Computer Science GCES EDEXCEL
-
Decomposition And Abstraction Edexcel2 主题
-
Algorithms Edexcel11 主题
-
Follow And Write Algorithms Edexcel
-
Introduction To Programming Concepts Edexcel
-
Basic Programming Concepts Edexcel
-
Variables Constants And Assignments Edexcel
-
Data Structures And Arrays Edexcel
-
Arithmetic Relational And Logical Operations Edexcel
-
Determine Outputs Of An Algorithm Edexcel
-
Types Of Errors Edexcel
-
Standard Sorting Algorithms Edexcel
-
Standard Searching Algorithms Edexcel
-
Algorithm Efficiency Edexcel
-
Follow And Write Algorithms Edexcel
-
Truth Tables Edexcel3 主题
-
Binary Edexcel6 主题
-
Data Representation Edexcel4 主题
-
Data Storage And Compression Edexcel2 主题
-
Hardware Edexcel5 主题
-
Software Edexcel3 主题
-
Programming Languages Edexcel2 主题
-
Networks Edexcel7 主题
-
Network Security Edexcel2 主题
-
Environmental Issues Edexcel1 主题
-
Ethical And Legal Issues Edexcel3 主题
-
Cybersecurity Edexcel2 主题
-
Develop Code Edexcel6 主题
-
Constructs Edexcel4 主题
-
Data Types And Data Structures Edexcel5 主题
-
Operators Edexcel1 主题
-
Subprograms Edexcel2 主题
Representing Images Edexcel
Exam code:1CP2
Bitmap Images
What is a bitmap?
-
A bitmap image is made up of squares called pixels
-
A pixel is the smallest element of a bitmap image
-
The size of an image is expressed as width x height in pixels
-
Each pixel is stored as a binary code
-
Binary codes are unique to the colour in each pixel
-
A typical example of a bitmap image is a photograph
-
The more colours and more detail in the image, the higher the quality of the image and the more binary that needs to be stored
Resolution & Colour Depth
What is resolution?
-
Resolution is the physical size of an image when displayed on screen or in print
-
The resolution is measured in pixels per inch (ppi)
-
In general, the higher the resolution, the more pixels per inch, the better the image quality
-
A lower resolution has fewer pixels per inch and can become pixelated if stretched to fit into a larger space
What is colour depth?
-
Colour depth is the number of bits used to represent the colour of a pixel
-
The colour depth is dependent on the number of colours needed in the image
-
In general, the higher the colour depth the more detail in the image (higher quality)
-
In a black & white image the colour depth would be 1, meaning 1 bit is enough to create a unique binary code for each colour in the image (1=white, 0=black)

-
In an image with a colour depth of 2, you would have 00, 01, 10 & 11 available binary codes, so 4 colours
-
As colour depth increases, so does the amount of colours available in an image
-
The amount of colours can be calculated as 2n (n = colour depth)
|
Colour Depth |
Amount of Colours |
|---|---|
|
1 bit |
2 (B&W) |
|
2 bit |
4 |
|
4 bit |
16 |
|
8 bit |
256 |
|
24 bit |
16,777,216 (True Colour) |
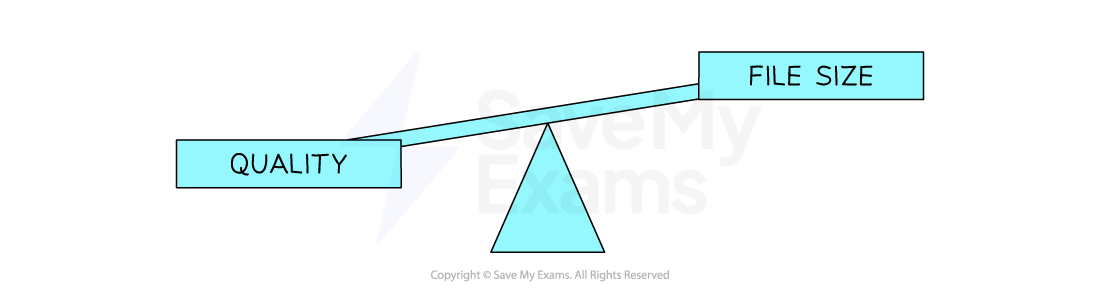
What is the impact of resolution and colour depth?
-
As the resolution and/or colour depth increases, the bigger the size of the file becomes on secondary storage
-
The higher the resolution, the more pixels are in the image, the more bits are stored
-
The higher the colour depth, the more bits per pixel are stored
-
Striking a balance between quality and file size is always a consideration
Metadata & Binary to Bitmap
How do you convert binary data into a bitmap image?
-
To convert binary data into a bitmap image:
-
Image metadata is read
-
Using this information binary data can be mapped to individual pixels
-
A bitmap image is created
-
What is metadata?
-
Metadata is data about data
-
Metadata is additional information stored with the image, it provides context and information
-
Examples of metadata that are stored are:
-
Resolution
-
Colour depth
-
Author – Who created the image?
-
Date/Time – When and what time was the image created/taken?
-
Location – Where was the image taken?
-
Example
-
A bitmap image with binary data:
|
Binary data |
|---|
|
111111111110111011100010001100000001100000001110000011111000111111101111111111111 |
-
And metadata of:
-
Width: 9 pixels
-
Height: 9 pixels
-
Colour depth: 1 bit
-
-
1 bit is a monochrome image (B&W), typically 1 = black and 0 = white
-
Every 9 pixels a new line is created
-
The resulting image would be:


Worked Example
1. Define the term Pixel [1]
2. If an image has a colour depth of 4 bits, how many colours can the image represent? [1]
3. Describe the impact of changing the bitmap image size from 500×500 pixels to 1000×1000 pixels [2]
Answers
-
The smallest element of a bitmap image [1]
-
16
-
The image quality would be higher [1] the file size would be larger [1]

Responses