Maths Gcse Aqa Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Functions Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Iteration Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Surds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Aqa Higher
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Higher
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmas-Bodmas Aqa Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Aqa Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
Bearings Aqa Higher
Exam code:8300
Bearings
What are bearings?
-
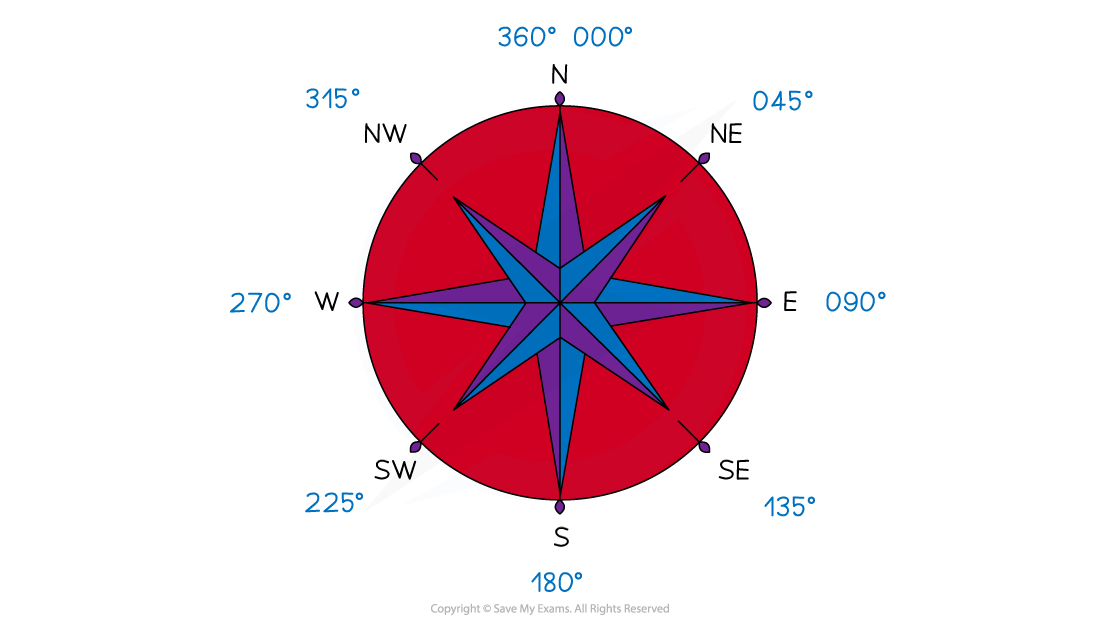
Bearings are a way of describing an angle
-
They are commonly used in navigation
-
-
There are three rules which must be followed when using a bearing:
-
They are measured from North
-
North is usually straight up on a scale drawing or map, and should be labelled on the diagram
-
-
They are measured clockwise
-
The angle should always be written with 3 digits
-
059° instead of just 59°
-
-
-
Knowing the compass directions and their respective bearings can be helpful
How do I find a bearing between two points?
-
Identify where you need to start
-
“The bearing of A from B” means start at B and find the bearing to A
-
“The bearing of B from A” means start at A and find the bearing to B
-
-
Draw a North line at the starting point
-
Draw a line between the two points
-
Measure the angle between the North line and the line joining the points
-
Measure clockwise from North
-
-
Write the angle using 3 figures
How do I draw a point on a bearing?
-
You might be asked to plot a point that is a given distance from another point and on a given bearing
-
STEP 1
Draw a North line at the point you wish to measure the bearing from-
If you are given the bearing from A to B draw the North line at A
-
-
STEP 2
Measure the angle of the bearing given from the North line in the clockwise direction -
STEP 3
Draw a line and add the point B at the given distance
How do I find the bearing of B from A if I know the bearing of A from B?
-
If the bearing of A from B is less than 180°
-
Add 180° to it to find the bearing of B from A
-
-
If the bearing of A from B is more than 180°
-
Subtract 180° from it to find the bearing of B from A
-
How do I answer trickier questions involving bearings?
-
Bearings questions may involve the use of Pythagoras or trigonometry to find missing distances (lengths) and directions (angles)
-
You should always draw a diagram if there isn’t one given
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
Make sure you have all the equipment you need for your maths exams
-
A rubber and pencil sharpener can be essential as these questions are all about accuracy
-
Make sure you can see and read the markings on your ruler and protractor
-
-
Always draw a big, clear diagram and annotate it, be especially careful to label the angles in the correct places!
