Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
Trees Data Structures
What is a tree?
-
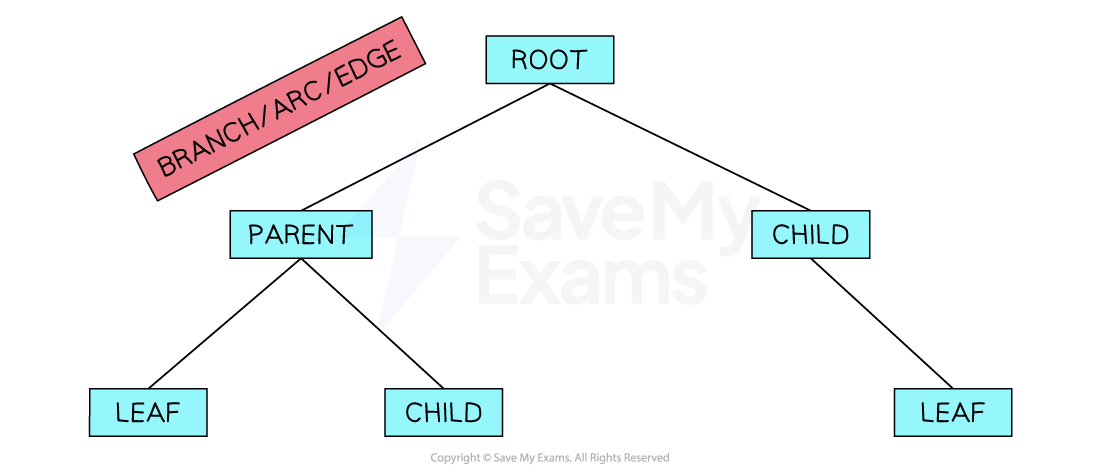
A tree is a connected, undirected form of a graph with nodes and pointers
-
Trees have a root node which is the top node; we visualise a tree with the roots at the top and the leaves at the bottom
-
Nodes are connected to other nodes using pointers/edges/branches, with the lower-level nodes being the children of the higher-level nodes
-
The endpoint of a tree is called a leaf
-
The height of a tree is equal to the number of edges that connect the root node to the leaf node that is furthest away from it
-
Nodes are connected by parent-child relationships
-
If a path is marked from the root towards a node, a parent node is the first one and the child node is the next
-
A node can have multiple children
-
A leaf node is a node with no children
-
A null pointer shows that a node does not point to another node (for example, when a node has no children)
What are trees used for?
-
Trees can be used for a range of applications:
-
Managing folder structures
-
Binary Trees are used in routes to store routing tables
-
Binary Search Trees can be built to speed up searching
-
Expression trees can be used to represent algebraic and Boolean expressions that simplify the processing of the expression
-
Traversing Tree Data Structures
What is a binary tree?
-
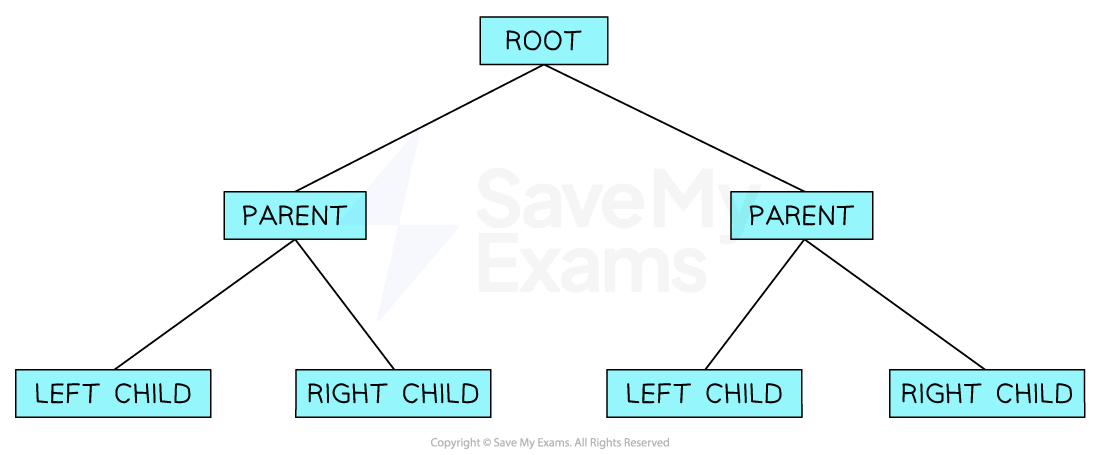
A binary tree is a rooted tree where every node has a maximum of 2 nodes
-
A binary tree is essentially a graph and therefore can be implemented in the same way
-
For your A Level Computer Science exam, you must understand:
-
tree traversal of a tree data structure
-
add new data to a tree
-
remove data from a tree
-
-
The most common way to represent a binary tree is by storing each node with a left and right pointer. This information is usually implemented using 2D arrays

