |
 |
 |
 |
|
Surface Area |
6s2 |
2lh + 2lw + 2wh |
1x rectangle = 2πrh 2x circular ends = 2πr2 SA = 2πrh + 2πr2 |
|
Volume |
s3 |
l × w × h |
πr2h |
|
Example |
If s = 1 cm then SA = (1×1)×6 SA = 6cm2 V = s3 = 13 =1cm3 ∴ SA:V ratio = 6:1 |
If l = 4cm, w = 2cm, h = 1cm, then SA = 2((4×1)+(4×2)+(2×1)) = 28cm2 V = 4 × 2 × 1 = 8cm3 ∴ SA:V ratio = 28:8 = 3.5:1 |
If r = 2 cm and h = 6cm, then SA = 2πrh + 2πr2 = 8π +24π = 32π cm2 V = π(2)2 × 6 = 24π cm2 ∴ SA : V ratio = 32 : 24 = 1.33:1 |
Worked Example
Calculate the surface area-to-volume ratios of the two following microorganisms:
-
A bacterial cell from the species Staphylococcus aureus; you can assume that each cell is a cube with side length of 800 nm (8 × 10-9 m)
-
A bacterial cell from the species Bacillus subtilis; these are rod-shaped cells which you can assume to be cylindrical in shape. They are 5 µm long and 1 µm in diameter
Comment on your calculated answers.
Solution
1. For the Staphylococcus aureus cell: side length = 800 nm
Convert this value into µm by dividing by 1000
Surface area of cube = 6(s2)
= 6 × (0.8 × 0.8) = 3.84 µm2
Volume = 0.8 × 0.8 × 0.8
= 0.512 µm3
A ratio is one number divided by another with the larger number divided by the smaller number, so
<img alt=”SA colon straight V space ratio space equals space fraction numerator 3.84 over denominator 0.512 end fraction equals fraction numerator 7.5 over denominator 1 end fraction equals 7.5 space colon space 1 space open parentheses or space simply space 7.5 close parentheses” data-mathml='<math style=”font-family:Arial” ><semantics><mrow><mi>SA</mi><mo>:</mo><mi mathvariant=”normal”>V</mi><mo> </mo><mi>ratio</mi><mo> </mo><mo>=</mo><mo> </mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>3</mn><mo>.</mo><mn>84</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>0</mn><mo>.</mo><mn>512</mn></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>7</mn><mo>.</mo><mn>5</mn></mrow><mn>1</mn></mfrac><mo>=</mo><mn>7</mn><mo>.</mo><mn>5</mn><mo> </mo><mo>:</mo><mo> </mo><mn>1</mn><mo> </mo><mfenced><mrow><mi>or</mi><mo> </mo><mi>simply</mi><mo> </mo><mn>7</mn><mo>.</mo><mn>5</mn></mrow></mfenced></mrow><annotation encoding=”application/vnd.wiris.mtweb-params+json”>{“language”:”en”,”fontFamily”:”Times New Roman”,”fontSize”:”18″,”autoformat”:true}</annotation></semantics></math>’ height=”49″ role=”math” src=”data:image/svg+xml;charset=utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F2000%2Fsvg%22%20xmlns%3Awrs%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wiris.com%2Fxml%2Fmathml-extension%22%20height%3D%2249%22%20width%3D%22410%22%20wrs%3Abaseline%3D%2231%22%3E%3C!–MathML%3A%20%3Cmath%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.or

Responses