Exam code:9609
The need for accurate cost information
-
Cost information refers to data about all the costs involved in producing and selling a product
Why is accurate cost information needed?
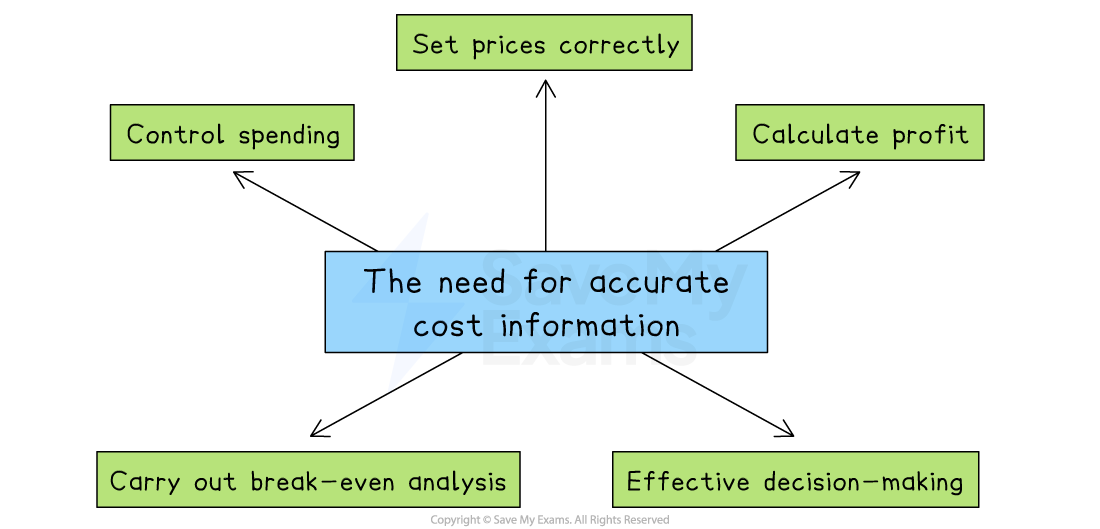
-
To set prices correctly
-
If a business underestimates its costs, it may set prices too low and make a loss
-
Overestimating costs may lead to prices that are too high, reducing demand
-
-
To calculate profit
-
Accurate costs help calculate gross profit and net profit, important for judging performance
-
-
For decision-making
-
Managers use cost data to decide whether to
-
Launch a new product
-
Continue or stop production
-
Change suppliers or production methods
-
-
-
To carry out break-even analysis
-
This helps decide how many units need to be sold to cover all costs.
-
Accurate costs make break-even analysis more reliable
-
-
To control spending
-
Comparing actual costs with budgets helps identify areas of overspending and take action
-
Types of costs
-
In preparing goods and services for sale, businesses incur a range of costs
-
These costs can be broken into different categories
Fixed costs
-
Fixed costs do not change according to output
-
These have to be paid whether the output is zero or 5,000
-
Examples include rent, management salaries, insurance and bank loan repayments
-

-
Fixed costs in this instance are $4,000
Variable costs
-
Variable costs rise proportionally with output
-
These increase as output rises and decrease as output falls
-
Examples include raw material costs and wages of workers directly involved in production and packaging
-
-
At some point, a business may benefit from a purchasing economies, so the rise will no longer be proportional

Total costs

-
Total costs is the combination of all fixed and variable costs involved in producing a certain level of output
-
Total costs cannot be zero, as all organisations have some level of fixed costs
An alternative way to classify costs
Direct costs
-
These are costs that can be directly traced to a specific product, service, or department
-
They relate specifically and exclusively to the production of a particular item
-
Direct costs can be fixed or variable
-
For example, a one-off licence fee for a software product is a direct fixed cost if it applies only to that product
-
-
Examples of direct costs include:
-
The cost of raw materials used to make a table
-
Wages paid to factory workers assembling a specific product
-
Packaging for a single product line
-
Indirect costs
-
Indirect costs are costs that cannot be traced directly to a specific product, job, or service
-
They support overall operations and are shared across departments or products
-
These costs are necessary for production or business operations, but they are not directly linked to any one unit of output
-
-
Indirect costs can also be fixed or variable
-
For example, the monthly rent paid for a shared office space is an indirect fixed cost, as it supports multiple departments but does not vary with output
-
-
Examples of indirect costs include:
-
Rent and utility bills for a factory or office
-
Salaries of supervisors or administrative staff
-
Office supplies and insurance
-
Depreciation of machinery used across several product lines
-

Comparison: direct vs indirect costs
|
Feature |
Direct costs |
Indirect costs |
|---|---|---|
|
Traceability |
|
|
|
Examples |
|
|
|
Can be fixed or variable? |
|
|
Using cost information to make decisions
-
Cost data helps businesses make key decisions
Total costs (TC)
-
Total costs information can be used to assess how much money is needed to produce at a certain level and is vital for budgeting and cash flow forecasting

Responses