Biology AS AQA
-
1-1-biological-molecules-carbohydrates11 主题
-
1-1-1-biological-molecules-key-terms
-
1-1-2-biological-molecules-reactions
-
1-1-3-monosaccharides
-
1-1-4-glucose
-
1-1-5-the-glycosidic-bond
-
1-1-6-chromatography-monosaccharides
-
1-1-7-disaccharides
-
1-1-8-starch-and-glycogen
-
1-1-9-cellulose
-
1-1-10-biochemical-tests-sugars-and-starch
-
1-1-11-finding-the-concentration-of-glucose
-
1-1-1-biological-molecules-key-terms
-
1-2-biological-molecules-lipids3 主题
-
1-3-biological-molecules-proteins5 主题
-
1-4-proteins-enzymes12 主题
-
1-4-1-many-proteins-are-enzymes
-
1-4-2-enzyme-specificity
-
1-4-3-how-enzymes-work
-
1-4-4-required-practical-measuring-enzyme-activity
-
1-4-5-drawing-a-graph-for-enzyme-rate-experiments
-
1-4-6-using-a-tangent-to-find-initial-rate-of-reaction
-
1-4-7-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-temperature
-
1-4-8-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-ph
-
1-4-10-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-enzyme-concentration
-
1-4-11-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-substrate-concentration
-
1-4-12-limiting-factors-affecting-enzymes-inhibitors
-
1-4-14-control-of-variables-and-uncertainty
-
1-4-1-many-proteins-are-enzymes
-
1-5-nucleic-acids-structure-and-dna-replication8 主题
-
1-5-2-nucleotide-structure-and-the-phosphodiester-bond
-
1-5-3-dna-structure-and-function
-
1-5-4-rna-structure-and-function
-
1-5-5-ribosomes
-
1-5-6-the-origins-of-research-on-the-genetic-code
-
1-5-8-the-process-of-semi-conservative-replication
-
1-5-9-calculating-the-frequency-of-nucleotide-bases
-
1-5-10-the-watson-crick-model
-
1-5-2-nucleotide-structure-and-the-phosphodiester-bond
-
1-6-atp-water-and-inorganic-ions4 主题
-
2-1-cell-structure7 主题
-
2-2-the-microscope-in-cell-studies4 主题
-
2-3-cell-division-in-eukaryotic-and-prokaryotic-cells8 主题
-
2-4-cell-membranes-and-transport9 主题
-
2-4-1-the-structure-of-cell-membranes
-
2-4-3-the-cell-surface-membrane
-
2-4-4-diffusion
-
2-4-5-osmosis
-
2-4-7-osmosis-in-animal-cells
-
2-4-9-required-practical-investigating-water-potential
-
2-4-10-active-transport-and-co-transport
-
2-4-11-adaptations-for-rapid-transport
-
2-4-13-required-practical-factors-affecting-membrane-permeability
-
2-4-1-the-structure-of-cell-membranes
-
2-5-cell-recognition-and-the-immune-system7 主题
-
2-6-vaccines-disease-and-monoclonal-antibodies6 主题
-
3-1-adaptations-for-gas-exchange6 主题
-
3-2-human-gas-exchange14 主题
-
3-2-5-the-alveolar-epithelium
-
3-2-1-the-human-gas-exchange-system
-
3-2-2-dissecting-the-gas-exchange-system
-
3-2-3-microscopy-and-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
3-2-4-investigating-gas-exchange
-
3-5-5-investigating-heart-rate
-
3-5-6-blood-vessels
-
3-5-7-capillaries-and-tissue-fluid
-
3-5-8-cardiovascular-disease-data
-
3-2-10-risk-factor-data
-
3-2-11-correlations-and-causal-relationships
-
3-2-6-ventilation-and-gas-exchange
-
3-2-8-the-effects-of-lung-disease
-
3-2-9-pollution-and-smoking-data
-
3-2-5-the-alveolar-epithelium
-
3-3-digestion-and-absorption5 主题
-
3-4-mass-transport-in-animals6 主题
-
3-5-the-circulatory-system-in-animals4 主题
-
3-6-mass-transport-in-plants6 主题
-
4-1-dna-genes-and-chromosomes10 主题
-
4-2-dna-and-protein-synthesis3 主题
-
4-3-genetic-diversity-mutations-and-meiosis7 主题
-
4-4-genetic-diversity-and-adaptation6 主题
-
4-5-species-and-taxonomy4 主题
-
4-6-biodiversity9 主题
1-4-6-using-a-tangent-to-find-initial-rate-of-reaction
Exam code:7401
Using a tangent to find the initial rate of reaction
-
For linear graphs (i.e. graphs with a straight line), the gradient is the same throughout
-
This makes it easy to calculate the rate of change (rate of change = change ÷ time)
-
-
The initial rate of reaction is the rate of reaction at the start of the line (i.e. where time = 0)
-
However, many enzyme rate experiments produce non-linear graphs (i.e. graphs with a curved line), meaning they have an ever-changing gradient
-
They are shaped this way because the reaction rate is changing over time
-
-
In these cases, a tangent can be used to find the reaction rate at any one point on the graph:
Worked Example
The graph below shows the results of an enzyme-catalysed reaction. Using this graph, calculate the initial rate of reaction.
