Biology AS Edexcel Snab Revision
-
lifestyle-health-and-risk as19 主题
-
diet-and-health interpreting-data-on-risk-factors
-
diet-and-health treatment-of-cvd
-
diet-and-health energy-budgets-and-diet
-
diet-and-health monosaccharides
-
diet-and-health the-glycosidic-bond
-
diet-and-health disaccharides
-
diet-and-health polysaccharides
-
diet-and-health lipids-and-ester-bonds
-
diet-and-health reducing-risk-factors-of-cvd
-
diet-and-health practical-vitamin-c-content
-
the-circulatory-system the-need-for-a-circulatory-system
-
the-circulatory-system the-importance-of-water-in-transport
-
the-circulatory-system mammalian-heart-structure-and-function
-
the-circulatory-system blood-vessels-structure-and-function
-
the-circulatory-system cardiac-cycle
-
the-circulatory-system investigating-heart-rate
-
the-circulatory-system atherosclerosis
-
the-circulatory-system blood-clotting
-
diet-and-health cardiovascular-disease
-
diet-and-health interpreting-data-on-risk-factors
-
genes-and-health as28 主题
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport properties-of-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport ficks-law-of-diffusion
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport the-mammalian-lung
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport cell-membranes
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport practical-investigating-membrane-permeability
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport diffusion-and-facilitated-diffusion
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport active-transport
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport osmosis
-
nucleic-acids nucleotides-and-phosphodiester-bonds
-
nucleic-acids dna-structure
-
nucleic-acids rna-structure
-
proteins transcription
-
proteins translation
-
proteins nature-of-the-genetic-code
-
proteins amino-acids-and-peptide-bonds
-
proteins levels-of-protein-structure
-
proteins globular-proteins-structure-and-function
-
proteins fibrous-proteins-structure-and-function
-
proteins the-role-of-enzymes
-
proteins mode-of-enzyme-action
-
proteins enzyme-and-substrate-concentrations
-
inheritance dna-replication
-
inheritance mutations
-
inheritance inheritance-key-terms
-
inheritance pedigree-diagrams
-
inheritance monohybrid-crosses
-
inheritance chi-squared-test
-
inheritance genetic-screening
-
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport properties-of-gas-exchange-surfaces
-
voice-of-the-genome as19 主题
-
cell-structure-and-organisation cell-theory
-
cell-structure-and-organisation eukaryotic-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation prokaryotic-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation organisation-of-cells
-
cell-structure-and-organisation microscopy
-
cell-structure-and-organisation magnification-calculations
-
cell-structure-and-organisation recognising-organelles
-
cell-division the-cell-cycle
-
cell-division mitosis
-
cell-division practical-identifying-mitosis-in-plant-cells
-
reproduction-and-inheritance mammalian-gametes
-
reproduction-and-inheritance fertilisation-in-mammals
-
reproduction-and-inheritance genes-and-linkage
-
reproduction-and-inheritance meiosis-source-of-genetic-variation
-
differentiation-and-variation stem-cells
-
differentiation-and-variation stem-cells-in-medicine
-
differentiation-and-variation cell-differentiation
-
differentiation-and-variation epigenetics
-
differentiation-and-variation phenotypes-and-variation
-
cell-structure-and-organisation cell-theory
-
biodiversity-and-natural-resources as19 主题
-
biodiversity the-variety-of-life
-
biodiversity measuring-biodiversity-within-a-habitat
-
biodiversity comparing-biodiversity-between-habitats
-
biodiversity ecological-niches-and-adaptations
-
biodiversity natural-selection
-
biodiversity hardy-weinberg-equation
-
biodiversity reproductive-isolation
-
biodiversity classification
-
biodiversity conservation-of-biodiversity
-
resources-from-plants plant-cell-structure
-
resources-from-plants plant-stems
-
resources-from-plants importance-of-water-and-inorganic-ions-to-plants
-
resources-from-plants starch-and-cellulose-structure-and-function
-
resources-from-plants plant-fibres
-
resources-from-plants practical-identifying-tissue-types-within-stems
-
resources-from-plants tensile-strength-plant-fibres
-
resources-from-plants development-of-drug-testing
-
resources-from-plants antimicrobial-properties-of-plants
-
resources-from-plants sustainability-and-plant-materials
-
biodiversity the-variety-of-life
gas-exchange-cell-membranes-and-transport active-transport
Exam code:8BN0
Active Transport
-
Active transport is the movement of molecules and ions through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
-
Active transport requires energy in the form of ATP from respiration to move substances against their concentration gradient; hence this is an active process
-
-
Active transport requires carrier proteins
-
Each carrier protein is specific to a particular type of molecule or ion
-
-
Energy is required to allow the carrier protein to change shape; this transfers the molecules or ions across the cell membrane
-
The energy required is provided by ATP (adenosine triphosphate) produced during respiration
-
The ATP is hydrolysed to release energy
-