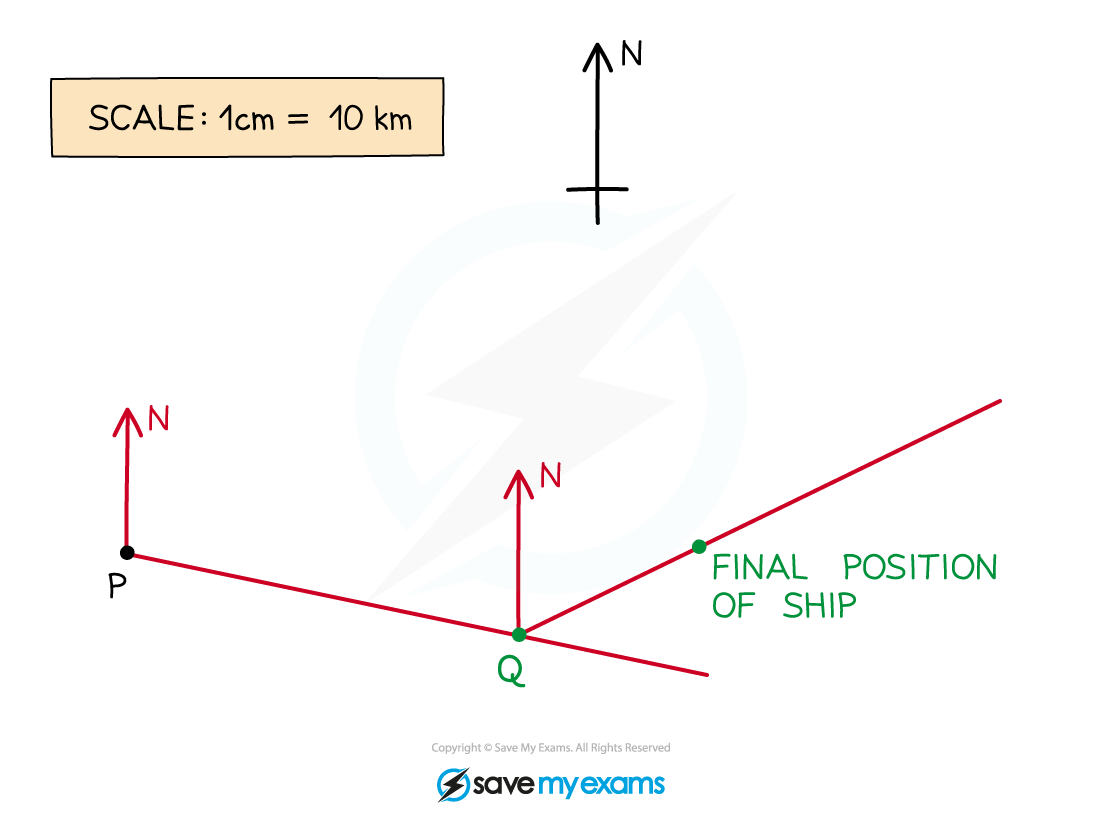
Worked Example
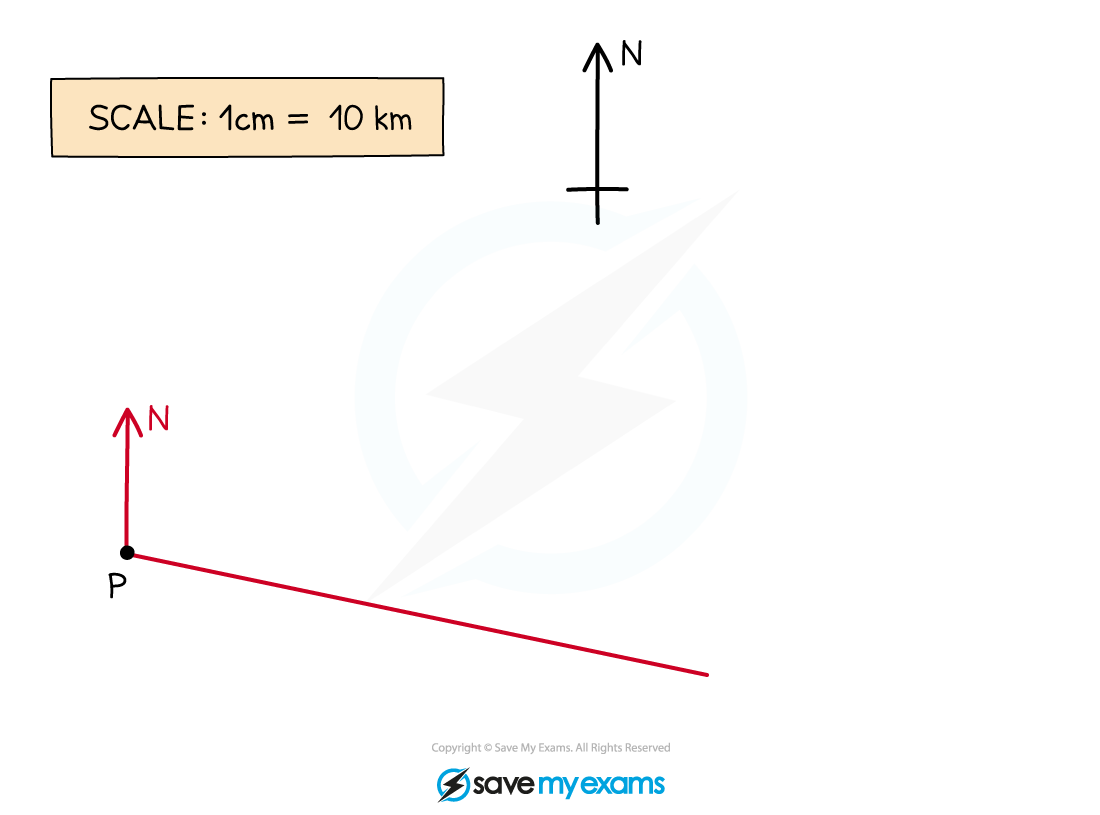
A ship sets sail from the point P, as shown on the map below.
It sails on a bearing of 105° until it reaches the point Q, 70 km away. The ship then changes path and sails on a bearing of 065° for a further 35 km, where its journey finishes.
Show on the map below the point Q and the final position of the ship.

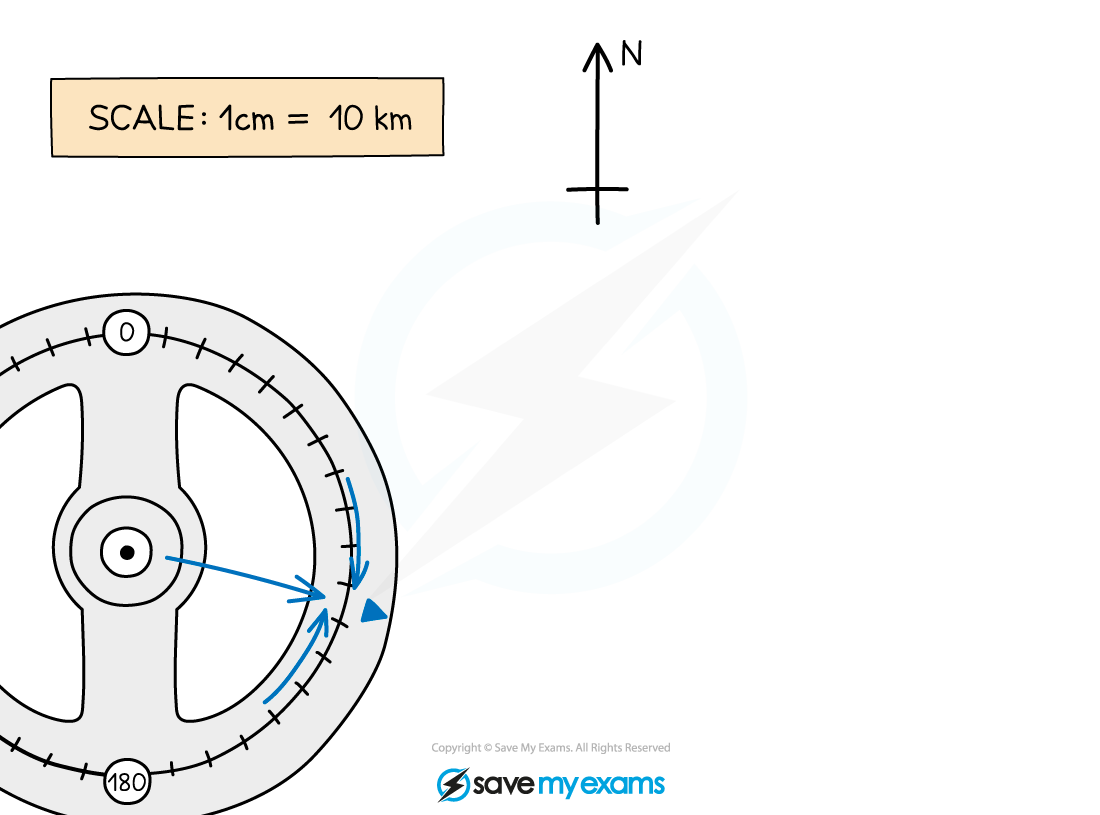
Draw in a north line at the point P
