Computer Science GCES AQA
-
Representing Algorithms Aqa4 主题
-
Efficiency Of Algorithms Aqa1 主题
-
Searching Algorithms Aqa3 主题
-
Sorting Algorithms Aqa3 主题
-
Data Types Aqa1 主题
-
Programming Concepts Aqa5 主题
-
Arithmetic Relational And Boolean Operations Aqa1 主题
-
Data Structures Aqa3 主题
-
String Manipulation Aqa1 主题
-
Random Number Generation Aqa1 主题
-
Structured Programming Aqa2 主题
-
Robust And Secure Programming Aqa4 主题
-
Number Bases Aqa2 主题
-
Converting Between Number Bases Aqa3 主题
-
Units Of Information Aqa9 主题
-
Hardware And Software Aqa4 主题
-
Boolean Logic Aqa3 主题
-
Programming Languages And Translators Aqa2 主题
-
Cpu Architecture Performance And Embedded Systems Aqa4 主题
-
Memory Aqa2 主题
-
Secondary Storage Aqa3 主题
-
Fundamentals Of Computer Networks Aqa8 主题
-
Fundamentals Of Cyber Security Aqa1 主题
-
Methods Of Preventing Cyber Security Threats Aqa1 主题
-
Relational Databases Aqa2 主题
-
Ethical Legal And Environmental Impacts Aqa2 主题
Binary Search Aqa
Exam code:8525
Binary Search
What is a searching algorithm?
-
Searching algorithms are precise step-by-step instructions that a computer can follow to efficiently locate specific data in massive datasets
-
Two common searching algorithms are:
-
Binary search
-
Linear search
-
What is a binary search?
-
A binary search keeps halving a dataset by comparing the target value with the middle value, going left if smaller, right if bigger, until it finds the value or realises it’s not there
-
To perform a binary search the data must be in order!
-
A binary search can be performed on datasets containing numbers or words.
-
Searching for a word instead of a number is the same process, except comparisons are made based on position in the alphabet (alphabetically) instead of numerical size
How do you perform a binary search?

Example 1 – numbers
-
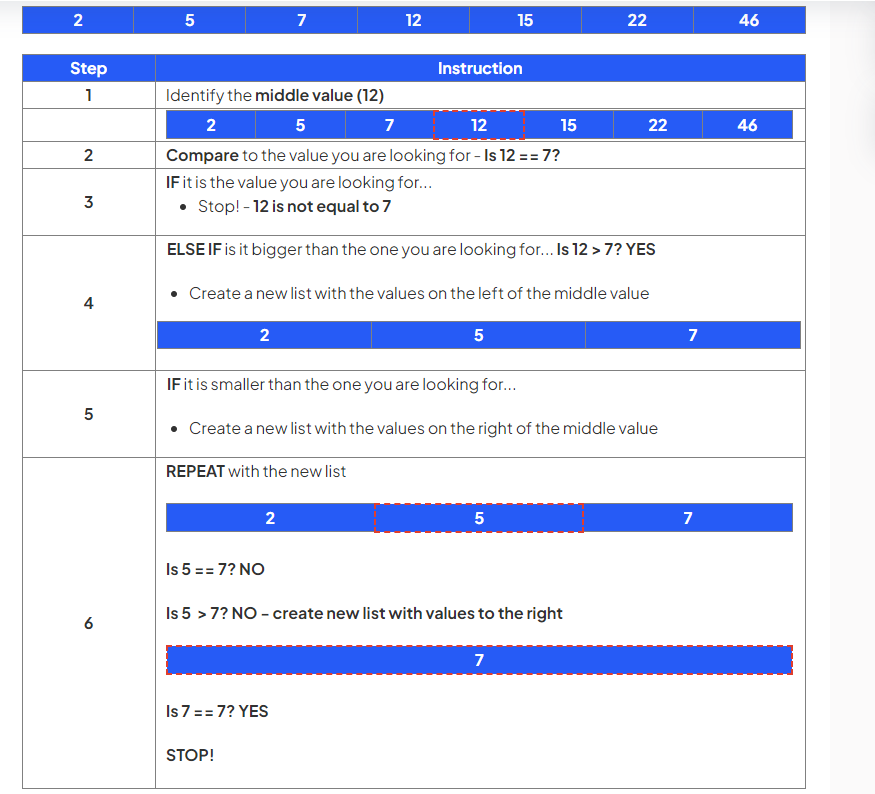
Perform a binary search to locate number 7 in the following dataset
