Maths Gcse Edexcel Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Edexcel Higher7 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Edexcel Higher8 主题
-
Capture-Recapture Edexcel Higher
-
Population-And-Sampling Edexcel Higher
-
Comparing-Data-Sets Edexcel Higher
-
Range-And-Interquartile-Range Edexcel Higher
-
Averages-From-Grouped-Data Edexcel Higher
-
Averages-From-Tables Edexcel Higher
-
Calculations-With-The-Mean Edexcel Higher
-
Mean-Median-And-Mode Edexcel Higher
-
Capture-Recapture Edexcel Higher
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Edexcel Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Edexcel Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Edexcel Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Edexcel Higher7 主题
-
Circle-Theorem-Proofs Edexcel Higher
-
The-Alternate-Segment-Theorem Edexcel Higher
-
Angles-In-The-Same-Segment Edexcel Higher
-
Angles-In-Cyclic-Quadrilaterals Edexcel Higher
-
Theorems-With-Chords-And-Tangents Edexcel Higher
-
Angle-In-A-Semicircle Edexcel Higher
-
Angles-At-Centre-And-Circumference Edexcel Higher
-
Circle-Theorem-Proofs Edexcel Higher
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Edexcel Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Edexcel Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Edexcel Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Edexcel Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Functions Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Iteration Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Edexcel Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Introduction Edexcel Higher7 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Edexcel Higher1 主题
-
Surds Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Edexcel Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Edexcel Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Edexcel Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Edexcel Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Edexcel Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Edexcel Higher
-
Related-Calculations Edexcel Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Edexcel Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Edexcel Higher
-
Money-Calculations Edexcel Higher
-
Negative-Numbers Edexcel Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Edexcel Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmas-Bodmas Edexcel Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Edexcel Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Edexcel Higher
Rotations Edexcel Higher
Exam code:1MA1
Rotations
What is a rotation?
-
A rotation turns a shape around a point
-
This is called the centre of rotation
-
-
The rotated image is the same size as the original image
-
It will have a new position and orientation
-
-
If the centre is a point on the original shape then that point is not changed by the rotation
-
It is called an invariant point
-
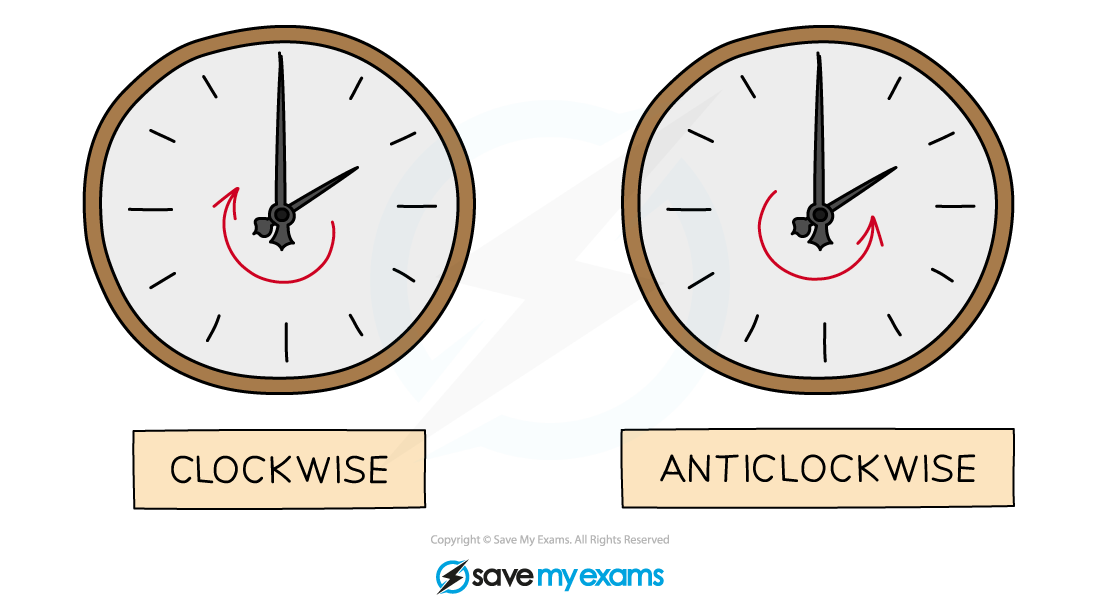
How do I rotate a shape?