Tree traversal
-
There are 2 methods of traversing a binary tree; depth-first and breadth-first
-
Both are important to understand and you should be able to output the order of the nodes using both methods
Depth-first traversal of a binary tree
-
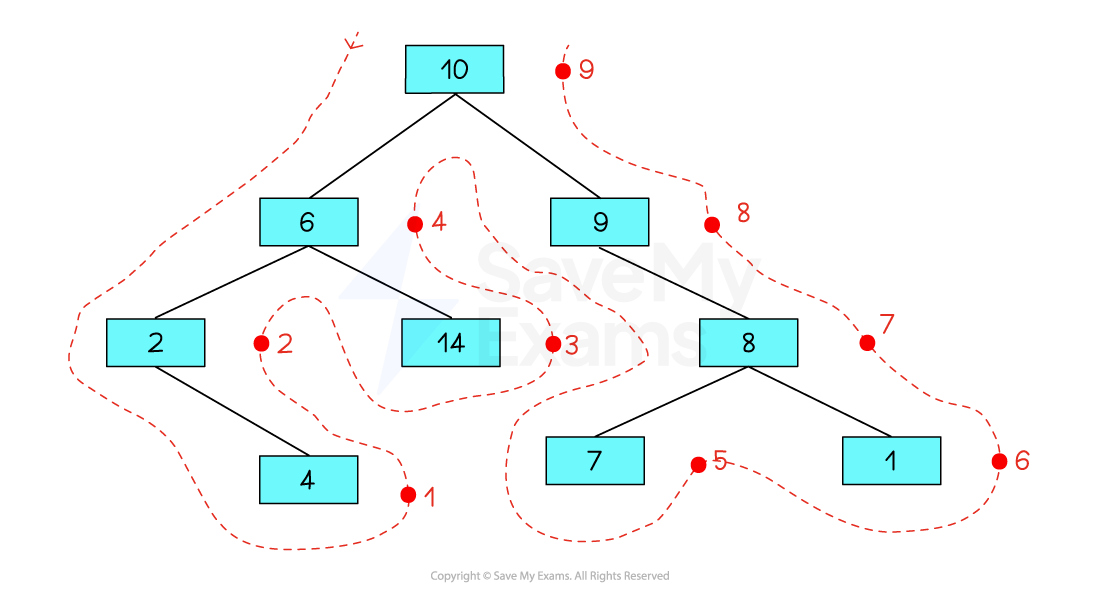
There are 3 methods to traverse a binary tree using a depth-first traversal: Pre-Order, In-Order and Post-Order. For the OCR specification, you are only required to understand post-order traversal
-
Post-order traversal
-
Left Subtree
-
Right Subtree
-
Root Node
-
-
Using the outline method, imagine there is a dot on the right-hand side of each node
-
Nodes are traversed in the order in which you pass them on the right
-
Start at the bottom left of the binary tree
-
Work your way up the left half of the tree
-
Visit the bottom of the right half of the tree
-
Making your way back up toward the root node at the top
-
-
The order of traversal is: 4, 2, 14, 6, 7, 1, 8, 9, 10
Breadth first traversal of a binary tree
-
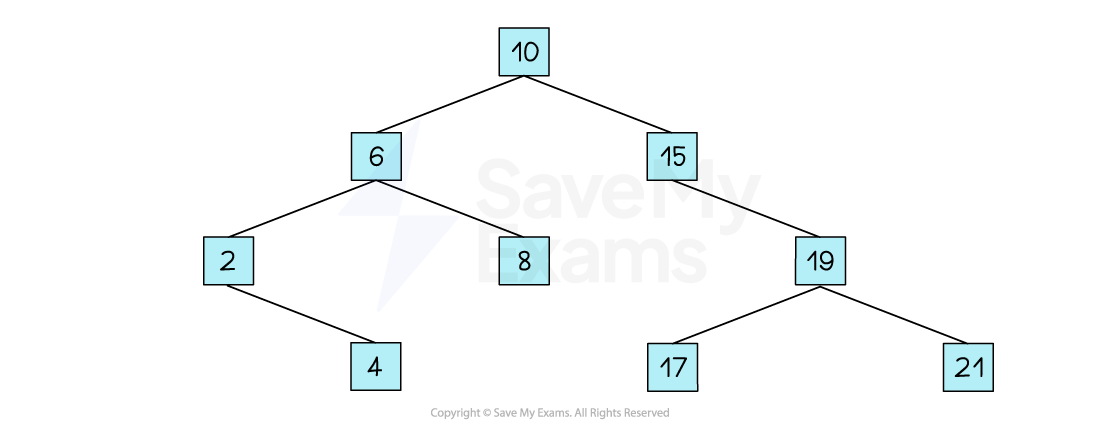
The breadth-first traversal of a tree simply means to:
-
Begin with the root node
-
Move to the left-most node under the root
-
Output each node, moving from left to right, just as though you were reading a book
-
Continue through each level of the tree
-
-
Using the image above, a breadth-first traversal would output:
-
10, 6, 15, 2, 8, 19, 4, 17, 21
-
Adding Data to a Tree
How do you add data to a binary tree?
-
As mentioned above, a tree is a fundamental data structure in Computer Science and students must be able to understand how data can be added and removed in trees
-
To add a value to a binary tree you need to complete the following:
-
Start with an empty tree or existing tree

-
Identify the position where the new value should be inserted according to the rules of a binary tree
-
If the tree is empty, the new value will become the root node
-
If the value is less than the current node’s value, move to the left child
-
If the value is greater than the current node’s value, move to the right child
-
Repeat this process until you reach a vacant spot where the new value can be inserted

-
-
Insert the new value into the identified vacant spot, creating a new node at that position
<img alt=”adding-to-a-binary-tree-3″ class=”ContentBlock_figure__vJw2q” data-nimg=”1″ decoding=”async” height=”309″ loading=”lazy” sizes=”(max-width: 320px) 320w, (max-width: 640px) 640w, (max-width: 960px) 960w, (max-width: 1280px) 1280w, 1920w” src=”https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=3840/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png” srcset=”https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=16/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 16w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=32/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 32w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=48/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 48w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=64/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 64w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=96/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 96w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=128/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 128w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=256/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 256w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=384/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 384w, https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=640/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/01/adding-to-a-binary-tree-3.png 640w, https://cdn.savemyexams.

Responses