Biology AS CIE
-
1-cell-structure10 主题
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS prokaryotic-v-eukaryotic-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS the-vital-role-of-atp
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS animal-and-plant-cells
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS eukaryotic-cell-structures-and-functions
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS calculating-actual-size
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS resolution-and-magnification
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS eyepiece-graticules-and-stage-micrometers
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS magnification-calculations
-
1-1-the-microscope-in-cell-studies AS the-microscope-in-cell-studies
-
1-2-cells-as-the-basic-units-of-living-organisms AS viruses
-
2-biological-molecules19 主题
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
2-4-water AS the-role-of-water-in-living-organisms
-
2-3-proteins AS collagen
-
2-3-proteins AS haemoglobin
-
2-3-proteins AS globular-and-fibrous-proteins
-
2-3-proteins AS protein-shape
-
2-3-proteins AS the-four-levels-of-protein-structure
-
2-3-proteins AS amino-acids-and-the-peptide-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS phospholipids
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS triglycerides
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS cellulose
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS starch-and-glycogen
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS the-glycosidic-bond
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS reducing-and-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS covalent-bonds-in-polymers
-
2-2-carbohydrates-and-lipids AS biological-molecules-key-terms
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS testing-for-non-reducing-sugars
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS the-benedicts-test
-
2-1-testing-for-biological-molecules AS biological-molecule-tests
-
2-4-water AS water-and-the-hydrogen-bond
-
3-enzymes13 主题
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-inhibitors
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS vmax-and-the-michaelis-menten-constant
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-inhibitor-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-substrate-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-enzyme-concentration
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-ph
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS rate-temperature
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS colorimetry
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS measuring-enzyme-activity
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS how-enzymes-work
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzyme-action
-
3-1-mode-of-action-of-enzymes AS enzymes
-
3-2-factors-that-affect-enzyme-action AS enzyme-activity-immobilised-v-free
-
4-cell-membranes-and-transport16 主题
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-animals
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-plant-cells
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS estimating-water-potential-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-surface-area
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS surface-area-to-volume-ratios
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-diffusion
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS investigating-transport-processes-in-plants
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS endocytosis-and-exocytosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS active-transport
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS diffusion
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS cell-signalling
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-cell-surface-membrane
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS components-of-cell-surface-membranes
-
4-1-fluid-mosaic-membranes AS the-fluid-mosaic-model
-
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS comparing-osmosis-in-plants-and-animals
-
5-the-mitotic-cell-cycle8 主题
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS the-stages-of-mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS how-tumours-form
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-stem-cells
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-role-of-telomeres-
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS the-cell-cycle
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS mitosis
-
5-1-replication-and-division-of-nuclei-and-cells AS chromosome-structure
-
5-2-chromosome-behaviour-in-mitosis AS observing-mitosis
-
6-nucleic-acids-and-protein-synthesis9 主题
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS transcription
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS constructing-polypeptides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS the-universal-genetic-code
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS from-gene-to-polypeptide
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-rna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS semi-conservative-dna-replication
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS the-structure-of-dna
-
6-1-structure-of-nucleic-acids-and-replication-of-dna AS nucleotides
-
6-2-protein-synthesis AS gene-mutations
-
