Biology AS AQA
-
1-1-biological-molecules-carbohydrates11 主题
-
1-1-1-biological-molecules-key-terms
-
1-1-2-biological-molecules-reactions
-
1-1-3-monosaccharides
-
1-1-4-glucose
-
1-1-5-the-glycosidic-bond
-
1-1-6-chromatography-monosaccharides
-
1-1-7-disaccharides
-
1-1-8-starch-and-glycogen
-
1-1-9-cellulose
-
1-1-10-biochemical-tests-sugars-and-starch
-
1-1-11-finding-the-concentration-of-glucose
-
1-1-1-biological-molecules-key-terms
-
1-2-biological-molecules-lipids3 主题
-
1-3-biological-molecules-proteins5 主题
-
1-4-proteins-enzymes12 主题
-
1-4-1-many-proteins-are-enzymes
-
1-4-2-enzyme-specificity
-
1-4-3-how-enzymes-work
-
1-4-4-required-practical-measuring-enzyme-activity
-
1-4-5-drawing-a-graph-for-enzyme-rate-experiments
-
1-4-6-using-a-tangent-to-find-initial-rate-of-reaction
-
1-4-7-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-temperature
-
1-4-8-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-ph
-
1-4-10-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-enzyme-concentration
-
1-4-11-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-substrate-concentration
-
1-4-12-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-inhibitors
-
1-4-14-control-of-variables-and-uncertainty
-
1-4-1-many-proteins-are-enzymes
-
1-5-nucleic-acids-structure-and-dna-replication8 主题
-
1-5-2-nucleotide-structure-and-the-phosphodiester-bond
-
1-5-3-dna-structure-and-function
-
1-5-4-rna-structure-and-function
-
1-5-5-ribosomes
-
1-5-6-the-origins-of-research-on-the-genetic-code
-
1-5-8-the-process-of-semi-conservative-replication
-
1-5-9-calculating-the-frequency-of-nucleotide-bases
-
1-5-10-the-watson-crick-model
-
1-5-2-nucleotide-structure-and-the-phosphodiester-bond
-
1-6-atp-water-and-inorganic-ions4 主题
-
2-1-cell-structure7 主题
-
2-2-the-microscope-in-cell-studies4 主题
-
2-3-cell-division-in-eukaryotic-and-prokaryotic-cells8 主题
-
2-4-cell-membranes-and-transport9 主题
-
2-4-1-the-structure-of-cell-membranes
-
2-4-3-the-cell-surface-membrane
-
2-4-4-diffusion
-
2-4-5-osmosis
-
2-4-7-osmosis-in-animal-cells
-
2-4-9-required-practical-investigating-water-potential
-
2-4-10-active-transport-and-co-transport
-
2-4-11-adaptations-for-rapid-transport
-
2-4-13-required-practical-factors-affecting-membrane-permeability
-
2-4-1-the-structure-of-cell-membranes
-
2-5-cell-recognition-and-the-immune-system7 主题
-
2-6-vaccines-disease-and-monoclonal-antibodies6 主题
-
3-1-adaptations-for-gas-exchange6 主题
-
3-2-human-gas-exchange14 主题
-
3-2-5-the-alveolar-epithelium
-
3-2-1-the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
3-2-2-dissecting-the-gas-exchange-system
-
3-2-3-microscopy-and-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
3-2-4-investigating-gas-exchange
-
3-5-5-investigating-heart-rate
-
3-5-6-blood-vessels
-
3-5-7-capillaries-and-tissue-fluid
-
3-5-8-cardiovascular-disease-data
-
3-2-10-risk-factor-data
-
3-2-11-correlations-and-causal-relationships
-
3-2-6-ventilation-and-gas-exchange
-
3-2-8-the-effects-of-lung-disease
-
3-2-9-pollution-and-smoking-data
-
3-2-5-the-alveolar-epithelium
-
3-3-digestion-and-absorption5 主题
-
3-4-mass-transport-in-animals6 主题
-
3-5-the-circulatory-system-in-animals4 主题
-
3-6-mass-transport-in-plants6 主题
-
4-1-dna-genes-and-chromosomes10 主题
-
4-2-dna-and-protein-synthesis3 主题
-
4-3-genetic-diversity-mutations-and-meiosis7 主题
-
4-4-genetic-diversity-and-adaptation6 主题
-
4-5-species-and-taxonomy4 主题
-
4-6-biodiversity9 主题
4-6-8-mean-and-standard-deviation
Exam code:7401
Calculating mean values & standard deviation
-
Descriptive statistics are invaluable when interpreting data from experiments
-
Some experiments have thousands or millions of data values/observations, and descriptive statistics allow for sample data to be summarised in a concise manner
Mean
-
A mean value is what is usually meant by “an average” in biology
mean = sum of all measurements ÷ number of measurements
-
Problems with the mean occur when a dataset contains extreme, or outlying values, which can make the mean too high or too low to represent the data
-
The mean is sometimes referred to as X̄ in calculations
Worked Example
Fifteen rats were timed to see how long it took them to reach the end of a maze puzzle. Their times, in seconds, are given below.
