Maths Gcse Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams- Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Wjec-Eduqas Higher8 主题
-
Questionnaires Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Population-And-Sampling Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Comparing-Data-Sets Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Range-And-Interquartile-Range Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Averages-From-Grouped-Data Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Averages-From-Tables- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Calculations-With-The-Mean Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Mean-Median-And-Mode Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Questionnaires Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams- Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams- Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Introduction-To-Probability Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area- Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Wjec-Eduqas Higher7 主题
-
Circle-Theorem-Proofs Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
The-Alternate-Segment-Theorem Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angles-In-The-Same-Segment Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angles-In-Cyclic-Quadrilaterals Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Theorems-With-Chords-And-Tangents Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angle-In-A-Semicircle Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Angles-At-Centre-And-Circumference Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Circle-Theorem-Proofs Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units- Wjec-Eduqas Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle- Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations- Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulae Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Functions Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Iteration Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Wjec-Eduqas Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Introduction-To-Algebra Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Wjec-Eduqas Higher1 主题
-
Surds Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Wjec-Eduqas Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Wjec-Eduqas Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm- Wjec-Eduqas Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Wjec-Eduqas Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Related-Calculations- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Money-Calculations- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Negative-Numbers- Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Wjec-Eduqas Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Wjec-Eduqas Higher
Probability-Tree-Diagrams Wjec-Eduqas Higher
Exam code:C300
Tree diagrams
How do I draw a tree diagram?
-
Tree diagrams can be used for repeated experiments with two outcomes
-
The 1st experiment has outcome A or not A
-
The 2nd experiment has outcome B or not B
-
-
Read the tree diagram from left to right along its branches
-
For example, the top branches give A followed by B
-
This is called A and B
-
-
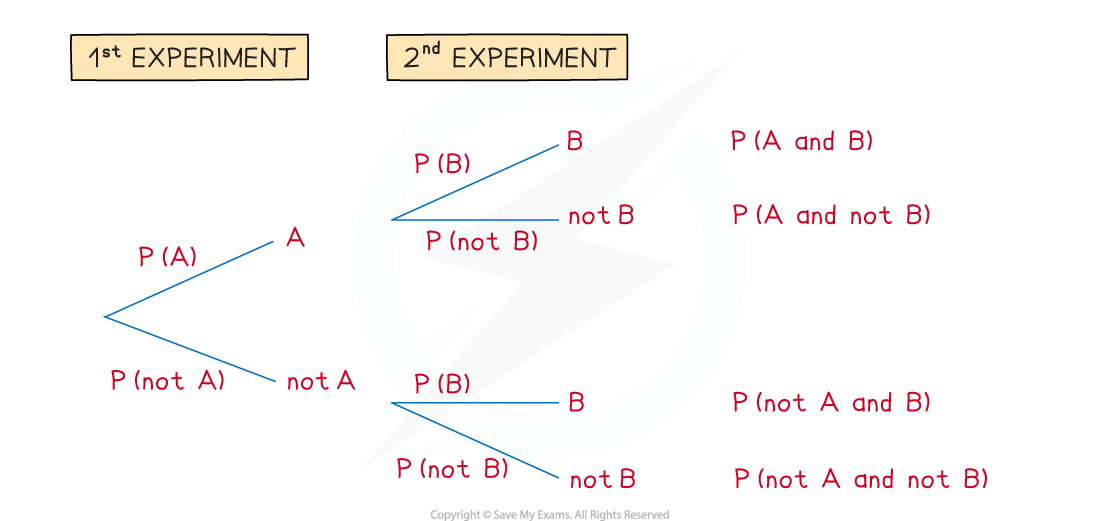
How do I find probabilities from tree diagrams?
-
Write the probabilities on each branch
-
Remember that P(not A) = 1 – P(A)
-
Probabilities on each pair of branches add to 1
-
-
-
Multiply along the branches from left to right
-
This gives P(1st outcome and 2nd outcome)
-
-
Add between the separate cases
-
For example
-
P(AA or BB) = P(AA) + P(BB)
-
-
-
The probabilities of all possible cases add to 1
-
If asked to find the probability of at least one outcome, it is quicker to do 1 – P(none)
How do I use tree diagrams with conditional probability?
-
Probabilities that depend on a particular thing having happened first in a tree diagram are called conditional probabilities
-
For example, the probability that a team wins a game may depend on whether they won or lost the previous game
-
The probabilities for ‘win’ on the first set of branches may be different to those for ‘win’ on the second set of branches
-
-
Another example of conditional probabilities is “without replacement” scenarios
-
e.g. two items are drawn from a bag of different coloured items without the first item drawn being replaced
-
The probabilities on the second set of branches will change depending on which branch has been followed on the first set of branches
-
The denominators in the probabilities for the second set of branches will be one less than those on the first set of branches
-
The numerators on the second set of branches will also change
-
-
-
Conditional probability questions are sometimes introduced by the expression ‘given that…’
-
e.g. ‘Find the probability that the team win their next game given that they lost their previous game’
-
-
The notation
is often used for conditional probabilities
-
That is read as ‘the probability of A given B’
-
e.g.
is the probability a team wins, given that they lost the previous game
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
When multiplying along branches with fractions, don’t cancel fractions in your working
-
Having the same denominator makes them easier to add together!
-
Worked Example
A worker drives through two sets of traffic lights on their way to work.
Each set of traffic lights has only two options: green or red.
The probability of the first set of traffic lights being on green is .
The probability of the second set of traffic lights being on green is .
(a) Draw and label a tree diagram. Show the probabilities of every possible outcome.
Work out the probabilities of each set of traffic lights being on red, R
Use P(red) = 1 – P(green)
<img alt=”str

Responses