7-transport-in-plants11 主题
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS the-sucrose-loading-mechanism
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS movement-in-the-phloem
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS xerophytic-plant-leaf-adaptations
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-the-transpiration-pull
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS transpiration-in-plants
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS water-and-mineral-ion-transport-in-plants
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS phloem-sieve-tube-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-vessels-elements
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS xylem-and-phloem-distribution
-
7-1-structure-of-transport-tissues AS plant-transverse-sections
-
7-2-transport-mechanisms AS phloem-mass-flow
-
8-transport-in-mammals16 主题
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-cardiac-cycle
-
8-3-the-heart AS the-walls-of-the-heart
-
8-3-the-heart AS structure-of-the-heart
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-bohr-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-oxygen-dissociation-curve
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS plasma-and-carbon-dioxide
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS the-chloride-shift
-
8-2-transport-of-oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide AS red-blood-cells-haemoglobin-and-oxygen
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-tissue-fluid-and-lymph
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-role-of-water-in-circulation
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS cells-of-the-blood
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS blood-vessels-structures-and-functions
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS observing-and-drawing-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS the-main-blood-vessels
-
8-1-the-circulatory-system AS circulatory-systems
-
8-3-the-heart AS heart-action
-
9-gas-exchange6 主题
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS structures-and-functions-of-the-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-structures
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS recognising-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS distribution-of-tissues
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
9-1-the-gas-exchange-system AS gas-exchange-processes
-
10-infectious-diseases6 主题
-
11-immunity10 主题
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS how-vaccines-work
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS types-of-immunity
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS uses-of-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS making-monoclonal-antibodies
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS antibodies
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS memory-cells-and-immunity
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS primary-immune-response
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS antigens
-
11-1-the-immune-system AS phagocytes
-
11-2-antibodies-and-vaccination AS vaccination-to-control-disease
4-2-movement-into-and-out-of-cells AS osmosis-in-animals
Exam code:9700
Osmosis: animal cells
-
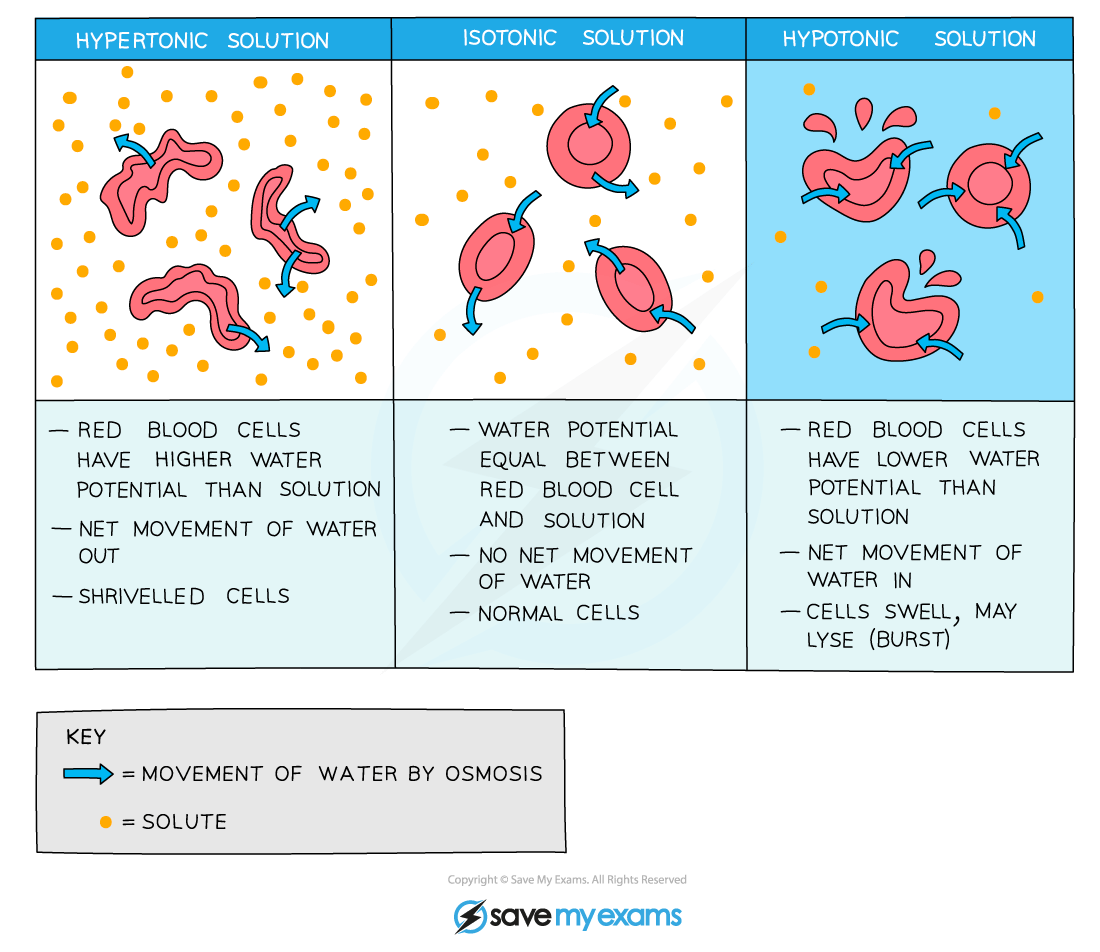
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentrated solution), through a selectively permeable membrane
-
Like plant cells, animal cells can also lose and gain water as a result of osmosis
-
Because animal cells do not have a supporting cell wall (unlike plant cells), the results of this loss or gain of water on the cell are more severe
-
For example, if an animal cell is placed in a solution with a lower water potential than the cell (such as a concentrated sucrose solution), water will leave the cell through its selectively permeable cell surface membrane by osmosis
-
This will cause the cell to shrink and shrivel up
-
This occurs when the cell is in a hypertonic environment (the solution outside of the cell has a higher solute concentration than the inside of the cell)
-
-
Conversely, if an animal cell is placed in pure water or a dilute solution, water will enter the cell through its selectively permeable cell surface membrane by osmosis, as the pure water or dilute solution has a higher water potential
-
The cell will continue to gain water by osmosis until the cell membrane is stretched too far and the cell bursts (cytolysis), as it has no cell wall to withstand the increased pressure created
-
This occurs when the cell is in a hypotonic environment (the solution outside of the cell has a lower solute concentration than the inside of the cell)
-
-
-
This is why a constant water potential must be maintained inside the bodies of animals
-
If an animal cell is in an isotonic environment (the solution outside of the cell has the same solute concentration as the inside of the cell), the movement of water molecules into and out of the cell occurs at the same rate (no net movement of water)
-
This means there is no change to the cells
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful with your scientific terminology—animal cells do not plasmolyse because they do not have a cell wall.
In a solution with a lower water potential than the cell itself, animal cells will shrink.
Plasmolysis only occurs in plant cells.

Responses