-
STEP 1
Place the tracing paper over page and draw over the original object
-
STEP 2
Place the point of your pencil on the centre of rotation
-
STEP 3
Rotate the tracing paper by the given angle in the given direction
-
The angle will be 90°, 180° or 270°
-
-
STEP 4
Carefully draw the image onto the coordinate grid in the position shown by the tracing paper
How do I describe a rotation?
-
To describe a rotation, you must:
-
State that the transformation is a rotation
-
State the centre of rotation
-
State the angle of rotation
-
This will be 90°, 180° or 270°
-
-
State the direction of rotation
-
Clockwise or anti-clockwise
-
A direction is not required if the angle is 180°
-
90° clockwise is the same as 270° anti-clockwise
-
-
-
To find the centre of rotation:
-
If the rotation is 90° or 270°
-
Use tracing paper and start on the original shape
-
Try a point as the centre and rotate the original shape
-
If the rotated shape matches the image then that point is the centre
-
Otherwise keep picking points until one works
-
-
If the rotation is 180°
-
Draw lines connecting each vertex on the original shape with the corresponding vertices on the image
-
These lines will intersect at the centre of rotation
-
-
How do I reverse a rotation?
-
If a shape has been rotated to a new position, you can perform a single transformation to return the shape to its original position
-
A rotation can be reversed by simply reversing the direction of rotation
-
The angle of rotation is the same
-
The centre of rotation is the same
-
-
For a shape rotated by 45º in a clockwise direction about the point (0, 3)
-
The reverse transformation is
-
a rotation of 45º
-
in an anti-clockwise direction
-
about the point (0, 3)
-
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
When you first go into the exam room, make sure there is some tracing paper on your desk ready for you
-
If there isn’t ask for some before the exam begins
-
-
Draw an arrow facing up on your tracing paper
-
The arrow will be facing left or right when you have turned 90° or 270°
-
The arrow will be facing down when you have turned 180°
-
-
Double-check that you have copied the rotated image into the correct position
-
Put the tracing paper over the original object and rotate it again to see that it lines up with your image
-
Worked Example
(a) On the grid below rotate shape A by 90° anti-clockwise about the point (0, 2).
Label your answer A’.
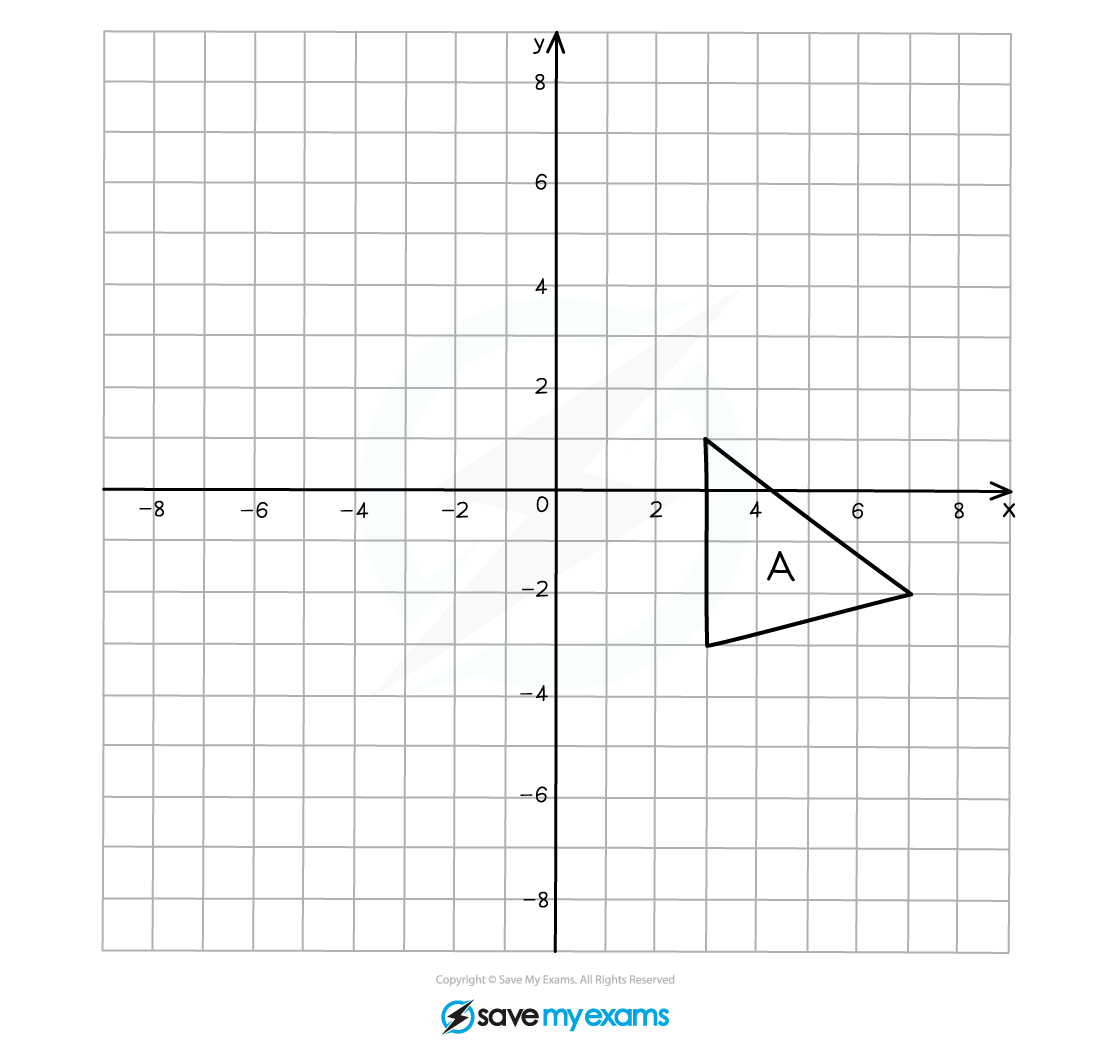
Using tracing paper, draw over the original object and mark one vertex.
Mark on the centre of rotation.
Draw an arrow pointing vertically upwards on the paper.
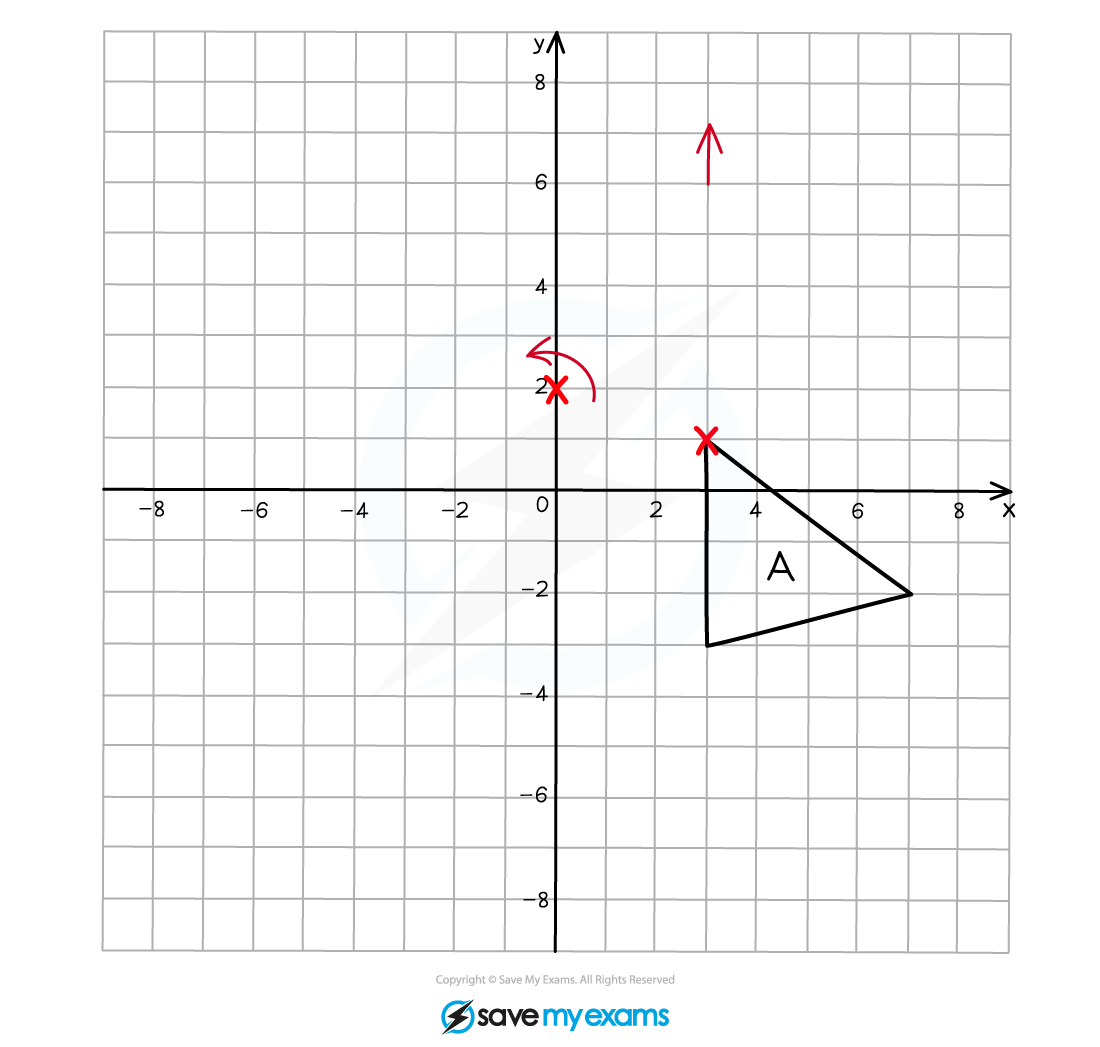
With your pencil fixed on the point of rotation, rotate the tracing paper 90o anti-clockwise, the arrow that you drew should now be pointing left.