Measure an angle of 105° clockwise from the north line
Making sure you are accurate, carefully make a small but visible mark on the map
Draw a line from P through the mark you have made. Make this line long so that you can easily measure along it accurately
Use the scale given on the map (1 cm = 10 km) to work out the number of cm that would represent 70 km
70 km = 70 ÷ 10 = 7 cm
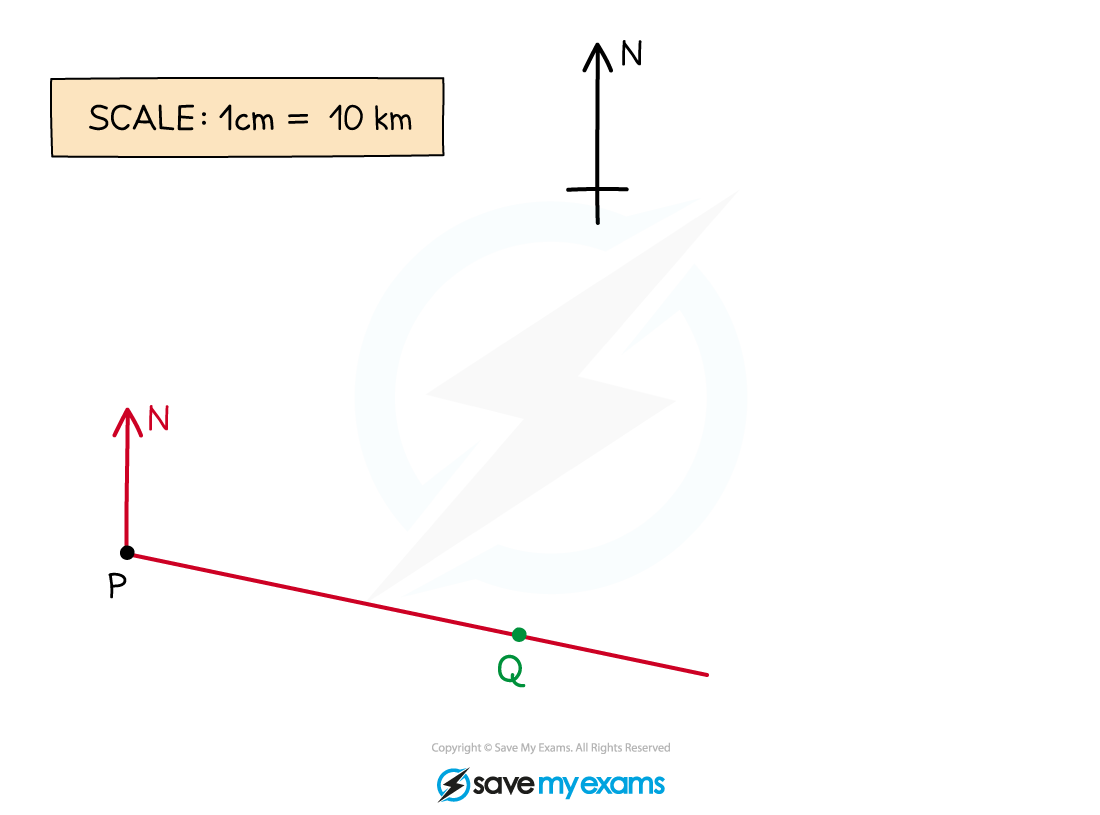
Accurately measure 7 cm from the point P along the line and make a clear mark on the line
Label this point Q
A bearing of 065 means 65° clockwise from the North
First, draw a North line at the point Q, then carefully measure an angle of 65° clockwise from this line. Make a mark and then draw a line from Q through this mark
Using the scale, find the distance in cm along the line you will need to measure.
35 km = 35 ÷ 10 = 3.5 cm
Accurately measure 3.5 cm from the point Q along this new line and make a clear mark on the line
This is the final position of the ship.

Responses