Computer Science GCES EDEXCEL
-
Decomposition And Abstraction Edexcel2 主题
-
Algorithms Edexcel11 主题
-
Follow And Write Algorithms Edexcel
-
Introduction To Programming Concepts Edexcel
-
Basic Programming Concepts Edexcel
-
Variables Constants And Assignments Edexcel
-
Data Structures And Arrays Edexcel
-
Arithmetic Relational And Logical Operations Edexcel
-
Determine Outputs Of An Algorithm Edexcel
-
Types Of Errors Edexcel
-
Standard Sorting Algorithms Edexcel
-
Standard Searching Algorithms Edexcel
-
Algorithm Efficiency Edexcel
-
Follow And Write Algorithms Edexcel
-
Truth Tables Edexcel3 主题
-
Binary Edexcel6 主题
-
Data Representation Edexcel4 主题
-
Data Storage And Compression Edexcel2 主题
-
Hardware Edexcel5 主题
-
Software Edexcel3 主题
-
Programming Languages Edexcel2 主题
-
Networks Edexcel7 主题
-
Network Security Edexcel2 主题
-
Environmental Issues Edexcel1 主题
-
Ethical And Legal Issues Edexcel3 主题
-
Cybersecurity Edexcel2 主题
-
Develop Code Edexcel6 主题
-
Constructs Edexcel4 主题
-
Data Types And Data Structures Edexcel5 主题
-
Operators Edexcel1 主题
-
Subprograms Edexcel2 主题
Basic Programming Concepts Edexcel
Exam code:1CP2
What is a Programming Concept?
-
A programming construct determines the order in which lines of code are executed
-
They control the logic and behaviour of code
-
There are four core programming constructs:
-
Sequence
-
Selection
-
Iteration
-
Repetition
-
Sequence
What is a sequence?
-
Sequence refers to lines of code which are run one line at a time
-
The lines of code are run in the order that they are written from the first line of code to the last line of code
-
Sequence is crucial to the flow of a program, any instructions out of sequence can lead to unexpected behaviour or errors
Example
-
A simple program to ask a user to input two numbers, number two is subtracted from number one and the result is outputted
|
Line |
Pseudocode |
|---|---|
|
01 |
|
|
02 |
|
|
03 |
|
|
04 |
|
|
05 |
|
|
06 |
|
-
A simple swap of line 01 and line 02 would lead to an unexpected behaviour, the user would be prompted to input information without knowing what they should enter
Selection
What is selection?
-
Selection is when the flow of a program is changed, depending on a set of conditions
-
The outcome of this condition will then determine which lines or blocks of code are run next
-
Selection is used for validation, calculation and making sense of a user’s choices
-
There are two ways to write selection statements:
-
if… then… else… statements – this is when you test conditions sequentially
-
case select or switch… statements – this is when you test an expression against multiple possible constant values (known as cases)
-
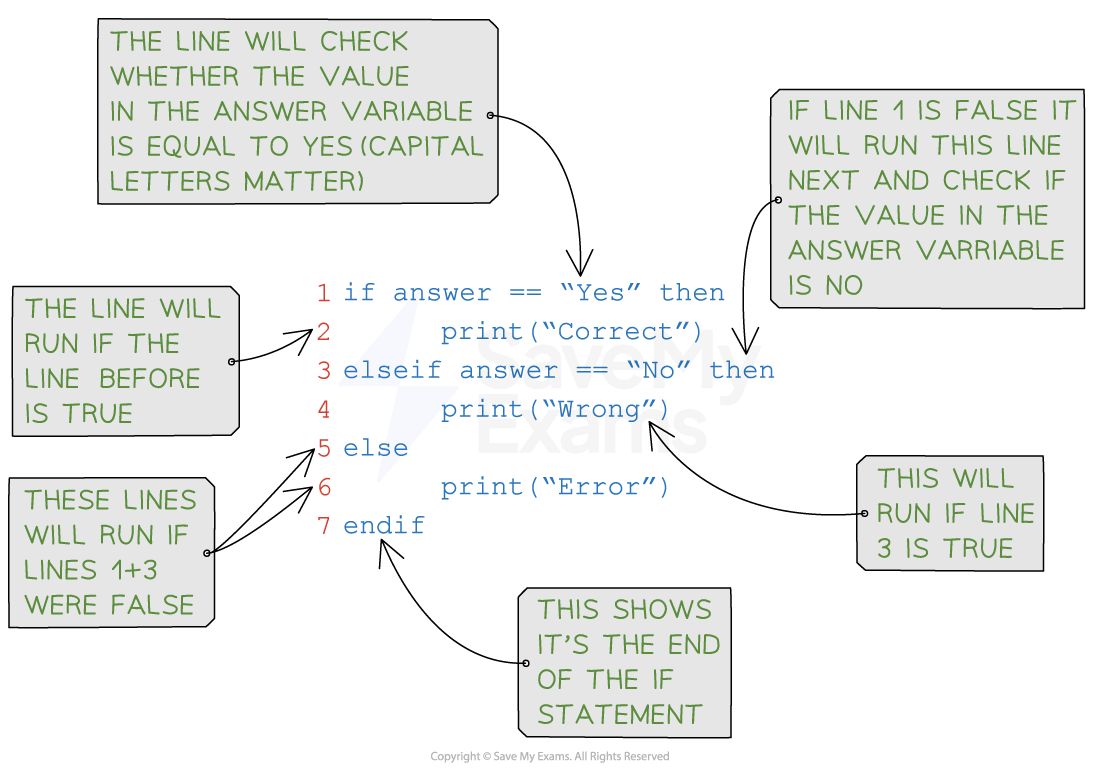
Example
|
Concept |
Python |
|---|---|
|
IF-THEN-ELSE |
|
Repetition
What is repetition?