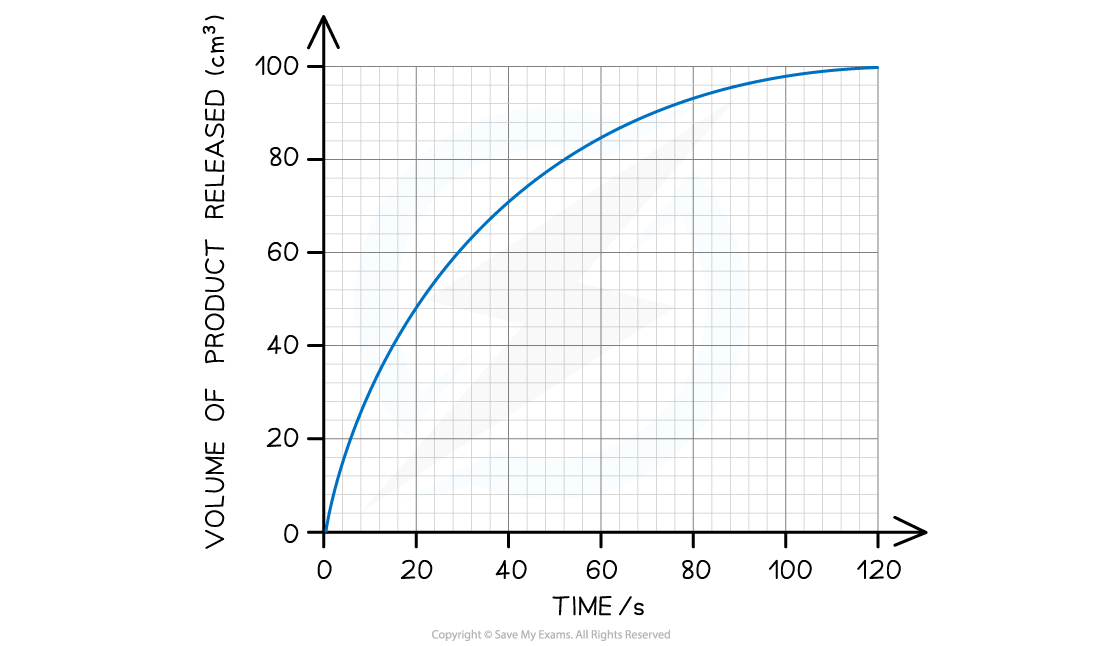
Step 1: Estimate the extrapolated curve of the graph
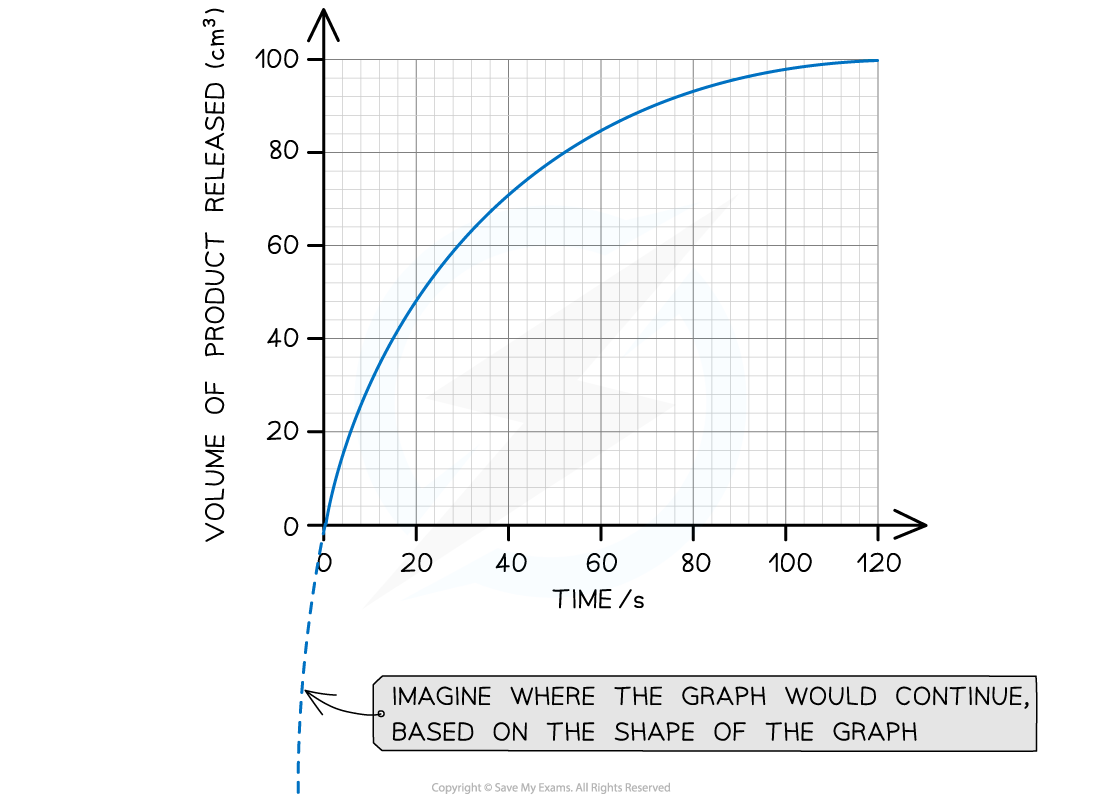
Step 2: Find the tangent to the curve at 0 seconds (the start of the reaction)
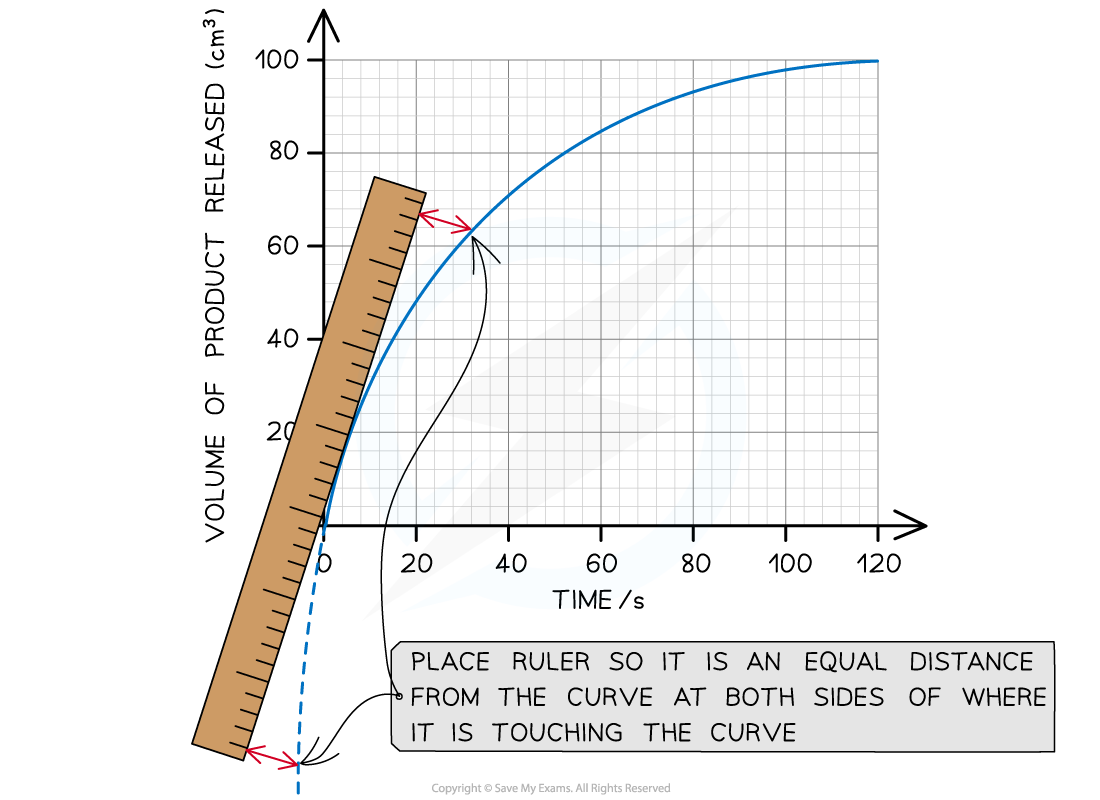
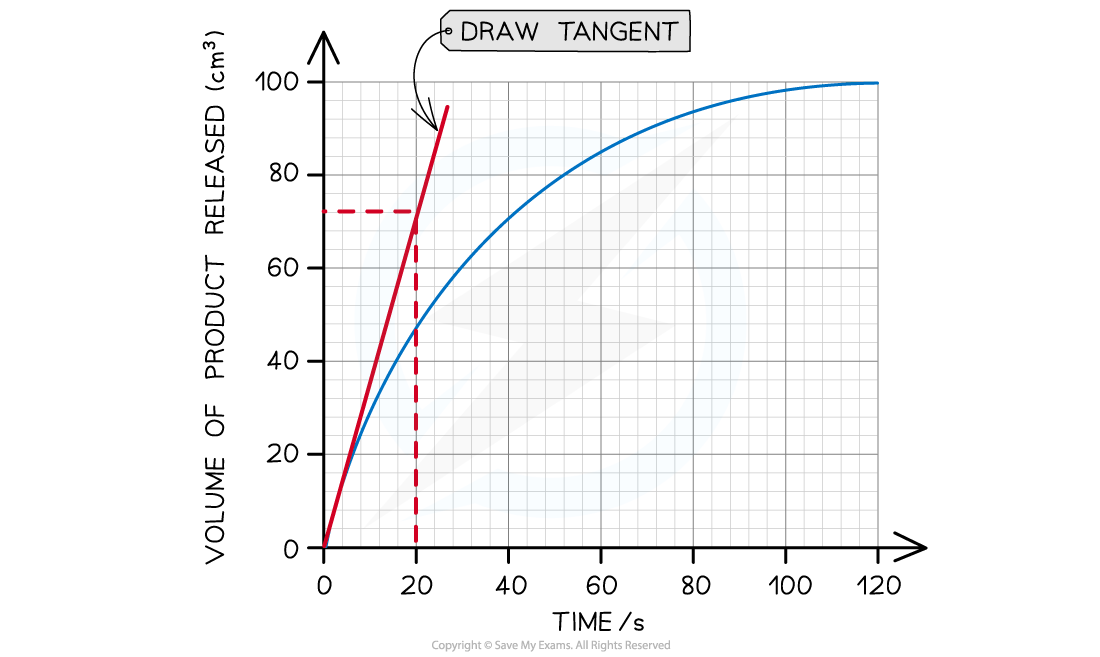
The tangent drawn in the graph above shows that 72 cm3 of product was produced in the first 20 seconds.
Step 3: Calculate the gradient of the tangent (this will give you the initial rate of reaction):
Gradient = change in y-axis ÷ change in x-axis
Initial rate of reaction = 72 cm3 ÷ 20 s
Initial rate of reaction = 3.6 cm3 s-1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When drawing a tangent, use a ruler and pencil to draw a perfectly straight line that just touches the curve at the chosen point. Make sure the curve remains visible (not hidden under the ruler).
To calculate the gradient, remember this handy phrase:
“Rise over run” – divide the vertical change by the horizontal change.

Responses