Make a mental note of the new coordinates of the vertex that you marked on your tracing paper.
Draw the new position of this vertex onto the grid.
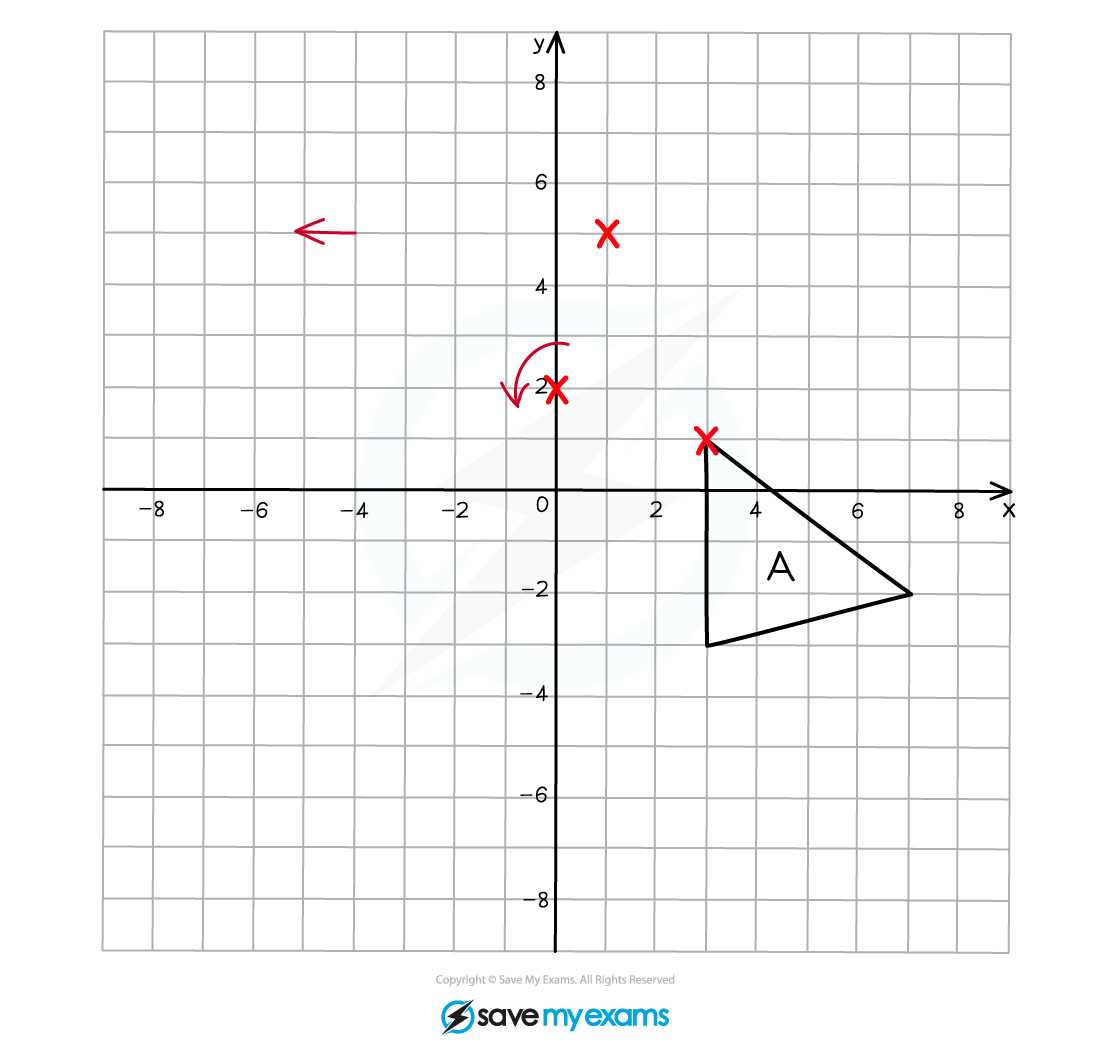
Repeat this process for the other two vertices on the triangle.
