Computer Science AS OCR
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor as5 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor as3 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage as2 主题
-
2-1-systems-software as8 主题
-
2-3-software-development as5 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language as4 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing as3 主题
-
3-2-databases as3 主题
-
3-3-networks as8 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies as13 主题
-
html as
-
css as
-
css-styling as
-
javascript as
-
variables-and-constants-in-javascript as
-
outputs-in-javascript as
-
selection-in-javascript- as
-
for-loops-in-javascript- as
-
while-loops-in-javascript- as
-
strings-in-javascript- as
-
operators-in-javascript- as
-
nested-statements-in-javascript as
-
functions-and-procedures-in-javascript as
-
html as
-
4-1-data-types as8 主题
-
4-2-data-structures as4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra as1 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation as4 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues as9 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly as3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead as1 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally as3 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically as2 主题
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently as2 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques as9 主题
-
8-1-standard-algorithms-and-big-o-notation as8 主题
modularity-functions-and-procedures as
Exam code:H046
Modularity
What is modularity?
-
Modularity is a concept where problems are broken down into more manageable pieces
-
Each piece of the problem should be carried out by one single subroutine
-
Subroutines, also known as modules are standalone blocks of code and when called they will complete a task
-
They promote code reusability, modularity, and organisation, enabling a programmer to write efficient and maintainable programs
-
Functions and procedures are examples of subroutines and they are both very similar in nature
Difference between functions and procedures
-
Functions will return a value. For example if a function completes a calculation, then the result of the calculation will be returned to the part of the programming code that called the function
-
Procedures can also be called to complete a task, however, they do not return a value back to the part of the programming code that called the procedure
-
Both functions and procedures may need a parameter. These are pieces of data which are passed into the function or procedure to allow it to complete its task
Considerations and best practices
-
Naming: Choose descriptive and meaningful names for your functions and procedures that indicate their purpose
-
Parameter names: Use clear and meaningful parameter names to improve code readability
-
Focus: Aim for functions and procedures that are short and focused so they they complete a specific task
-
Return values: Functions should have explicit return statements with meaningful return values, while procedures should not have return statements
Functions
-
The syntax for defining a function is as follows:
function functionName(parameter1, parameter2) // Code block to perform the task // Return value;endfunction
Pseudocode example
-
In the example below two numbers are passed as parameters (a and b) into the function which adds them together and returns the result.
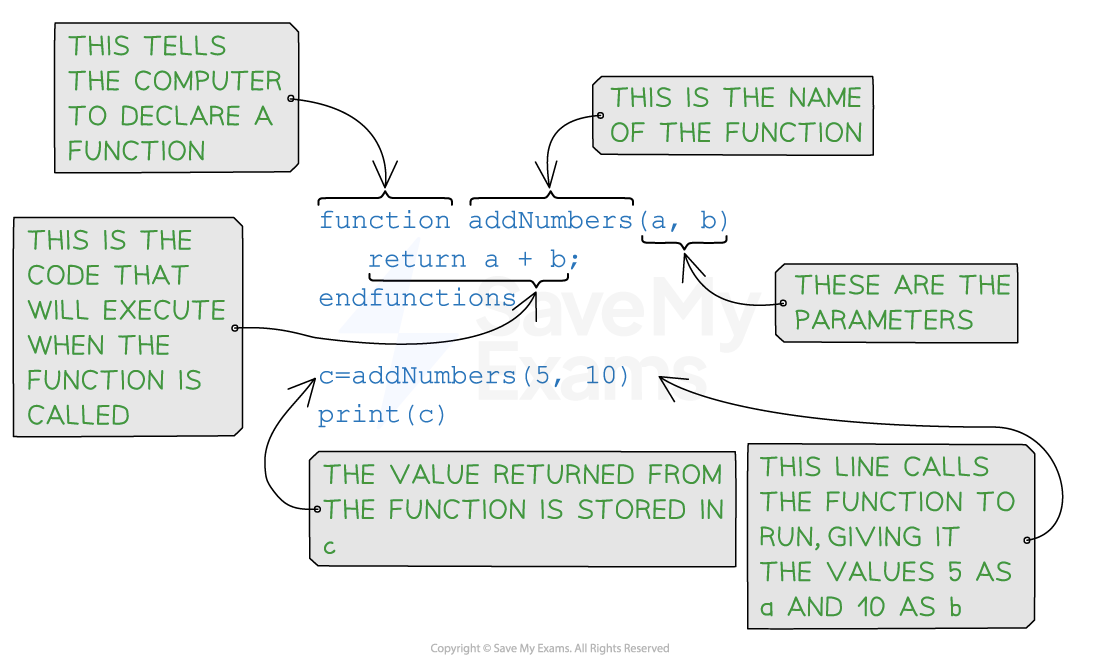
Function example in pseudocode
Python example
def add_numbers(a, b): return a + bc = add_numbers(5, 10)print(c)
Java example
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int c = addNumbers(5, 10); System.out.println(c); } public static int addNumbers(int a, int b) { return a + b; }}
Procedures
-
A procedure is similar to a function but does not return a value. Instead, it performs a series of actions or operations which could be anything the programmer wants the procedure to execute
-
A procedure is essentially a function without a
returnstatement or with areturnstatement that has no value to return -
The syntax is the same as for functions:
procedure procedureName(parameter1, parameter2) // Code block to perform actions // No return statement or return with no value;endprocedure
Pseudocode example
-
In the example below two numbers are passed as parameters (a and b) into the procedure which adds them together and prints the result
-
As this is a procedure, the result cannot be returned.
procedure addNumbers (a,b) total = a + b print (total) // The total is printed rather than returnedendprocedure
c = addNumbers(5,10)print (c)

Responses