Maths Gcse Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams- Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Wjec-Eduqas Higher8 主题
-
Questionnaires Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Population-And-Sampling Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Comparing-Data-Sets Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Range-And-Interquartile-Range Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Averages-From-Grouped-Data Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Averages-From-Tables- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Calculations-With-The-Mean Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Mean-Median-And-Mode Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Questionnaires Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams- Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams- Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Introduction-To-Probability Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area- Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Wjec-Eduqas Higher7 主题
-
Circle-Theorem-Proofs Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
The-Alternate-Segment-Theorem Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angles-In-The-Same-Segment Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angles-In-Cyclic-Quadrilaterals Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Theorems-With-Chords-And-Tangents Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angle-In-A-Semicircle Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angles-At-Centre-And-Circumference Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Circle-Theorem-Proofs Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units- Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations- Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulae Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Functions Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Iteration Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Introduction-To-Algebra Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Surds Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Wjec-Eduqas Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Related-Calculations- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Money-Calculations- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Negative-Numbers- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Wjec-Eduqas Higher
Geometrical-Proof Wjec-Eduqas Higher
Exam code:C300
Geometrical proof
What is a geometrical proof?
-
Geometric proof involves using known rules about geometry to prove a new statement about geometry
-
A proof question might start with “Prove…” or “Show that …”
-
The rules that you might need to use to complete a proof include;
-
Properties of 2D shapes
-
Especially triangles and quadrilaterals
-
-
Basic angle properties
-
Angles in polygons
-
Angles in parallel lines
-
Congruence and similarity
-
Pythagoras theorem
-
-
You will need to be familiar with the vocabulary of the topics above, in order to fully answer many geometrical proof questions
How do I write a geometrical proof?
-
Usually you will need to write down two or three steps to prove the statement
-
At each step, you should write down a fact and a reason
-
For example, “AB = CD, opposite sides of a rectangle are equal length”
-
-
The proof is complete when you have written down all the steps clearly
-
Use the diagram!
-
Add key information such as angles or line lengths to the diagram as you work through the steps
-
but you must write them down in your written answer too
-
-
What geometric notation should I use?
-
Points or vertices of a shape are labelled with capital letters
-
A, B, C and D are the vertices of the quadrilateral
-
O is the centre of the circle
-
-
Two letters are used to represent the line between the points
-
AB is the line between points A and B
-
-
Three letters are used to represent the angle formed by the three points
-
Angle ABC is the angle between lines AB and BC
-
The letter in the middle is the point where the angle is at
-
-
Multiple letters are used to represent the whole shape
-
ABCD is a quadrilateral
-
The letters are written down so that they go clockwise around the shape
-
-
If you use a variable to represent a length or an angle then write it down
-
Angle ABC =
-

How can I prove that the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior angles at the other two vertices?
-
Let a, b and c be the three interior angles in a triangle
-
Let d be the exterior angle next to the interior angle c
-
Split d into two angles by drawing a parallel line to the other side of the triangle
-
There will be an angle alternate to angle a
-
There will be an angle corresponding to angle b
-
-
Therefore the exterior angle is the sum of the two opposite interior angles

What are common geometric reasons I can use?
-
There are common phrases that are sufficient as explanations and should be learnt
-
These will be what mark schemes look for
-
-
For triangles and quadrilaterals
-
Angles in a triangle add up to 180°
-
Base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal
-
Angles in an equilateral triangle are equal
-
Angles in a quadrilateral add up to 360°
-
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles
-
-
For straight lines
-
Vertically opposite angles are equal
-
Angles on a straight line add up to 180°
-
Angles at a point add up to 360°
-
-
For parallel lines
-
Alternate angles are equal
-
Corresponding angles are equal
-
Allied (or co-interior) angles add up to 180°
-
-
For polygons
-
Exterior angles of a polygon add up to 360°
-
The interior and exterior angle of any polygon add up to 180°
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
DO show all the key steps
-
If in doubt, include it
-
-
DON’T write in full sentences
-
For each step, just write down the fact, followed by the key mathematical reason that justifies it
-
Worked Example
In the diagram below, AC and DG are parallel lines. B lies on AC, E and F lie on DG and triangle BEF is isosceles.