Example 2 – words
-
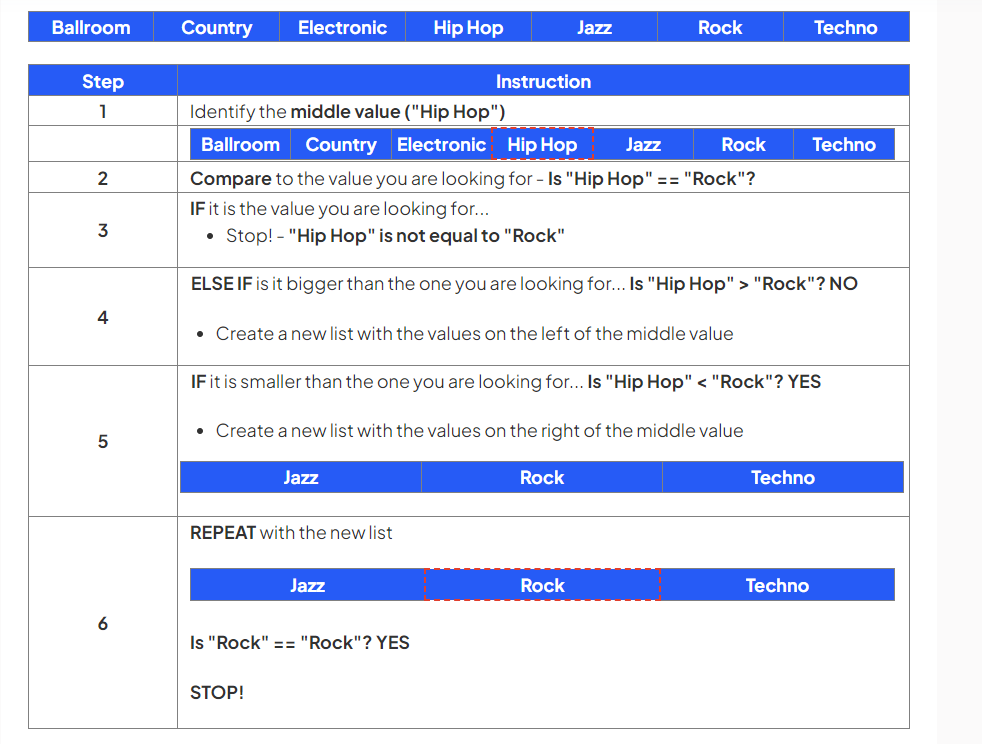
Perform a binary search to locate the word “Rock” in the following dataset
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If the dataset has an even number of values, the simplest way to identify the middle is to divide the total values by 2 and use that as a middle value i.e. a dataset with 8 values, 4 would be the middle value
Worked Example
Describe the steps a binary search will follow to look for a number in a sorted list [4]
Answer
-
Select / choose / pick middle number (or left/right of middle as even number) and …
-
…check if selected number is equal to / matches target number (not just compare)
-
…if searched number is larger, discard left half // if searched number is smaller, discard right half
-
Repeat until number found
-
… or remaining list is of size 1 / 0 (number not found)
Guidance
-
Can get a mark for bullet points 1 & 2 in one step (e.g. check if the middle value is the one we’re looking for”)
A binary search in python
# Identify the dataset to search, the target value and set the initial flagdata = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14]target = 8found = False
# Set the initial low and high pointers to the beginning and end of the datalow = 0high = len(data) - 1
# While the low pointer is less than or equal to the high pointerwhile found is False and low <= high: # Find the middle index mid = (low + high) // 2
# Check if the target is at the middle index if data[mid] == target: # If the target is found, output a message found = True print("Target found")
# If the target is less than the middle value, search in the left half of the data elif data[mid] > target: high = mid - 1
# Otherwise, search in the right half of the data else: low = mid + 1
# If the target is not found, output a messageif found is False: print("Target not found")

Responses