Exam code:1ST0
Characteristics of the Normal Distribution
What is a normal distribution?
-
A normal distribution is a probability distribution that can be used with continuous quantities
-
The distribution is symmetrical and bell-shaped about the mean
-
The mean, median, and mode are all equal
-
-
The notation for a normal distribution is
-
is the mean of the distribution
-
is called the variance of the distribution
-
it is a measure of how spread out the data is
-
it is equal to the standard deviation (
) squared
-
-
-
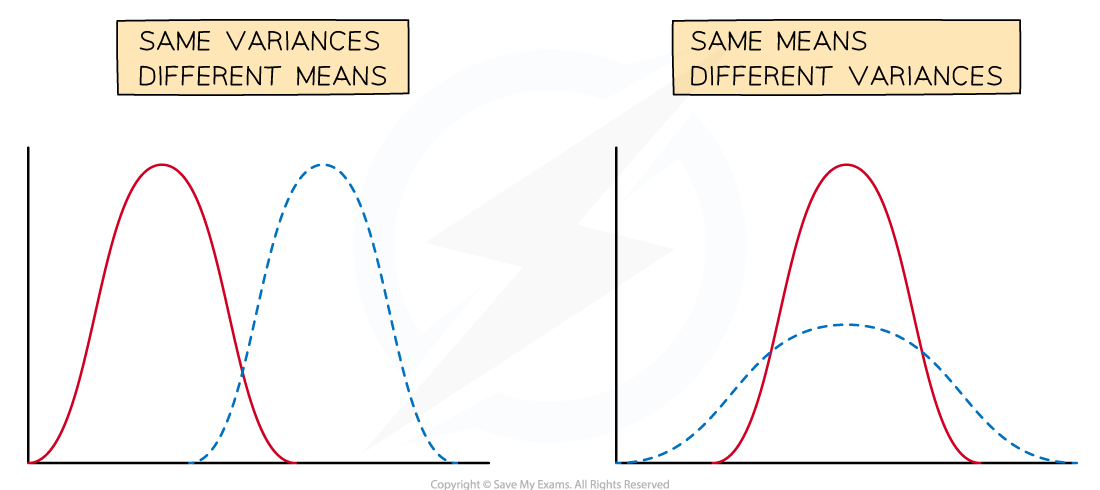
If the mean changes but the standard deviation (or variance) stays the same
-
then the shape of the distribution stays the same
-
-
If the standard deviation (or variance) increases but the mean stays the same then the distribution is stretched out horizontally
-
A small standard deviation (small variance) means a tall curve with a narrow centre
-
A large standard deviation (large variance) leads to a short curve with a wide centre
-
When is a normal distribution a suitable model for a distribution of data?
-
To use a normal distribution to model a distribution of data, the following must be true
-
The data must be continuous
-
e.g. height or weight (in the real world, heights and weights of populations are often normally distributed)
-
-
The distribution must be symmetrical and bell-shaped
-
Most data points near the middle
-
Decreasing evenly to right and left
-
-
The mean, median and mode must be approximately equal
-
They don’t need to be exactly equal, but should be close
-
This means that a normal distribution is not appropriate for skewed data
-
-
How are the data points distributed in a normal distribution?
-
For a normal distribution
-
The mean (and mode and median) is μ
-
The standard deviation is <img alt=”sigma” data-mathml=”<math ><semantics><mi>σ</mi><annotation encoding=”application/vnd.wiris.mtweb-params+json”>{“fontFamily”:”Times New Roman”,”fontSize”:”18″,”autoformat”:true,”toolbar”:”<toolbar ref=’general’><tab ref=’general’><removeItem ref=’setColor’/><removeItem ref=’bold’/><removeItem ref=’italic’/><removeItem ref=’autoItalic’/><removeItem ref=’setUnicode’/><removeItem ref=’mtext’ /><removeItem ref=’rtl’/><removeItem ref=’forceLigature’/><removeItem ref=’setFontFamily’ /><removeItem ref=’setFontSize’/></tab></toolbar>”}</annotation></semantics></math>” height=”22″ role=”math” src=”data:image/svg+xml;charset=utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F2000%2Fsvg%22%20xmlns%3Awrs%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wiris.com%2Fxml%2Fmathml-extension%22%20height%3D%2222%22%20width%3D%2212%22%20wrs%3Abaseline%3D%2216%22%3E%3C!–M
-

Responses