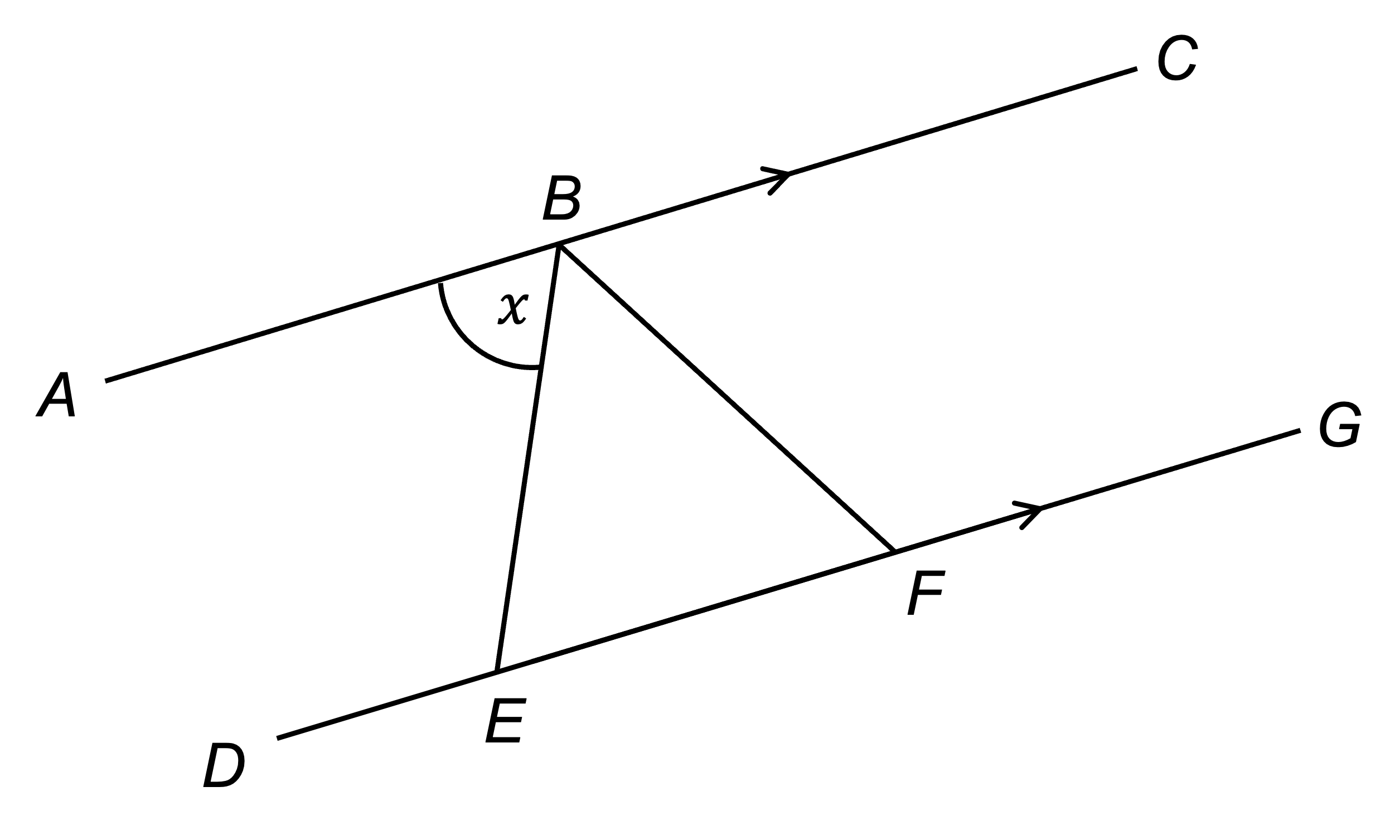
Prove that angle EBF is . Give reasons for each stage of your working.