Connect the vertices together to draw the rotated image.
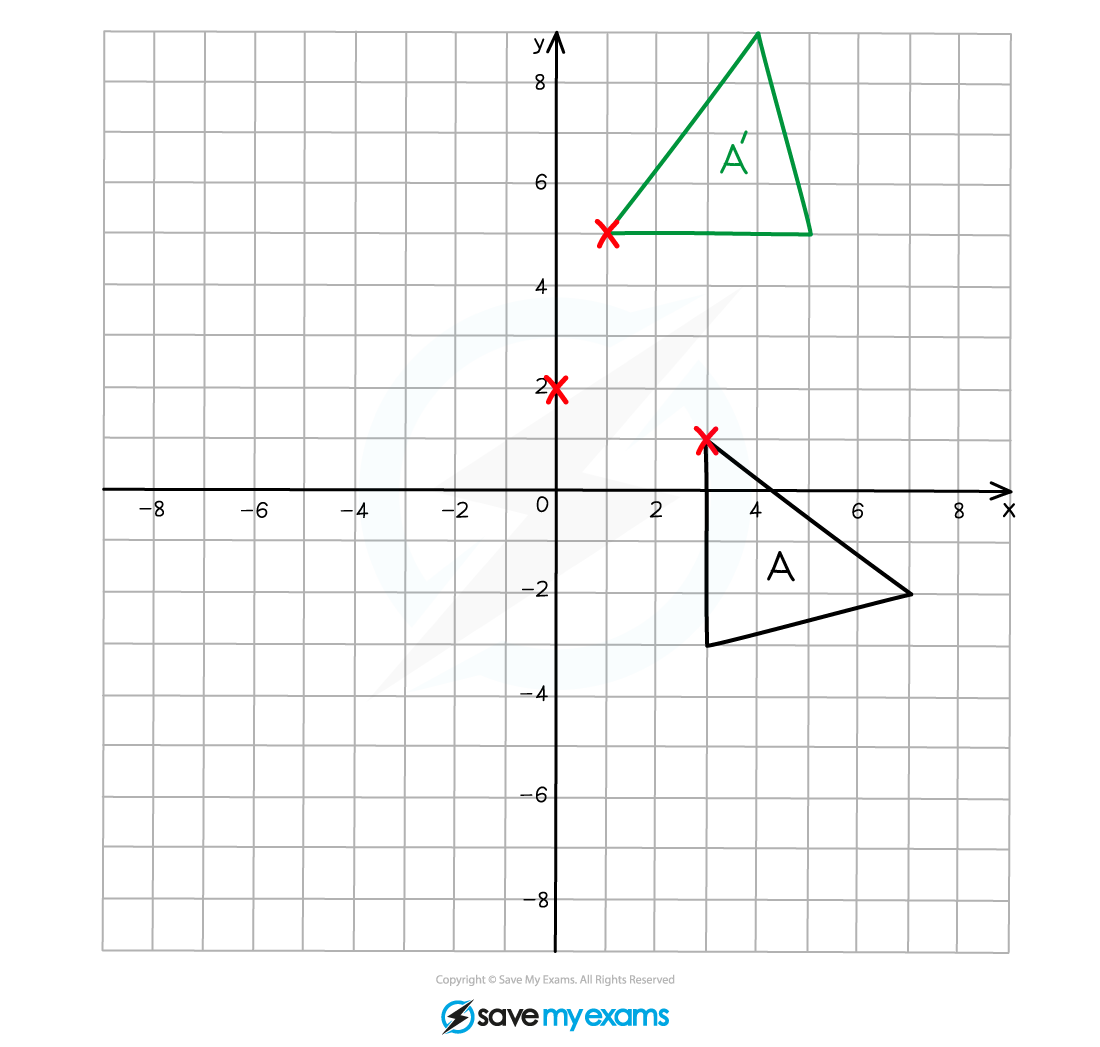
(b) Describe fully the single transformation that creates shape B from shape A.