Calculate the mean time.
12, 10, 15, 14, 17,
11, 12, 13, 9, 21,
14, 20, 19, 16, 23
Answer:
Step 1: calculate the mean
12 + 10 + 15 + 14 + 17 + 11 + 12 + 13 + 9 + 21 + 14 + 20 + 19 + 16 + 23 = 226
226 ÷ 15 = 15.067
Step 2: round to 3 significant figures
Mean (X̄) = 15.1 seconds
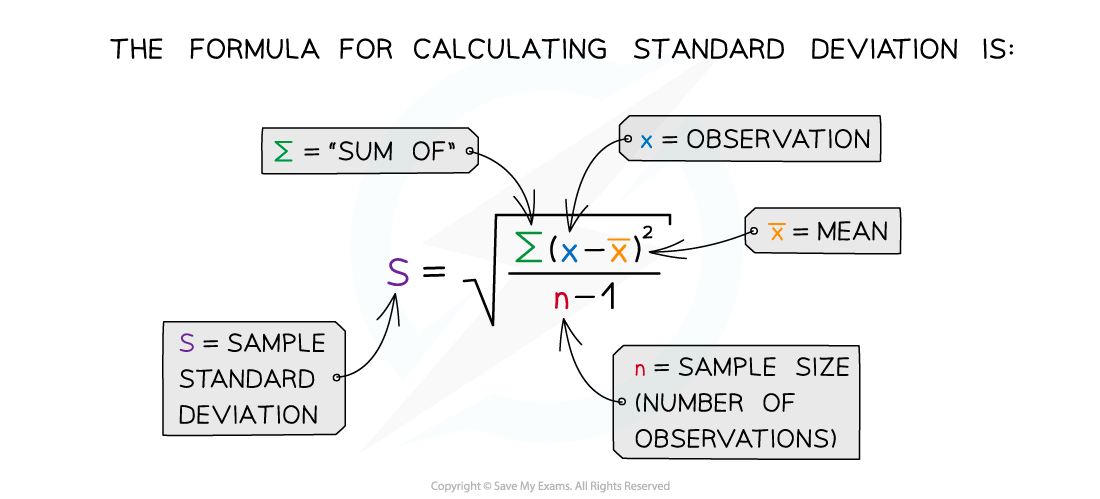
Standard deviation
-
The mean is a more informative statistic when it is provided alongside standard deviation
-
Standard deviation measures the spread of data around the mean value
-
It is useful when comparing consistency between different data sets
-
-
The mean must be calculated before working out the standard deviation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will not be required to calculate standard deviations in written papers, but you may need to calculate the standard deviation as part of practical work and investigations. You must understand what the standard deviation tells you about a data set as you may be asked to interpret mean values and their standard deviations.
Worked Example
The ear lengths of a population of rabbits were measured:
|
Ear length (mm) |
62, 60, 59, 61, 60, 58, 59, 60, 57, 56, 59, 58, 60, 59, 57 |
Calculate the mean and standard deviation.
Step 1: calculate the mean
mean = 885 ÷ 15 = 59 mm
Step 2: find the difference between each value and the mean
-
Subtract the mean from each value to find the difference
-
Example:
62 – 59 = 3
Step 3: square each difference (to remove any negative values)
-
Example:
32 = 9
Step 4: total the differences
|
Difference between value and mean (x – x̄) |
Difference between value and mean squared (x – x̄)2 |
|---|---|
|
62 – 59 = 3 |
9 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
|
61 – 59 = 2 |
4 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
|
58 – 59 = -1 |
1 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
|
57 – 59 = -2 |
4 |
|
56 – 59 = -3 |
9 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
|
58 – 59 = -1 |
1 |
|
60 – 59 = 1 |
1 |
|
59 – 59 = 0 |
0 |
|
57 – 59 = -2 |
4 |
|
Sum of (x – x̄)2 |
36 |
Step 5: divide the total by (n-1) to get value A
36 ÷ (15 – 1)
= 36 ÷ 14
= 2.571
Step 6: determine the square root of value A
= 1.604
Standard deviation = 1.60
This value is small compared to the mean value (59 mm), indicating that there is little spread around the mean.

Responses