Mark on the diagram that triangle BEF is isosceles
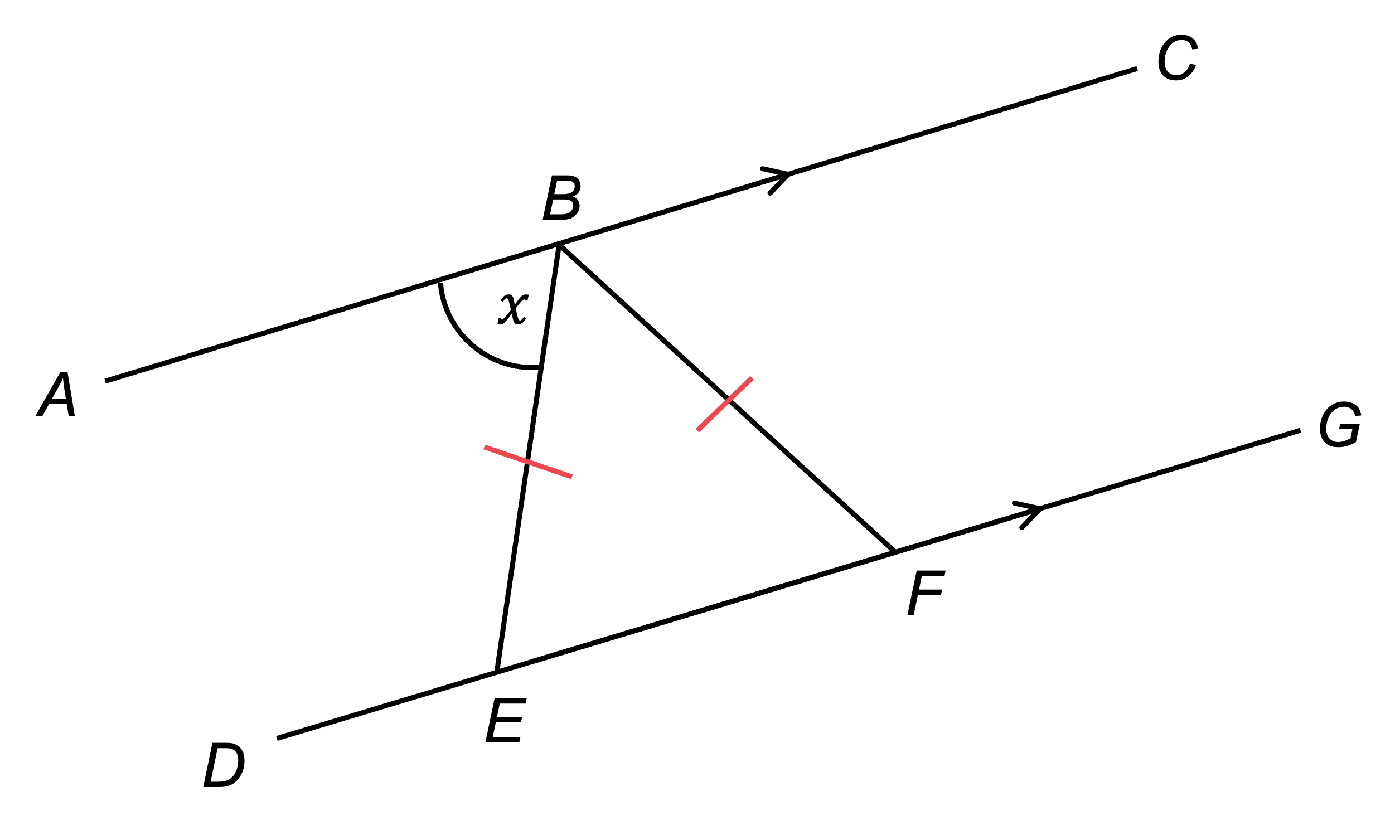
AC and DG are parallel lines, so using alternate angles we know that angle BEF =
Mark this on the diagram

Responses