Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
translators
Translators
What is a translator?
-
Translators convert source code from a high-level language to a low-level language
-
There are three main types of translators:
-
Interpreters
-
Compilers
-
Assemblers
-
Interpreters
-
Interpret source code line-by-line and executes it on the fly
-
Easier to debug, allows incremental testing, and is generally faster to start execution
-
Slower execution time overall and requires the interpreter to be present during the execution
Compilers
-
Translates the entire source code into machine code at once and then executes it
-
Faster execution time, no need for the compiler during execution
-
Longer initial compilation time and can be more challenging to debug
Assemblers
-
Assemblers translate assembly language into machine code
-
Unlike interpreters and compilers that work with high-level languages, assemblers deal with low-level languages
-
The diagram below shows examples of programming languages, from low-level to high-level
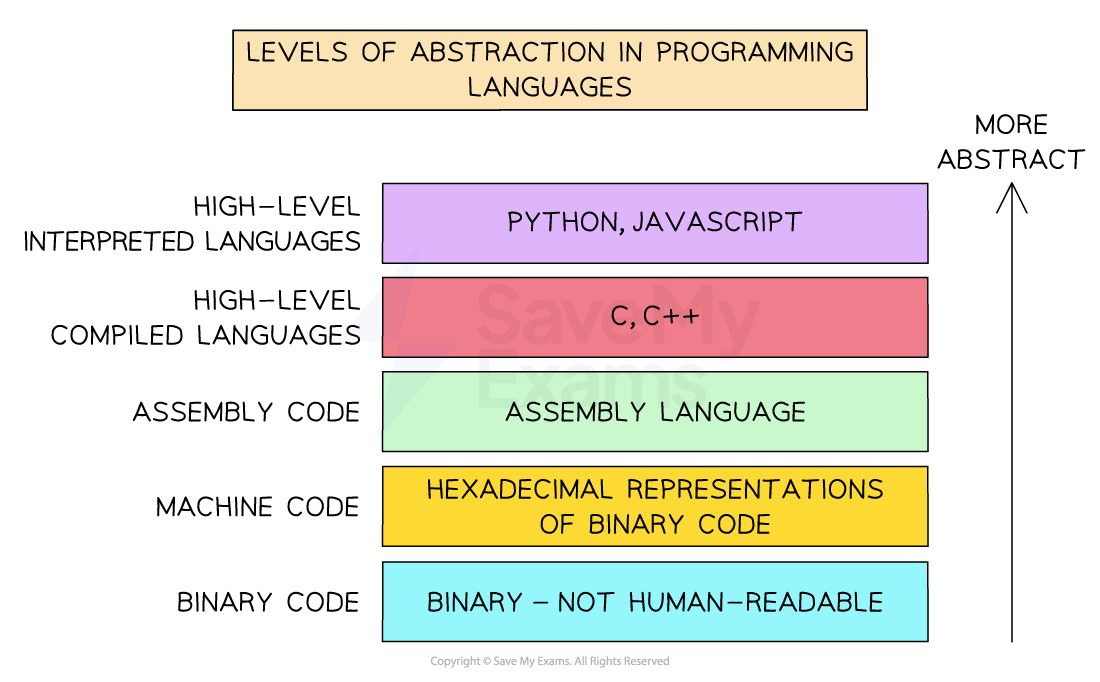
Levels of Abstraction in Programming Languages
Translators used for common languages
|
Programming Language |
Translator |
|---|---|
|
C |
Compiler |
|
C++ |
Compiler |
|
Java |
Compiler |
|
Python |
Interpreter |
|
JavaScript |
Interpreter |
|
Ruby |
Interpreter |
|
Swift |
Compiler |
|
Assembly Language |
Assembler |
|
PHP |
Interpreter |
Why do different languages have different translators? (non-syllabus content)
-
Level of Abstraction
-
High-level languages like Python or JavaScript are further from machine language and often use interpreters to allow more flexibility and ease of development
-
Low-level languages like C or Assembly are closer to machine code and typically use compilers or assemblers for efficiency
-
-
Execution Model
-
Languages like C and C++ are compiled into machine code specific to a target platform
-
This allows for optimisations to make the code run more efficiently
-
But the code is generally not portable between different platforms
-
Languages like Python and JavaScript are interpreted, meaning they are translated line-by-line at runtime on any platform
-
This provides greater portability, as the same code can run on different platforms
-
This may sacrifice some performance compared to compiled code
-
-
Development Paradigm
-
Interpreted languages allow determining variable types at runtime, which makes development faster
-
e.g.
var x = 5(Interpreter will calculatexto be a number at runtime)
-
-
Compiled languages enforce stricter type-checking at compile time, which requires additional work across the project
-
e.g.
String var name = 'Michael';(Compiler will demand thatnamehas a data type before compiling)
-
-
Worked Example
The program below is written in assembly code using the Little Man Computer instruction set. It is supposed to take in two numbers and output the higher.
INP
STA NUMA
INP
STA NUMB
SUB NUMA
BRP NOTA
LDA NUMB
BRA QUIT
NOTA LDA NUMA
QUIT OUT
HLT
NUMA DAT
NUMB DATState what type of translator program would be needed to convert the code above into machine code.
[1]
Answer:
Answer that gets full marks:
Assembler.

Responses