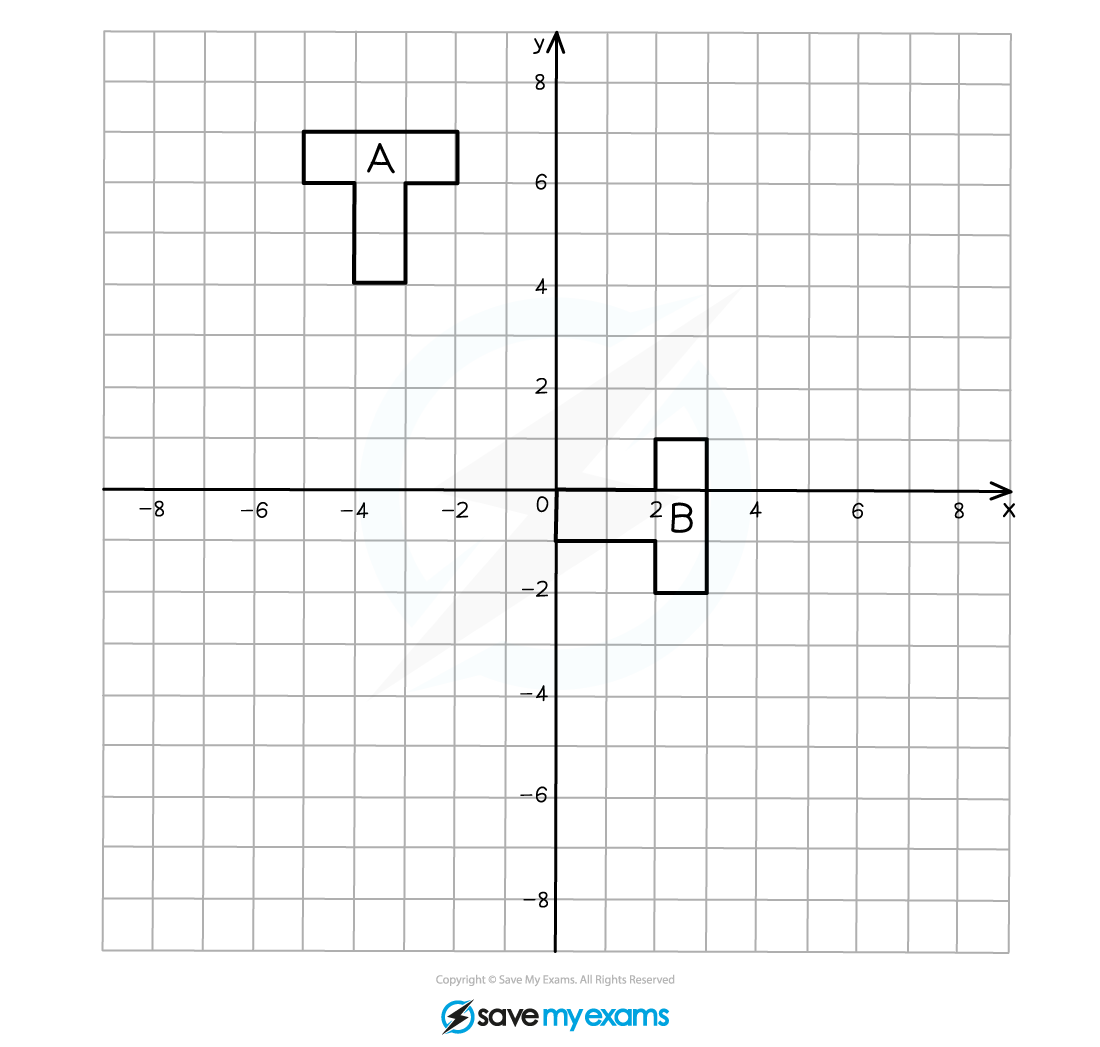
You should be able to see that the object has been rotated 90o clockwise (or 270o anti-clockwise).
You are likely to be able to see roughly where the centre of rotation is but it may take a little time to find its position exactly.

Responses