-
Repetition is repeating a line or a block of code using a loop
-
Repetition can be:
-
count controlled – this is when the code is repeated a fixed number of times (e.g. using a for loop)
-
condition controlled – this is when the code is repeated until a condition is met (e.g. using a while loop or a do while loop)
-
Count controlled
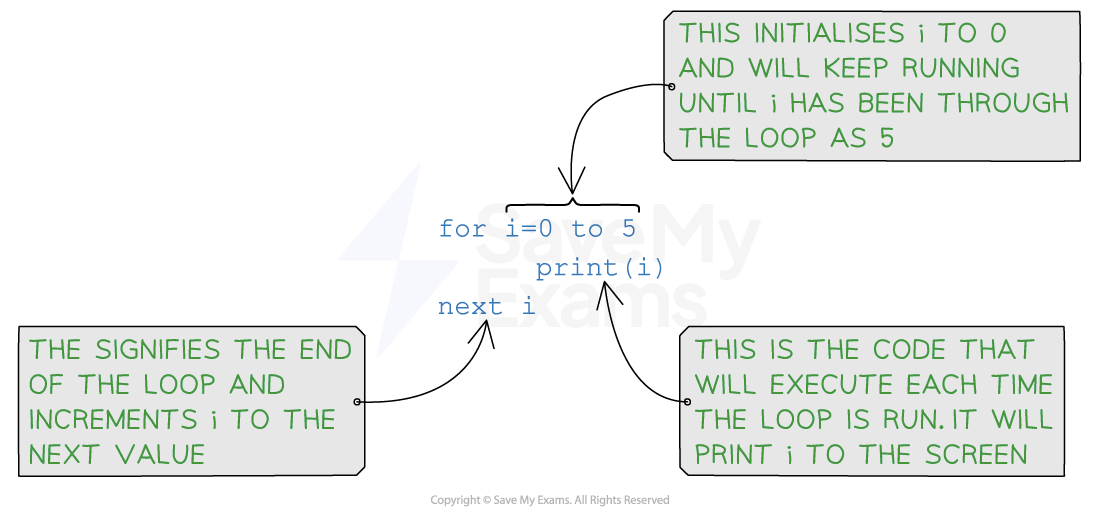
Condition controlled

Examples
|
Repetition |
Python |
|---|---|
|
FOR loop (Count controlled) |
|
|
This will print the word “Hello” 10 times (0-9 inclusive) |
|
|
|
|
This will print the even numbers from 2 to 10 inclusive |
|
|
|
|
This will print the numbers from 10 to 0 inclusive |
|
|
WHILE loop (Condition controlled) |
|
|
|
This will loop until the user inputs the colour “Red”. Check condition is carried out before entering loop |
Iteration
What is Iteration?
-
Iteration is going over every item in a data structure
-
An example of this would be searching through a list to find an item within the list
-
If a list was not sorted, a linear search may be used
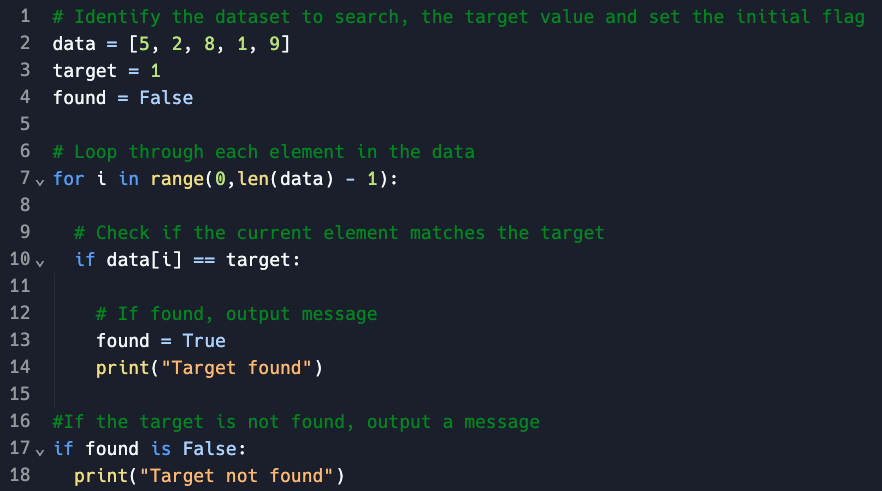
-
On line number 7, you can see where iteration takes place as it uses a for loop to iterate through the list of numbers to see if the number 1 is present
Worked Example
Tick (✓) one box in each row to identify whether each programming construct has or has not been used in the program [3]
total = 0
for i in range (1,5): num = input("Enter a number") total = total + num
print(total)|
Has been used |
Has not been used |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Sequence |
|
|
|
Selection |
|
|
|
Iteration |
|
|
|
Repetition |

Responses