Active transport moves substances across a membrane from low to high concentration. Note that ATP is required for carrier proteins to change shape.
-
Examples of active transport include
-
Reabsorption of useful molecules and ions into the blood after filtration into the kidney tubules
-
Absorption of some products of digestion from the digestive tract into the blood
-
Loading sugar from the photosynthesising cells of leaves into the phloem tissue for transport around the plant
-
Loading inorganic ions from the soil into root hair cells
-
Endocytosis
-
Some molecules are too large to travel via membrane proteins, e.g.
-
Proteins
-
Lipids
-
Some carbohydrates
-
-
In such cases a cell can surround a substance with a section of the cell surface membrane
-
The membrane engulfs the substance and pinches off inside the cell to form a temporary vacuole with the ingested substance contained inside
-
This is endocytosis
-
Phagocytosis is an example of endocytosis
-
-
-
Endocytosis is an active process and requires a source of energy

Phagocytosis is an example of endocytosis; the cell surface membrane extends around a pathogen, engulfing it and enclosing it within a temporary vacuole inside the cell
Exocytosis
-
Some substances produced by the cell need to be secreted, such as hormones, some enzymes, and lipids
-
Vesicles containing the substance pinch off from sacs of the Golgi apparatus
-
These vesicles are moved toward the cell surface and fuse with the cell surface membrane to be released outside the cell
-
This is exocytosis
-
-
Exocytosis is an active process and requires a source of energy

The active processes of endocytosis and exocytosis
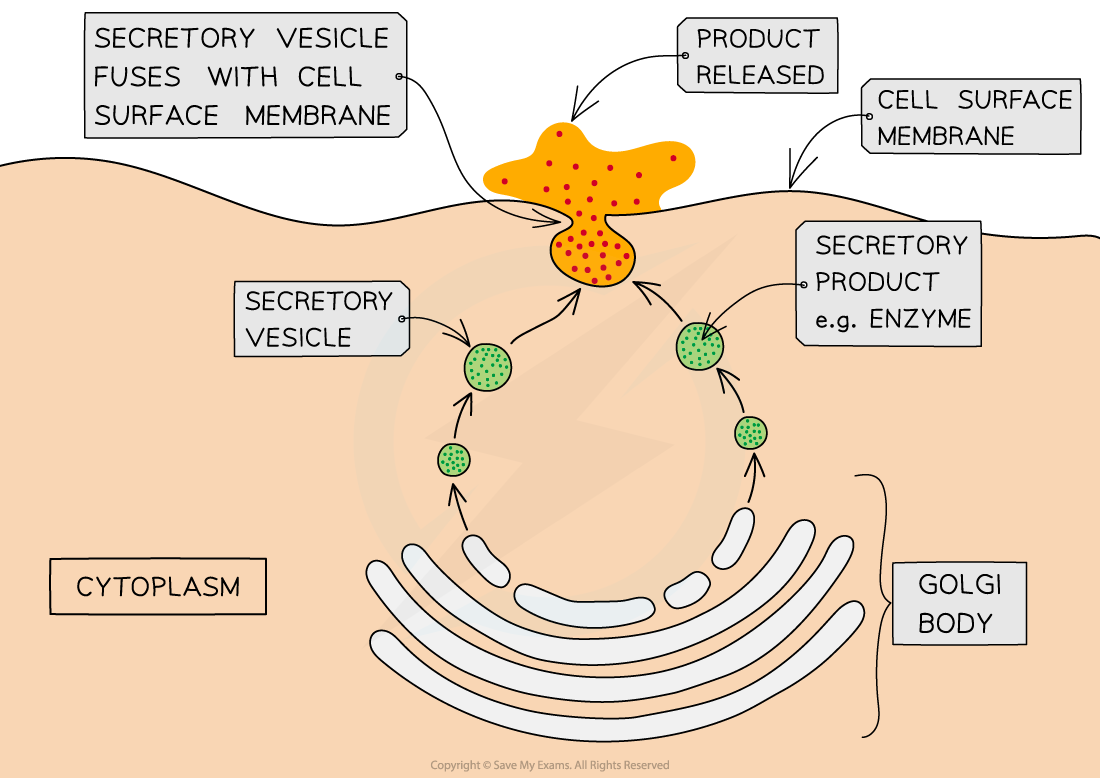
Exocytosis allows the bulk secretion of substances from cells
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful not to get carrier proteins and channel proteins confused when answering questions on active transport. Active transport requires carrier proteins (transmembrane transport proteins that undergo conformational change) not channel proteins.

Responses